《Flink-1.19.0源码详解8-ExecutionGraph生成-前篇》前篇已从Flink集群端调度开始解析ExecutionGraph生成的源码,解析了ExecutionGraph的ExecutionJobVertex节点、ExecutionVertex节点、IntermediateResult数据集、IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区与封装Task执行信息的Execution的创建完整过程。本篇接着前篇,继续解析ExecutionGraph生成的后续源码。
ExecutionGraph生成的完整源码:
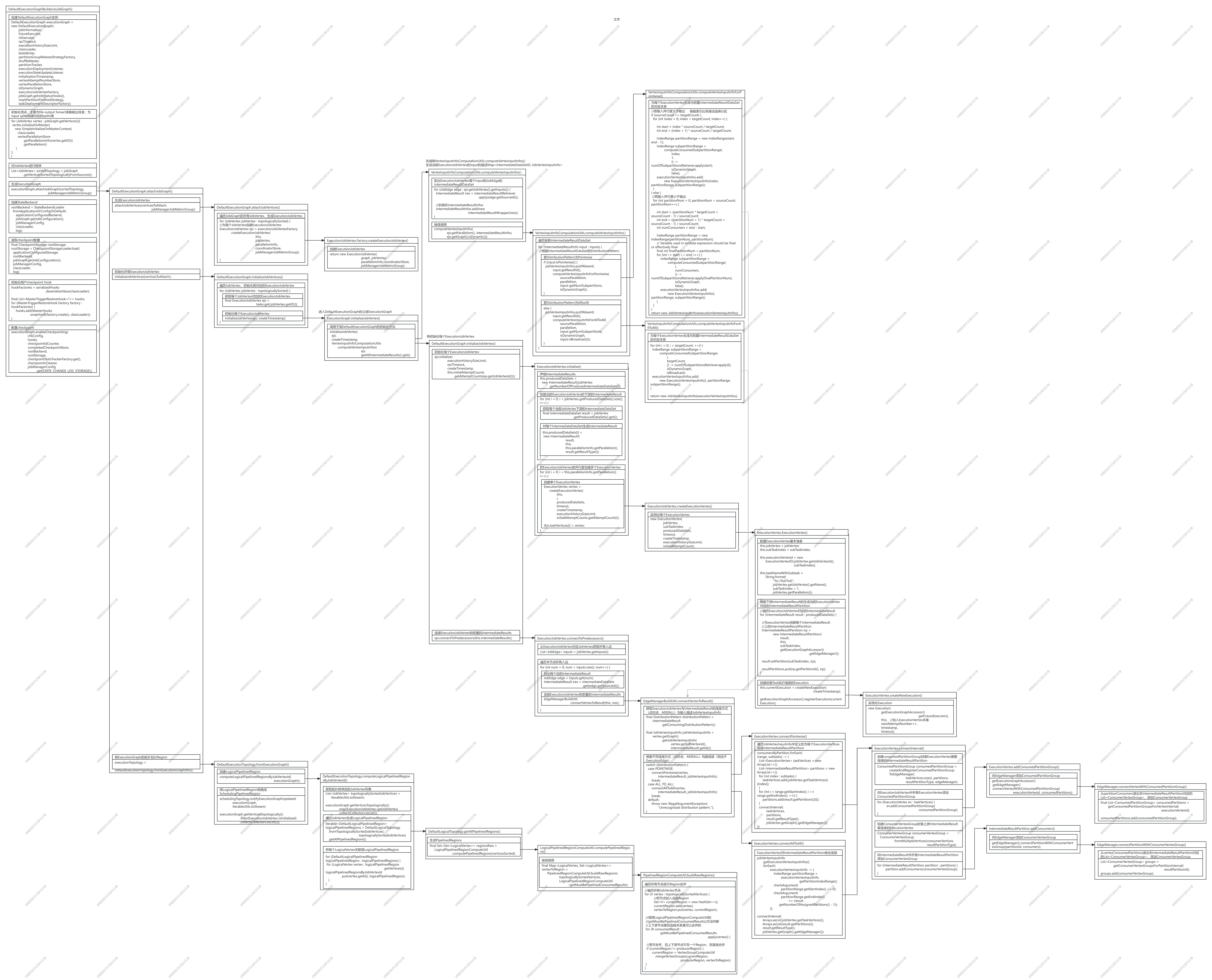
1.连接ExecutionJobVertex节点和前置的IntermediateResult数据集
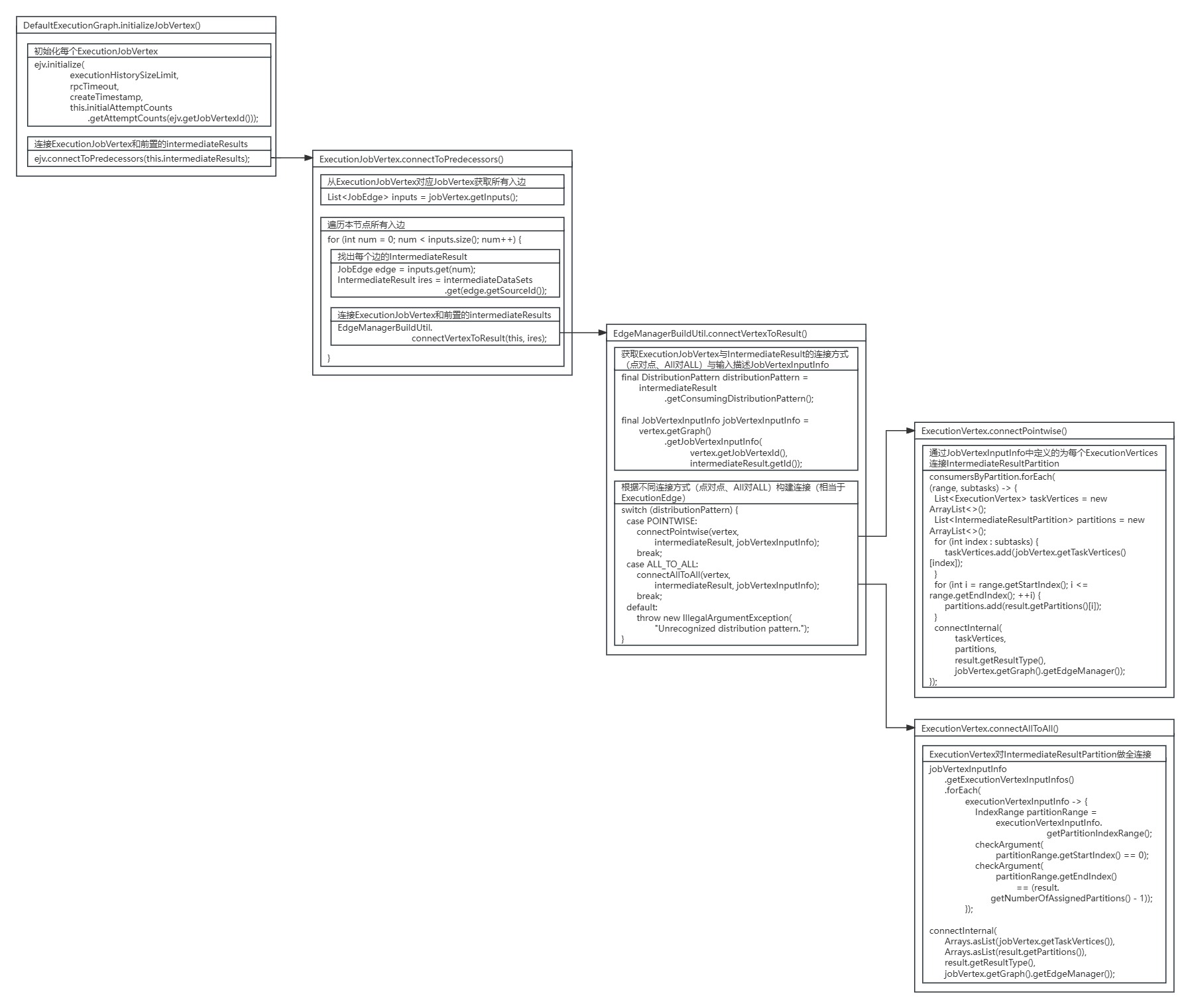
Flink在新版本(1.13后)取消了ExecutionEdge,用EdgeManager管理的vertexConsumedPartitions(Map<ExecutionVertexID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