标题【Java学习|黑马笔记|Day20】
今天看的是黑马程序员的《Java从入门到起飞》下部的95-118节,笔记包含IO流中的字节、字符缓冲流,转换流,序列化流反序列化流,打印流,解压缩流,常用工具包相关用法及练习

欢迎大家在评论区交流讨论,一起学习共同进步🕵🏻♀️
文章目录
- 标题【Java学习|黑马笔记|Day20】
- 10)上篇练习
- 1.拷贝一个文件夹,考虑子文件夹
- 2.文件加解密
- 3.修改文件中的数据
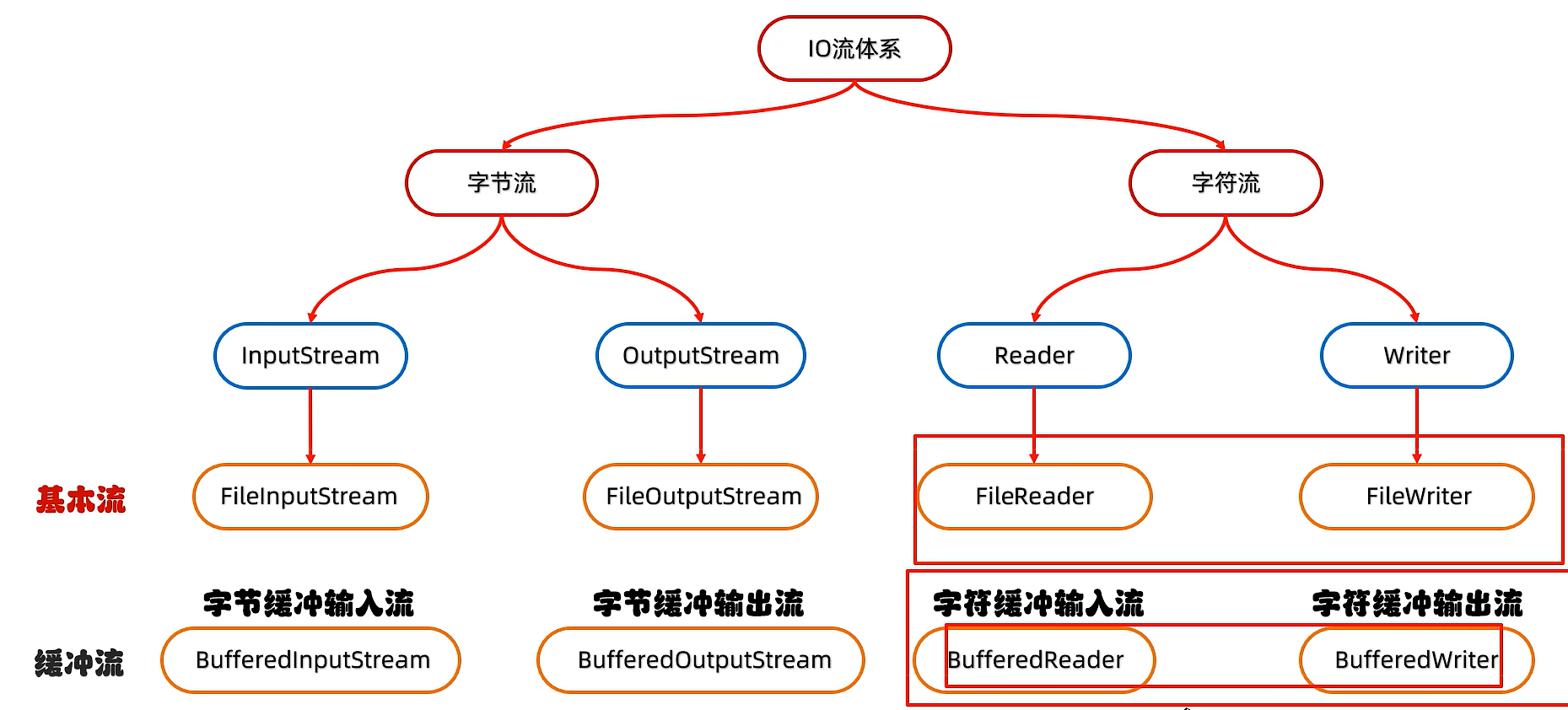
- 11)字节缓冲流
- 11.1)字节缓冲流拷贝文件(一次读一个字节)
- 11.2)字节缓冲流拷贝文件(一次读写多个字节)
- 11.3)底层原理
- 12)字符缓冲流
- 13)练习
- 1.四种拷贝方式效率对比
- 2.恢复出师表的顺序
- 3.控制软件运行的次数
- 14)转换流
- 14.1)练习
- 15)序列化流
- 16)反序列化流/对象操作输入流
- 17)(反)序列化流的细节
- 18)练习
- 19)打印流
- 19.1)字节打印流
- 19.2)字符打印流
- 20.1)解压缩流
- 20.2)压缩流
- 21.1)常用工具包Commons-io
- 21.2)常用工具包-Hutool
接上篇
10)上篇练习
1.拷贝一个文件夹,考虑子文件夹
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.数据源File src = new File("D:\\a\\bbb");//2.目的地File dest = new File("D:\\a\\aaa");copydir(src,dest);}private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {dest.mkdir();//如果dest不存在就创建一个File[] files = src.listFiles();for (File file : files) {if(file.isFile()){FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,file.getName()));byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}fos.close();fis.close();}else {copydir(file,new File(dest,file.getName()));}}}
}
2.文件加解密
加密:对原始文件的每一个字节数据进行更改,然后将更改后的数据存储到新的文件中
解密:读取加密之后的问价,按照加密的规则反向操作,编程原始文件
通过异或进行加解密
加密
//^异或 不同为true 一个数异或另一个数两次结果是它本身
//1.创建对象关联原始文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.jpg");
//2.创建对象关联机密文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\ency.jpg");
//3.加密处理
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
解密
//4.解密FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\ency.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\redu.jpg");
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
3.修改文件中的数据
排序文件中的数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileReader fr = new FileReader("src\\1.txt");StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int ch;while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {sb.append((char)ch);}fr.close();String s = sb.toString();String[] arrStr = s.split("-");Arrays.sort(arrStr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrStr));FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src\\1.txt");for (int i = 0; i < arrStr.length; i++) {fw.write(arrStr[i]);if(i != arrStr.length-1){fw.write("-");}}fw.close();
}
11)字节缓冲流
11.1)字节缓冲流拷贝文件(一次读一个字节)
原理:底层自带了长度为8192的缓冲区提高性能
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
| public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream is) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\copy.txt"));int b;while((b = bis.read()) != -1){bos.write(b);}bos.close();bis.close();}
}
11.2)字节缓冲流拷贝文件(一次读写多个字节)
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\copy.txt"));int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){bos.write(bytes,0,len);}bos.close();bis.close();}
}
11.3)底层原理
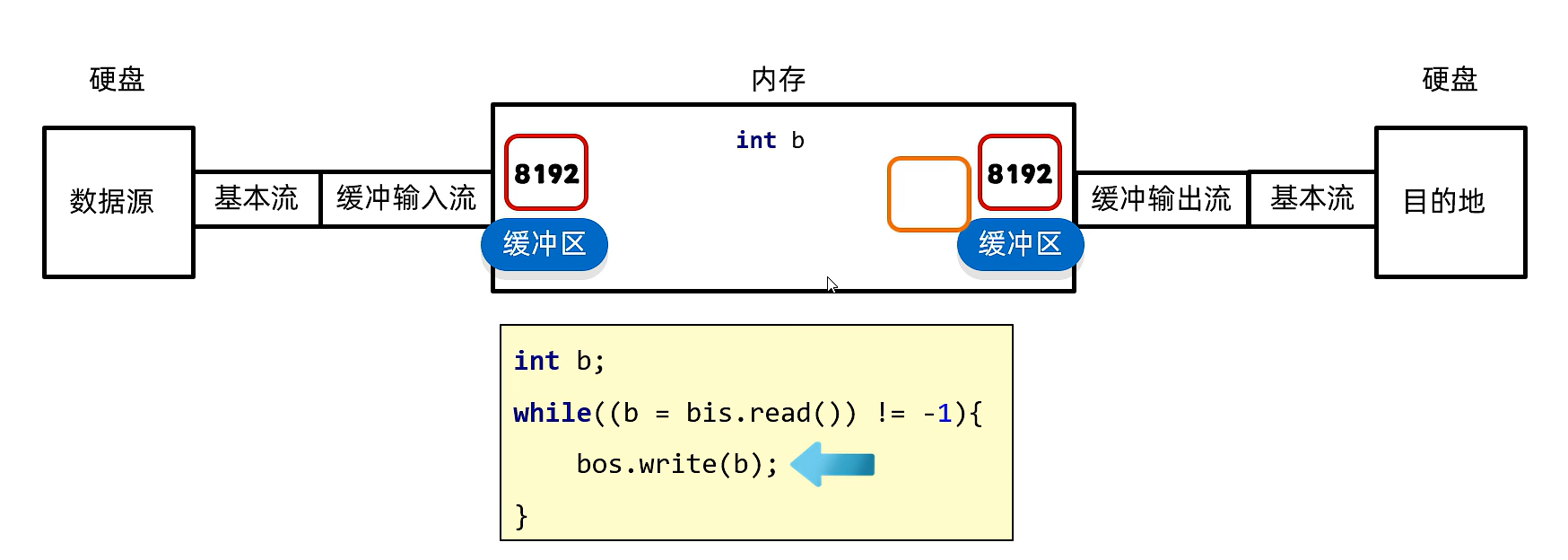
数据源通过基本流自动把数据加载到内存中的缓冲区,缓冲输出流的缓冲区自动把数据传给目的地,int b在两缓冲区之间移动传递数据
为什么节省时间?