>>)和partitionConsumers(Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumerVertexGroup>>)来保存IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区与ExecutionVertex节点的连接关系。
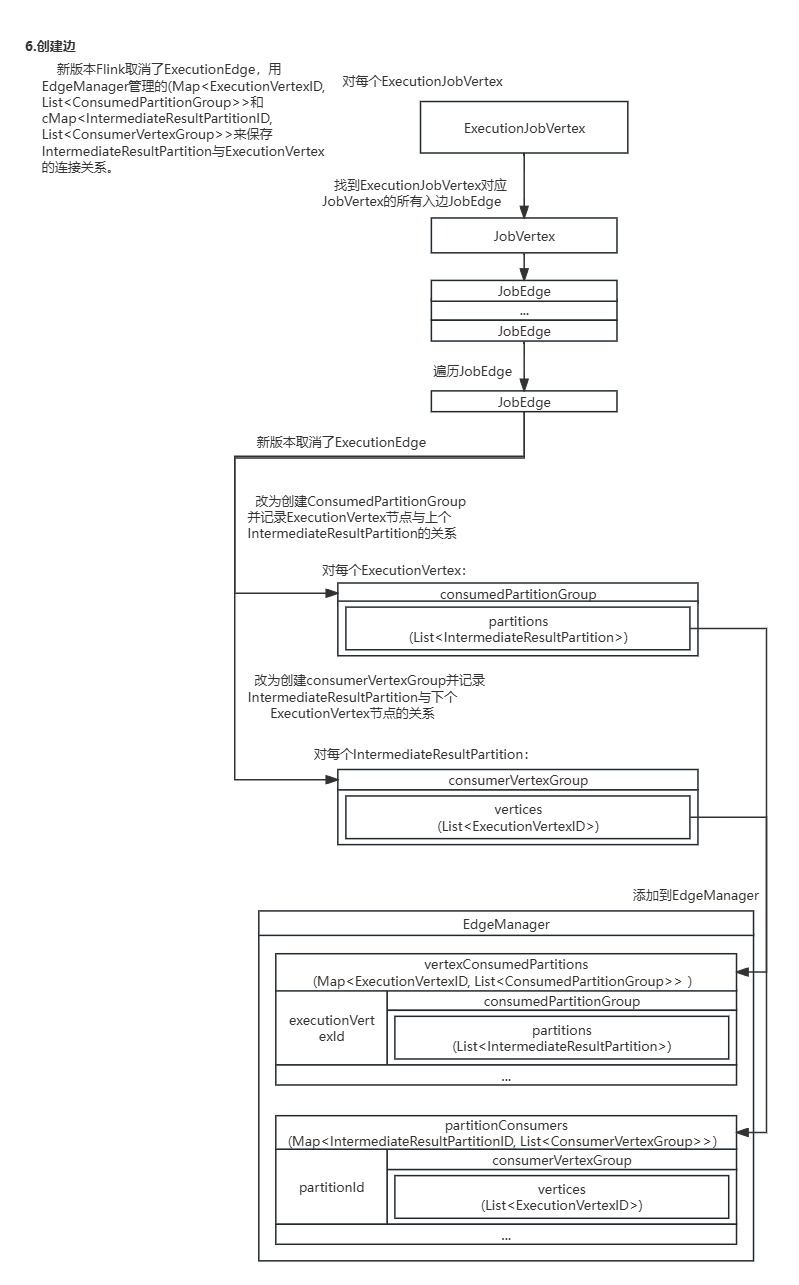
回到DefaultExecutionGraph的initializeJobVertex()方法,在完成ExecutionJobVertex的initialize()方法为每个ExecutionJobVertex节点创建其对应的ExecutionVertex节点和IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区后,DefaultExecutionGraph会继续调用ExecutionJobVertex的connectToPredecessors()方法,连接ExecutionJobVertex节点(包括其每个并行度上的ExecutionVertex节点)和前置的IntermediateResult数据集(包括其每个并行度上的IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区)。
源码图解:
DefaultExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法源码:
public void initializeJobVertex(ExecutionJobVertex ejv,long createTimestamp,Map<IntermediateDataSetID, JobVertexInputInfo> jobVertexInputInfos)throws JobException {//...//初始化每个ExecutionJobVertexejv.initialize(executionHistorySizeLimit,rpcTimeout,createTimestamp,this.initialAttemptCounts.getAttemptCounts(ejv.getJobVertexId()));//连接ExecutionJobVertex和前置的IntermediateResultejv.connectToPredecessors(this.intermediateResults);//...