因为在内存当中操作速度非常快,int b来回传递的速度可以忽略不计
12)字符缓冲流
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedReader(Reader r) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
| public BufferedWriter(Writer r) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
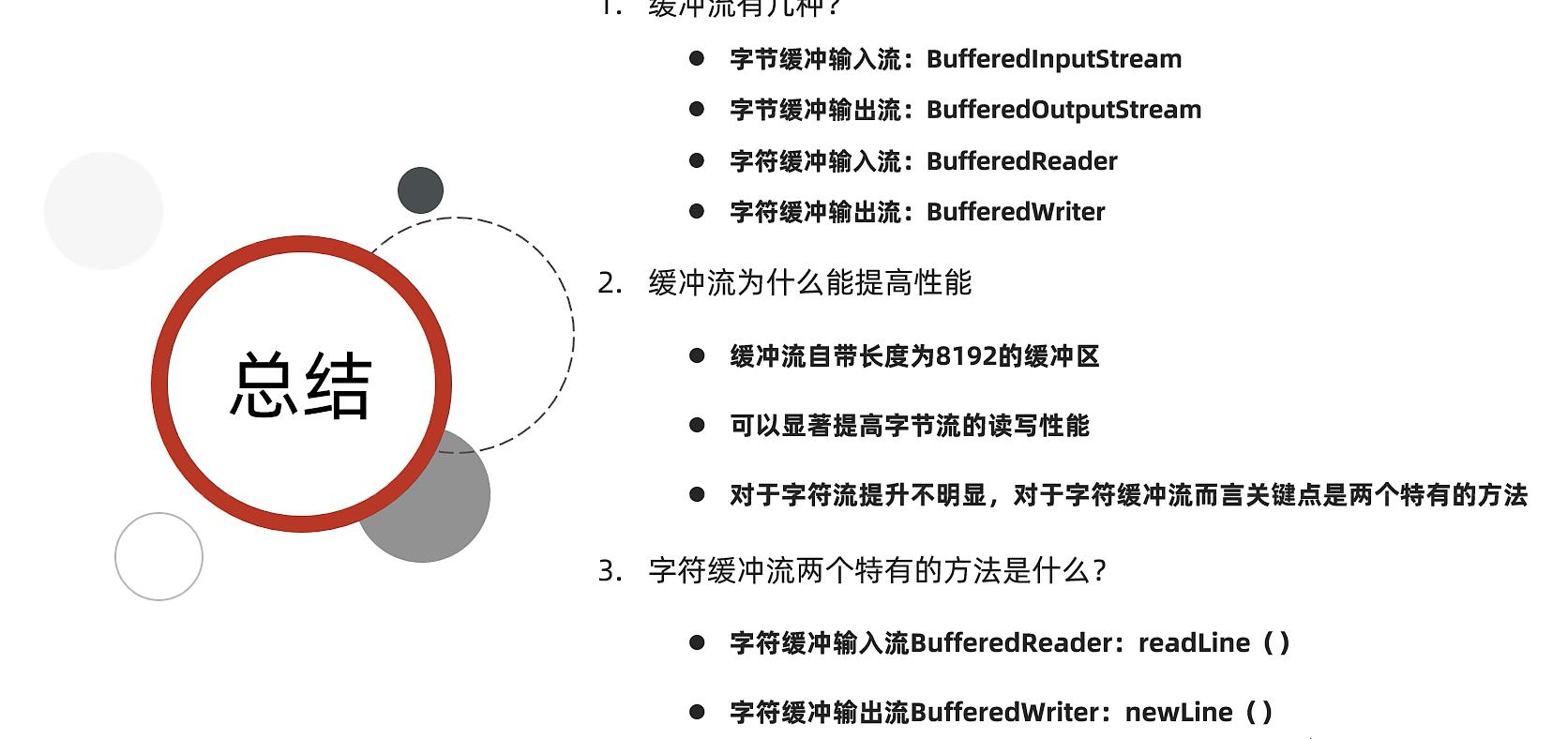
字符缓冲流特有方法
| 字符缓冲输入流特有方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String readLine() | 读取一行数据,如果没有数据可读了会返回null |
| 字符缓冲输出流特有方法 | 说明跨平台的换行 |
|---|---|
| public void newLine() | 读取一行数据,如果没有数据可读了会返回null |
字符缓冲输出流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建对象BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\1.txt"));//读取数据//readLine细节:在读取时读取一整行读到回车换行结束,// 但是不会把回车换行读到内存中String line;while((line = br.readLine()) != null){System.out.println(line);}//释放资源br.close();}
}
字符缓冲输入流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建对象BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\2.txt"));//读取数据bw.write("123456789");bw.newLine();//释放资源bw.close();}
}
总结
13)练习
1.四种拷贝方式效率对比
字节基本流一次读一个字节
字节基本流一次读一个字节数组
字节缓冲流一次读一个字节
字节缓冲流一个读一个字节数组
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//method1(); //method2();method3();//method4();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end - start) / 1000.0 + "秒");}private static void method4() throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt"));int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {bos.write(bytes);}bos.close();bis.close();}private static void method3() throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt"));int b;while ((b = bis.read()) != -1) {bos.write(b);}bos.close();bis.close();}private static void method2() throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt");int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(len);}fos.close();fis.close();}private static void method1() throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt");int b;while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {fos.write(b);}fos.close();fis.close();}}
2.恢复出师表的顺序
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\csb.txt"));String line;ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();while((line = br.readLine()) != null){list.add(line);}br.close();Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {//获取o1、o2序号return Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]) - Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);}});BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\csbnew.txt"));for (String s : list) {bw.write(s);bw.newLine();}bw.close();}
}
3.控制软件运行的次数

public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//定义一个计数器保存在本地文件中,程序停止数据不会消失//1.读取文件的数字count//原则:IO随用随建,不用就关闭BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\count.txt"));String line = br.readLine();br.close();int count = Integer.parseInt(line);count++;//又运行一次//2.判断 > 3 不能运行if(count <= 3){System.out.println("欢迎使用,第" + count + "次免费");}else {System.out.println("只能免费使用三次,请注册会员");}//bw创建在用的时候,如果创建到br下会清空文件使程序出错BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\count.txt"));bw.write(count + "");//把数字转换成字符bw.close();}
}
14)转换流
字符流和字节流之间的桥梁
InputStreamReader 将 字节流 转换为 字符流,并可以指定字符编码(如 UTF-8、GBK 等)来正确解析字节。
OutputStreamWriter 将 字符流写入到字节流中,并可以指定字符编码(如 UTF-8、GBK 等)。
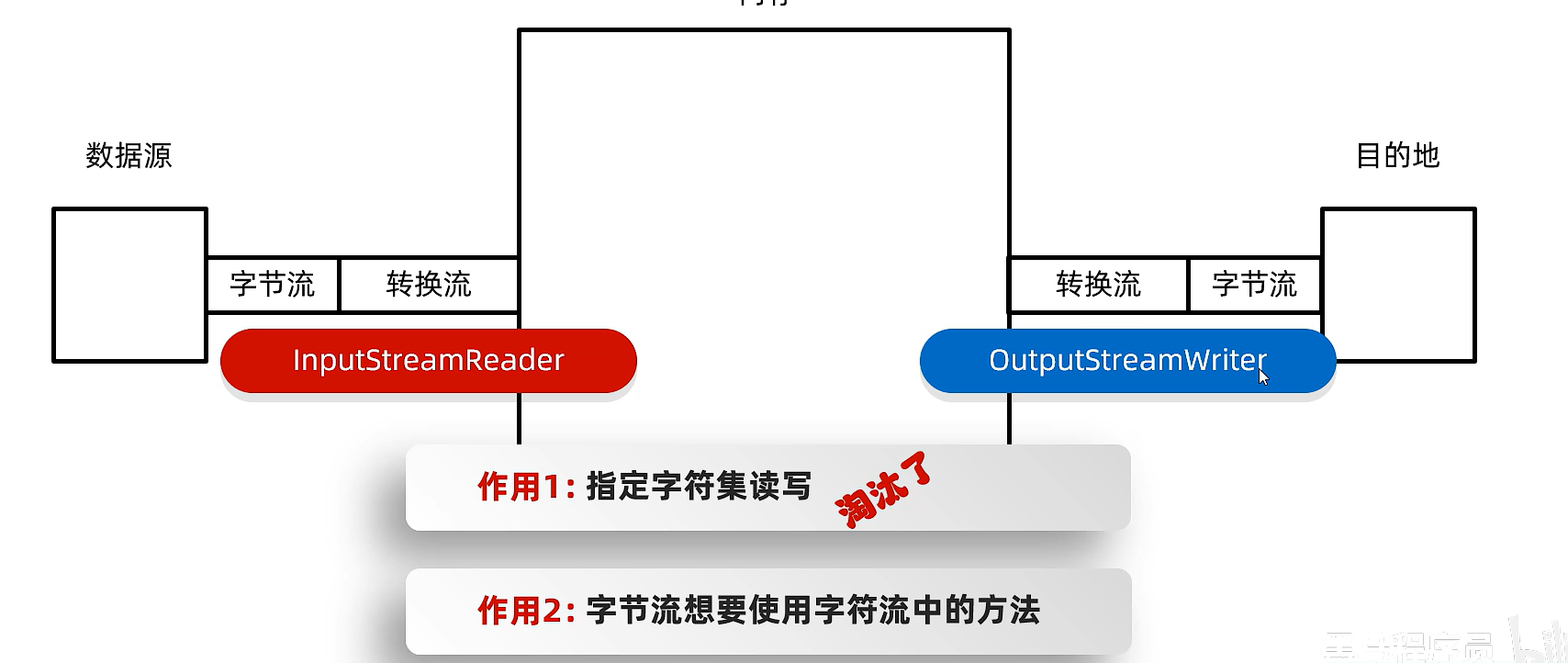
eg:利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//法一(已淘汰)InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\a\\1.txt"),"GBK");int ch;while((ch = isr.read()) != -1){System.out.print((char)ch);}isr.close();//法二:用FileReaderFileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\a\\1.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));int ch1;while((ch1 = fr.read()) != -1){System.out.print((char)ch1);}fr.close();}