}ExecutionJobVertex的connectToPredecessors()方法找到每个ExecutionJobVertex节点对应的JobVertex节点,从JobVertex节点中获取每个输入的JobEdge边和其连接前置的IntermediateDataSet数据集,继续调用EdgeManagerBuildUtil的connectVertexToResult()方法连接单个ExecutionJobVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集。
ExecutionJobVertex.connectToPredecessors()方法源码:
public void connectToPredecessors(Map<IntermediateDataSetID, IntermediateResult> intermediateDataSets)throws JobException {checkState(isInitialized());//从ExecutionJobVertex对应的JobVertex获取所有入边List<JobEdge> inputs = jobVertex.getInputs();//遍历本节点所有入边for (int num = 0; num < inputs.size(); num++) {//找出每个边的IntermediateResultJobEdge edge = inputs.get(num);//...IntermediateResult ires = intermediateDataSets.get(edge.getSourceId());//...//连接ExecutionJobVertex和前置的IntermediateResultEdgeManagerBuildUtil.connectVertexToResult(this, ires);}
}EdgeManagerBuildUtil的connectVertexToResult()方法获取了ExecutionJobVertex的DistributionPattern连接方式和由VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法生成的JobVertexInputInfo输入描述,并根据连接方式是POINTWISE还是ALL_TO_ALL,进行ExecutionJobVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集的连接。
EdgeManagerBuildUtil.connectVertexToResult()方法源码:
static void connectVertexToResult(ExecutionJobVertex vertex, IntermediateResult intermediateResult) {//获取ExecutionJobVertex与IntermediateResult的连接方式(点对点、All对ALL)final DistributionPattern distributionPattern =intermediateResult.getConsumingDistributionPattern();//获取输入描述final JobVertexInputInfo jobVertexInputInfo =vertex.getGraph().getJobVertexInputInfo(vertex.getJobVertexId(), intermediateResult.getId());//根据不同连接方式(点对点、All对ALL)构建连接(相当于ExecutionEdge)switch (distributionPattern) {case POINTWISE:connectPointwise(vertex, intermediateResult, jobVertexInputInfo);break;case ALL_TO_ALL:connectAllToAll(vertex, intermediateResult, jobVertexInputInfo);break;default:throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unrecognized distribution pattern.");}
}对于POINTWISE:
EdgeManagerBuildUtil会根据JobVertexInputInfo为每个ExecutionVertex节点分配需连接的IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区,并调用connectInternal()方法具体创建连接。
ExecutionVertex.connectPointwise()方法源码:
private static void connectPointwise(ExecutionJobVertex jobVertex,IntermediateResult result,JobVertexInputInfo jobVertexInputInfo) {Map<IndexRange, List<Integer>> consumersByPartition = new LinkedHashMap<>();//根据JobVertexInputInfo分配的为每个ExecutionVertex节点连接IntermediateResultPartition数据集。