}
14.1)练习
利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一行
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\a\\1.txt")));String str = br.readLine();System.out.println(str);br.close();}
}
15)序列化流
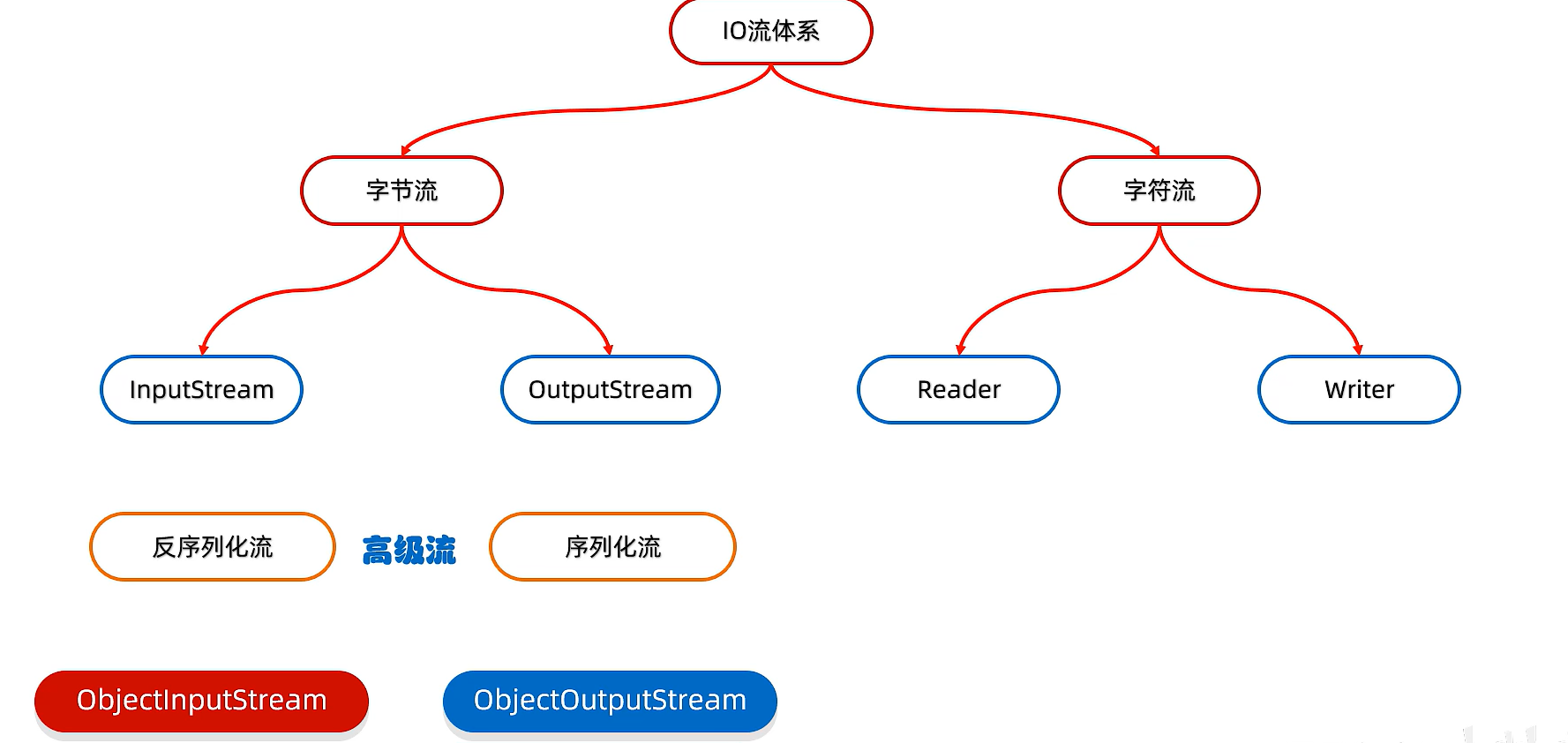
序列化流/对象操作输出流:可以把Java中的对象写到本地文件中
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectOutputStream(OubtputStream out) | 把基本流包装成高级流 |
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public final void writeObject(Object obj) | 把对象序列化写出到文件中 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Student stu = new Student("zs",23);//创建序列化流对象ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"));//细节:使用对象输出流保存到文件时会出现NotSerializableException异常// 解决方案:需要让Javabean类实现Serializable接口//写出数据oos.writeObject(stu);//关闭资源oos.close();}
}
//Serializable接口里没有抽象方法,是标记型接口
//一旦实现了找个接口表示当前的Student类可以被序列化
public class Student implements Serializable {private String name;private int age;//......}
16)反序列化流/对象操作输入流
可以把序列化到本地文件中的对象读取到程序中来
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectInputStream(InputStream out) | 把基本流升级为高级流 |
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Object readObject() | 把序列化到本地的对象读取到程序中 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {//创建对象ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src//1.txt"));//读取数据Student o = (Student)ois.readObject();//返回值类型是Object 可以强转成Student//打印对象System.out.println(o);//释放资源ois.close();}
}
17)(反)序列化流的细节
创建一个对象的序列化流后,又修改对象的成员变量会报错,报错原因:文件中的版本号跟Javabean的版本号不匹配
处理方法:固定版本号
public static Student implements Serializable{private static final long 版本号 = 1L;private Stirng name;private int age;private String address;
}
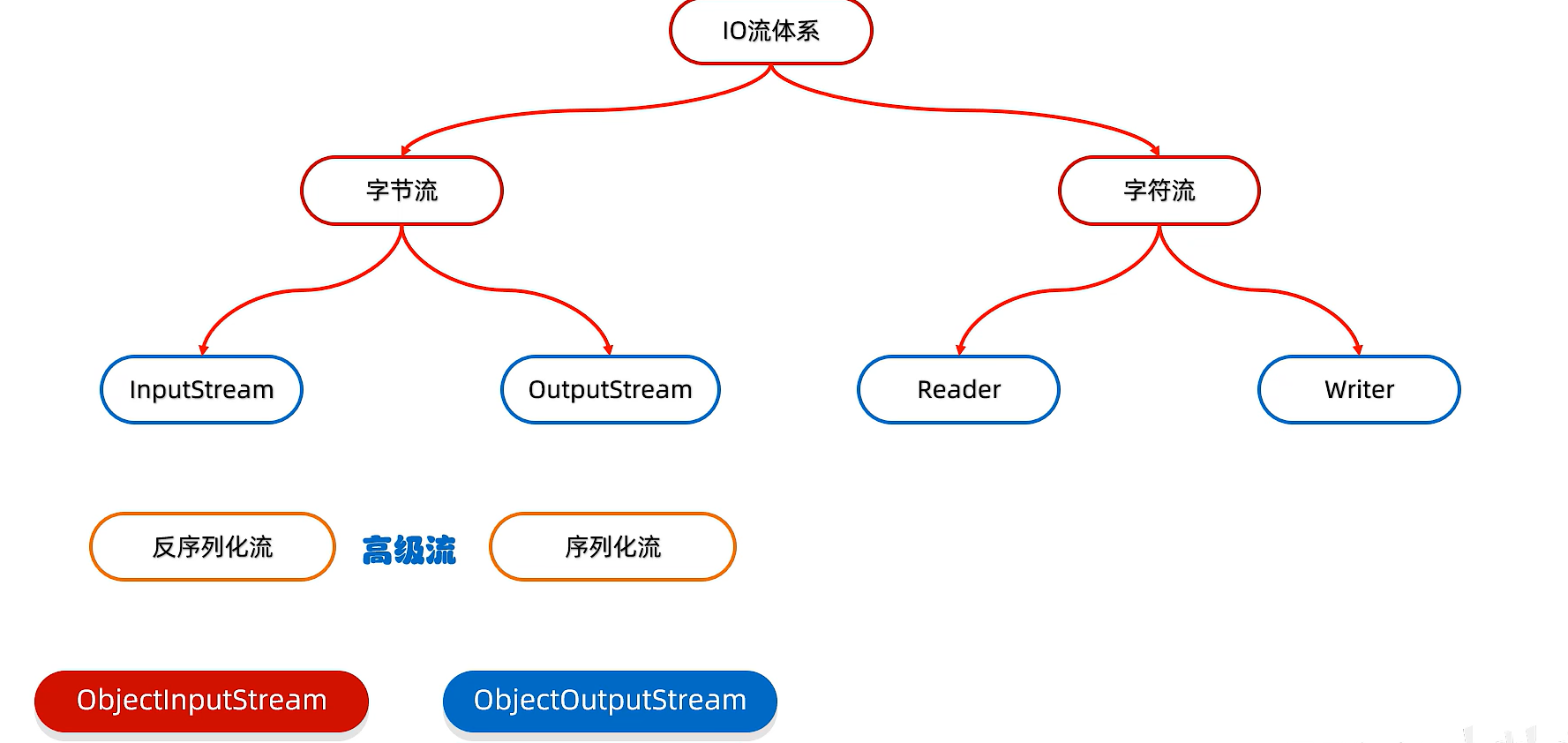
18)练习
读写多个对象,个数不确定
//序列化流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {Student s1 = new Student("zs",23);Student s2 = new Student("ls",24);Student s3 = new Student("ww",25);ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(s1);list.add(s2);list.add(s3);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"));oos.writeObject(list);oos.close();}
}
//反序列化流
public class T2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();for (Student student : list) {System.out.println(student);}ois.close();}
}
19)打印流
分类:PrintStream字节打印流,PrintWriter字符打印流
特点:
- 打印流只操作文件目的地,不操作数据源
- 特有的写出方法,数据原样写出 eg:打印97 文件中97
19.1)字节打印流
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String) | 灌流字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| public PrintStream(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码 |
| public PrintStream(OutputStream out,bollean autoFlush) | 自动刷新 |
| public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding) | 指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
字节流底层没有缓冲区,开不开自动刷新都一样
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int b) | 将指定的字节写出 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行 |
| public void print(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意数据,不换行 |
| public void printf(String format,Object…args) | 特有:带有占位符的打印语句,不换行 |
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"),true,Charset.forName("UTF-8"));ps.println(97);//写出+自动刷新+自动换行
ps.print(true);
ps.printf(" %s 1 %s","a","b");ps.close();
//占位符
//%n 换行
//%c 大写
//%b boolean类型的
//%d 小数的占位符
19.2)字符打印流
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintWrite(Write/File/String) | 关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| public PrintWrite(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码 |
| public PrintWrite(Write w,boolean autoFlush) | 自动刷新 |