for (ExecutionVertexInputInfo executionVertexInputInfo :jobVertexInputInfo.getExecutionVertexInputInfos()) {int consumerIndex = executionVertexInputInfo.getSubtaskIndex();IndexRange range = executionVertexInputInfo.getPartitionIndexRange();consumersByPartition.compute(range,(ignore, consumers) -> {if (consumers == null) {consumers = new ArrayList<>();}consumers.add(consumerIndex);return consumers;});}//调用connectInternal()方法具体创建连接consumersByPartition.forEach((range, subtasks) -> {List<ExecutionVertex> taskVertices = new ArrayList<>();List<IntermediateResultPartition> partitions = new ArrayList<>();for (int index : subtasks) {taskVertices.add(jobVertex.getTaskVertices()[index]);}for (int i = range.getStartIndex(); i <= range.getEndIndex(); ++i) {partitions.add(result.getPartitions()[i]);}connectInternal(taskVertices,partitions,result.getResultType(),jobVertex.getGraph().getEdgeManager());});
}对于ALL_TO_ALL:
对ExecutionVertex节点和IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区做全连接。
ExecutionJobVertex.connectToPredecessors()方法源码:
private static void connectAllToAll(ExecutionJobVertex jobVertex,IntermediateResult result,JobVertexInputInfo jobVertexInputInfo) {// check the vertex input info is legal//ExecutionVertex对IntermediateResultPartition做全连接jobVertexInputInfo.getExecutionVertexInputInfos().forEach(executionVertexInputInfo -> {IndexRange partitionRange =executionVertexInputInfo.getPartitionIndexRange();checkArgument(partitionRange.getStartIndex() == 0);checkArgument(partitionRange.getEndIndex()== (result.getNumberOfAssignedPartitions() - 1));});connectInternal(Arrays.asList(jobVertex.getTaskVertices()),Arrays.asList(result.getPartitions()),result.getResultType(),jobVertex.getGraph().getEdgeManager());
}
2.调用ExecutionVertex.connectInternal()进行具体连接
无论是POINTWISE还是ALL_TO_ALL,在为每个ExecutionVertex节点分配号上游IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区后,都是通过调用ExecutionVertex.connectInternal()方法进行具体连接的。
在ExecutionVertex的connectInternal()方法中,首先创建consumedPartitionGroup封装ExecutionVertex节点需要连接的IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区,并向EdgeManager的vertexConsumedPartitions(Map<ExecutionVertexID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>> )添加ExecutionVertex节点和对应的ConsumedPartitionGroup。
然后继续创建ConsumerVertexGroup封装上游IntermediateResult数据集需连接的ExecutionVertex节点,并向EdgeManager的partitionConsumers (Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumerVertexGroup>>)添加IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区和其对应的ConsumerVertexGroup。
源码图解:
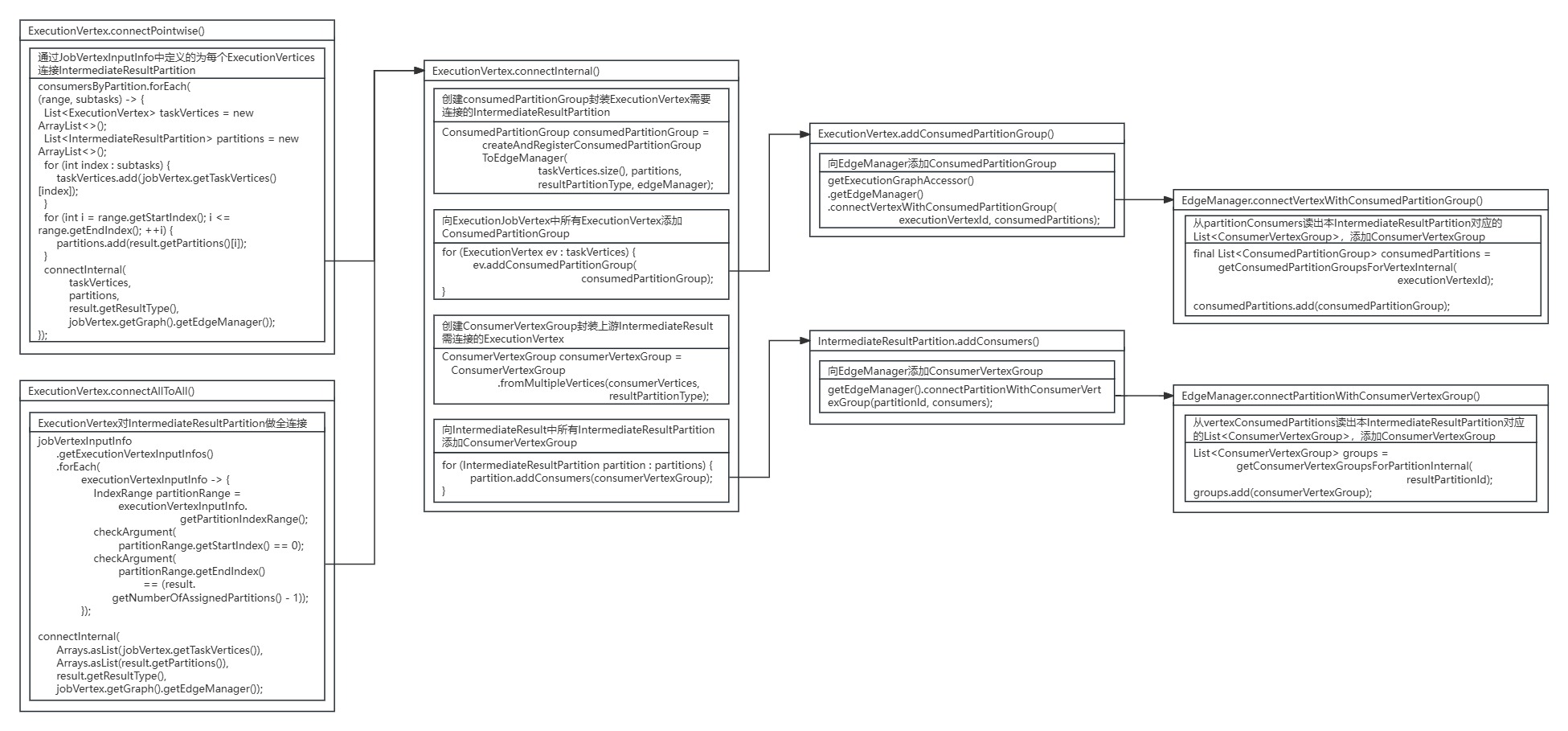
ExecutionVertex.connectInternal()方法源码:
private static void connectInternal(List<ExecutionVertex> taskVertices,List<IntermediateResultPartition> partitions,ResultPartitionType resultPartitionType,EdgeManager edgeManager) {checkState(!taskVertices.isEmpty());checkState(!partitions.isEmpty());//创建consumedPartitionGroup封装ExecutionVertex需要连接的IntermediateResultPartitionConsumedPartitionGroup consumedPartitionGroup =createAndRegisterConsumedPartitionGroupToEdgeManager(taskVertices.size(), partitions, resultPartitionType, edgeManager);//向ExecutionJobVertex中所有ExecutionVertex添加ConsumedPartitionGroupfor (ExecutionVertex ev : taskVertices) {ev.addConsumedPartitionGroup(consumedPartitionGroup);}//创建ConsumerVertexGroup封装上游IntermediateResult需连接的ExecutionVertexList<ExecutionVertexID> consumerVertices =taskVertices.stream().map(ExecutionVertex::getID).collect(Collectors.toList());ConsumerVertexGroup consumerVertexGroup =ConsumerVertexGroup.fromMultipleVertices(consumerVertices, resultPartitionType);//向IntermediateResult中所有IntermediateResultPartition添加ConsumerVertexGroup for (IntermediateResultPartition partition : partitions) {partition.addConsumers(consumerVertexGroup);}consumedPartitionGroup.setConsumerVertexGroup(consumerVertexGroup);consumerVertexGroup.setConsumedPartitionGroup(consumedPartitionGroup);
}因为在Flink1.13后取消了ExecutionEdge,ExecutionVertex与IntermediateResultPartition的连接关系由EdgeManager管理。
对于ExecutionJobVertex节点中所有ExecutionVertex节点,添加需要连接的IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区的ConsumedPartitionGroup,是调用ExecutionVertex节点的addConsumedPartitionGroup()方法,再进一步通过EdgeManager的connectVertexWithConsumedPartitionGroup()方法实现的。
ExecutionVertex.addConsumedPartitionGroup()方法源码:
public void addConsumedPartitionGroup(ConsumedPartitionGroup consumedPartitions) {//向EdgeManager添加ConsumedPartitionGroupgetExecutionGraphAccessor().getEdgeManager().connectVertexWithConsumedPartitionGroup(executionVertexId, consumedPartitions);
}最终EdgeManager从partitionConsumers中读出ExecutionVertex节点对应IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区的List<ConsumerVertexGroup>,向EdgeManager的vertexConsumedPartitions(Map<ExecutionVertexID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>> )添加ConsumerVertexGroup。
EdgeManager.connectVertexWithConsumedPartitionGroup()方法源码:
public void connectVertexWithConsumedPartitionGroup(ExecutionVertexID executionVertexId, ConsumedPartitionGroup consumedPartitionGroup) {checkNotNull(consumedPartitionGroup);//从partitionConsumers读出本IntermediateResultPartition对应的List<ConsumerVertexGroup>,添加ConsumerVertexGroupfinal List<ConsumedPartitionGroup> consumedPartitions =getConsumedPartitionGroupsForVertexInternal(executionVertexId);consumedPartitions.add(consumedPartitionGroup);
}同上,对于IntermediateResult数据集中所有IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区,添加要连接的ExecutionVertex节点的ConsumerVertexGroup,是调用IntermediateResultPartition的addConsumers()方法,再进一步通过EdgeManager的connectPartitionWithConsumerVertexGroup()方法实现的。
IntermediateResultPartition.addConsumers()方法源码:
public void addConsumers(ConsumerVertexGroup consumers) {//向EdgeManager添加ConsumerVertexGroupgetEdgeManager().connectPartitionWithConsumerVertexGroup(partitionId, consumers);
}最终EdgeManager从partitionConsumers中读出IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区对应ExecutionVertex节点的List<ConsumerVertexGroup>,向EdgeManager的partitionConsumers (Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumerVertexGroup>>)添加ConsumerVertexGroup。
EdgeManager.connectPartitionWithConsumerVertexGroup()方法源码:
public void connectPartitionWithConsumerVertexGroup(IntermediateResultPartitionID resultPartitionId,ConsumerVertexGroup consumerVertexGroup) {checkNotNull(consumerVertexGroup);//从vertexConsumedPartitions读出本IntermediateResultPartition对应的List<ConsumerVertexGroup>,添加ConsumerVertexGroupList<ConsumerVertexGroup> groups =getConsumerVertexGroupsForPartitionInternal(resultPartitionId);groups.add(consumerVertexGroup);
}最终遍历完所有ExecutionJobVertex节点,完成EdgeManager管理的vertexConsumedPartitions(Map<ExecutionVertexID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>>)和partitionConsumers(Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumerVertexGroup>>)的创建,就完整保存了每个ExecutionJobVertex节点所有并行度上的ExecutionVertex节点与每个IntermediateResult数据集对应IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区的连接关系。
3.SchedulingPipelinedRegion划分
SchedulingPipelinedRegion是Flink独立申请资源进行调度的单位,会把一系列通过流水线(pipelined)方式连接的算子组合起来,一起进行资源申请与调度。
当完成ExecutionJobVertex节点创建与初始化后,回到DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobGraph()方法 ,继续进行SchedulingPipelinedRegion的划分。
源码图解:
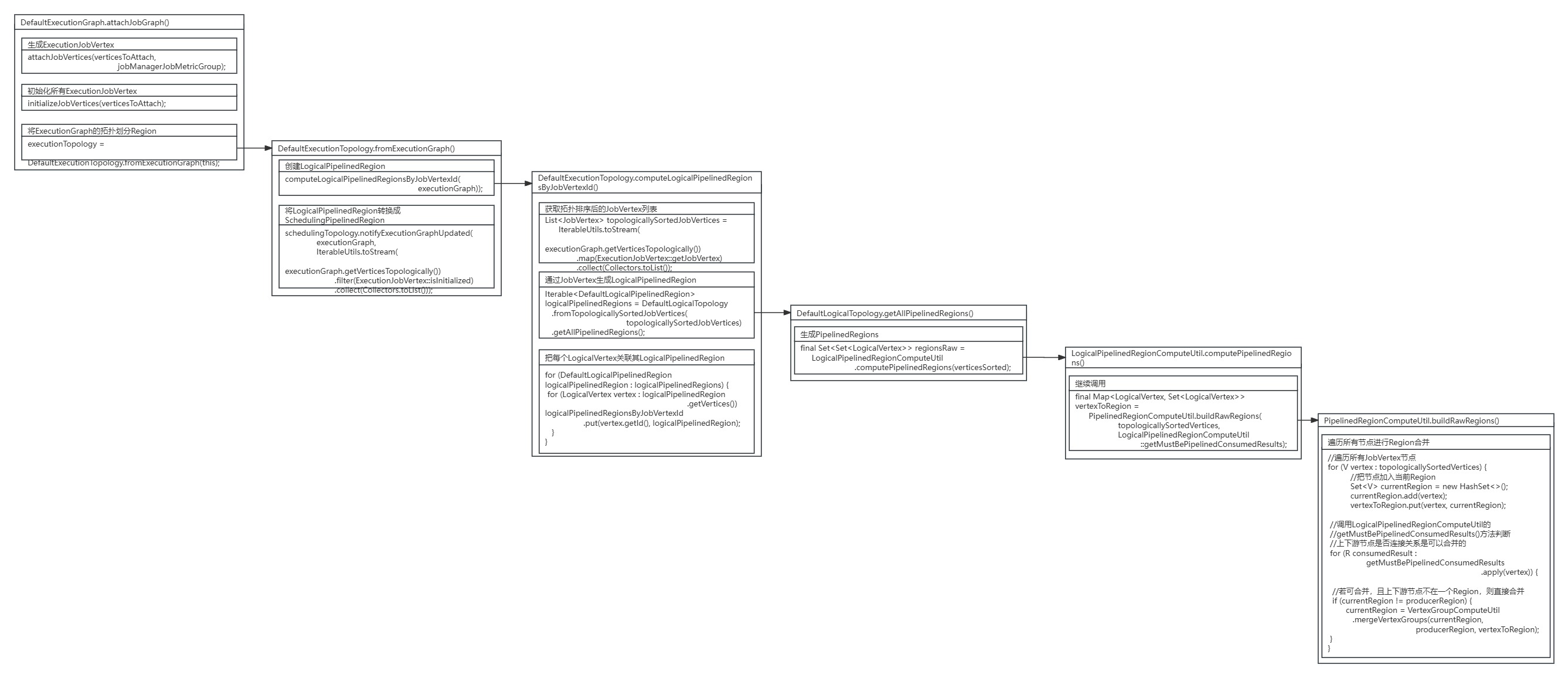
DefaultExecutionGraph.attachJobGraph()方法源码:
public void attachJobGraph(List<JobVertex> verticesToAttach, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup)throws JobException {assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread();LOG.debug("Attaching {} topologically sorted vertices to existing job graph with {} "+ "vertices and {} intermediate results.",verticesToAttach.size(),tasks.size(),intermediateResults.size());//生成ExecutionJobVertexattachJobVertices(verticesToAttach, jobManagerJobMetricGroup);if (!isDynamic) {//初始化所有ExecutionJobVertexinitializeJobVertices(verticesToAttach);}//将ExecutionGraph的拓扑划分Region// the topology assigning should happen before notifying new vertices to failoverStrategyexecutionTopology = DefaultExecutionTopology.fromExecutionGraph(this);partitionGroupReleaseStrategy =partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory.createInstance(getSchedulingTopology());
}进入DefaultExecutionTopology.fromExecutionGraph()方法中,DefaultExecutionTopology创建了LogicalPipelinedRegion,并将LogicalPipelinedRegion转换成SchedulingPipelinedRegion。