| public PrintWrite(OutputStream out,bollean autoFlush,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
字符流底层有缓冲区,相应自动刷新需要开启
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int b) | 将指定的字节写出 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行 |
| public void print(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意数据,不换行 |
| public void printf(String format,Object…args) | 特有:带有占位符的打印语句,不换行 |
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("src\\1.txt"),true);
pw.println("a");
pw.print("b");
pw.printf(" %s 1 %s","a","b");pw.close();
打印流的应用场景
//获取打印流的对象,此打印流在虚拟机,不能关闭,在系统中唯一启动时由虚拟机创建默认指向控制台//特殊的打印流,系统中的标准输出流PrintStream ps = System.out;//调用打印输出流的println写出数据自动换行自动刷新ps.println("123");ps.close();System.out.println("asd");//关闭后sout也不能打印了20.1)解压缩流
解压本质:把每一个ZipEntry按照层级拷贝到本地另一个文件夹中
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建一个File表示要解压的压缩包File src = new File("D:\\a\\1.zip");//2.创建一个File表示是解压的目的地File dest = new File("D:\\a");//调用方法unzip(src, dest);}public static void unzip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {//创建一个解压缩流用来读取压缩包中的数据ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));//获取压缩包里每一个zipEntry对象ZipEntry entry;//getNextEntry可以获取压缩包里的所有文件文件夹while((entry = zip.getNextEntry()) != null) {System.out.println(entry);//如果是文件夹需要再dest创建一个同样的文件夹//如果是文件拷贝到dest中if(entry.isDirectory()) {File file = new File(dest, entry.toString());file.mkdirs();//创建多层目录}else {FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, entry.toString()));int b;while((b=zip.read()) != -1) {fos.write(b);}fos.close();//表示压缩包中的一个文件处理完毕了}}zip.close();}
}
20.2)压缩流
压缩单个文件
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件File src = new File("D:\\a\\1.txt");//2.创建File对象表示压缩包的位置File dest = new File("D:\\a\\");//调用方法toZip(src,dest);}public static void toZip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {//1.创建压缩流关联压缩包ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,"a.zip")));//2.把ZipEntry对象表示压缩包里每一个对象ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");//3.把对象放到压缩包里zos.putNextEntry(entry);//4.把src文件中的数据写到压缩包中FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);int b;while((b = fis.read()) != -1) {zos.write(b);}fis.close();zos.closeEntry();zos.close();}
}
压缩整个文件夹
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件File src = new File("D:\\a\\aaa");//2.创建File对象表示元素包的父级目录File destParent = src.getParentFile();//3.创建File对象表示压缩包的位置File dest = new File( destParent,src.getName() +".zip");//4.创建压缩流关联压缩包ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));//5.获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象放到压缩包中toZip(src,zos,src.getName());zos.close();}public static void toZip(File src, ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {//1.进入src文件夹File[] files = src.listFiles();for (File file : files) {if(file.isFile()){//变成ZipEntry对象放到压缩包ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name + "\\" + file.getName());zos.putNextEntry(entry);//读取文件中的数据写到压缩包FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);int b;while((b = fis.read()) != -1){zos.write(b);}fis.close();zos.closeEntry();}else {toZip(file,zos,name + "\\"+file.getName());}}}
}
21.1)常用工具包Commons-io
是一组IO操作的开源工具包
作业:提高IO流的开发效率
使用步骤:
- 在项目中创建一个文件夹:
lib - 将
jar包复制粘贴到lib文件夹 - 右键点击
jar包,选择Add as Library -> 点击OK - 在类中导包使用
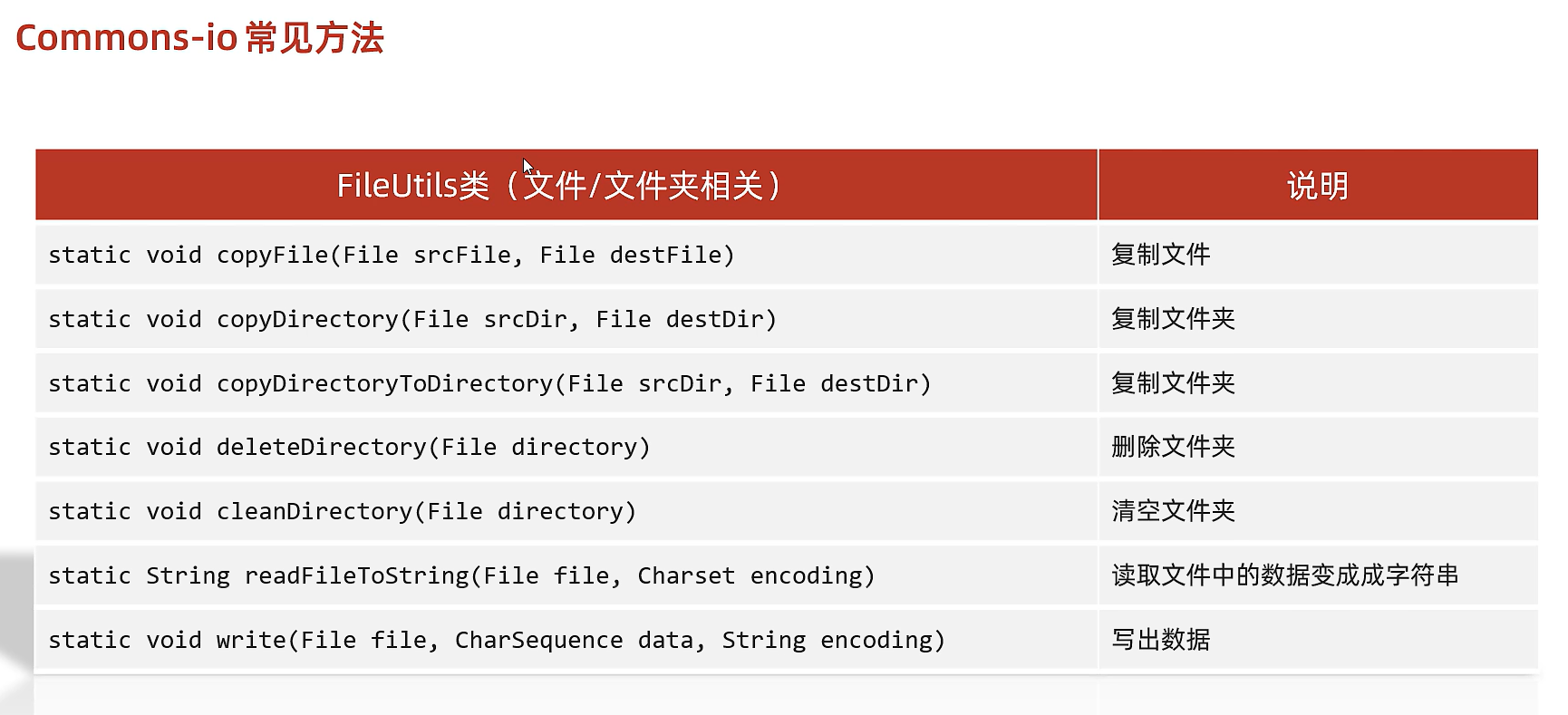

eg
File src = new File("src\\1.txt");
File dest = new File("src\\2.txt");
FileUtils.copyFile(src,dest);
21.2)常用工具包-Hutool
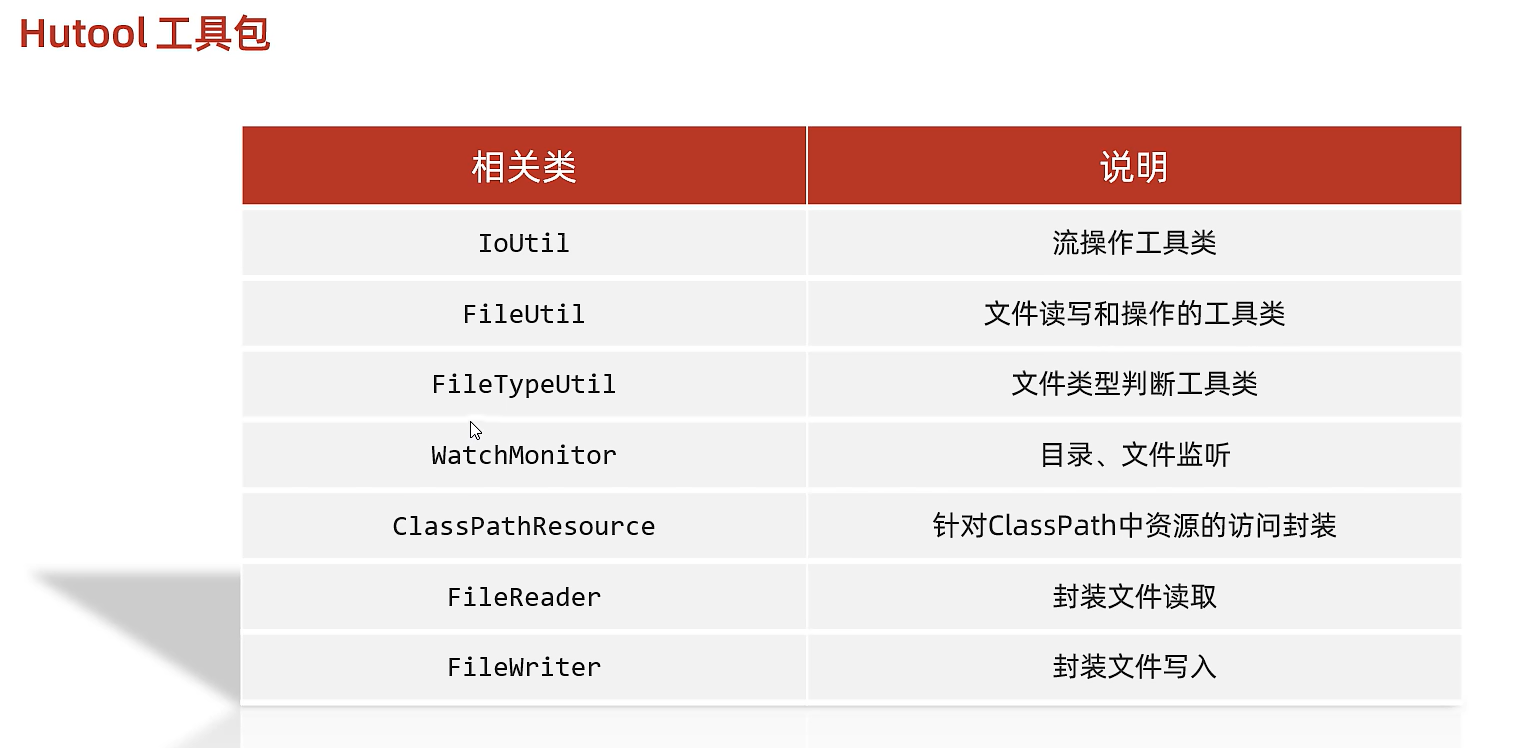
(笔记内容主要基于黑马程序员的课程讲解,旨在加深理解和便于日后复习)

希望这篇笔记能对大家的学习有所帮助,有啥不对的地方欢迎大佬们在评论区


 219. 存在重复元素 II (哈希表))



)







分布式事务)




)