DefaultExecutionGraph.attachJobGraph()方法源码:
public static DefaultExecutionTopology fromExecutionGraph(DefaultExecutionGraph executionGraph) {checkNotNull(executionGraph, "execution graph can not be null");//获取EdgeManagerEdgeManager edgeManager = executionGraph.getEdgeManager();//创建LogicalPipelinedRegionDefaultExecutionTopology schedulingTopology =new DefaultExecutionTopology(() ->IterableUtils.toStream(executionGraph.getAllExecutionVertices()).map(ExecutionVertex::getID).collect(Collectors.toList()),edgeManager,//创建LogicalPipelinedRegioncomputeLogicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId(executionGraph));//将LogicalPipelinedRegion转换成SchedulingPipelinedRegionschedulingTopology.notifyExecutionGraphUpdated(executionGraph,IterableUtils.toStream(executionGraph.getVerticesTopologically()).filter(ExecutionJobVertex::isInitialized).collect(Collectors.toList()));return schedulingTopology;
}进入DefaultExecutionTopology的computeLogicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId()方法继续分析LogicalPipelinedRegion的创建。首先DefaultExecutionTopology先对JobVertex节点进行排序,再根据JobVertex节点生成LogicalPipelinedRegion,最后再将把每个LogicalVertex关联用其对于的LogicalPipelinedRegion。
DefaultExecutionTopology.computeLogicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId()方法源码:
private static Map<JobVertexID, DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion>computeLogicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId(final ExecutionGraph executionGraph) {//获取拓扑排序后的JobVertex列表List<JobVertex> topologicallySortedJobVertices =IterableUtils.toStream(executionGraph.getVerticesTopologically()).map(ExecutionJobVertex::getJobVertex).collect(Collectors.toList());//通过JobVertex生成LogicalPipelinedRegionIterable<DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion> logicalPipelinedRegions =DefaultLogicalTopology.fromTopologicallySortedJobVertices(topologicallySortedJobVertices).getAllPipelinedRegions();//把每个LogicalVertex关联其LogicalPipelinedRegionMap<JobVertexID, DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion> logicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId =new HashMap<>();for (DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion logicalPipelinedRegion : logicalPipelinedRegions) {for (LogicalVertex vertex : logicalPipelinedRegion.getVertices()) {logicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId.put(vertex.getId(), logicalPipelinedRegion);}}return logicalPipelinedRegionsByJobVertexId;
}通过JobVertex节点生成LogicalPipelinedRegion是依次调用DefaultLogicalTopology的getAllPipelinedRegions()方法、LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil的computePipelinedRegions()方法,最终进入PipelinedRegionComputeUtil的buildRawRegions()方法。
DefaultLogicalTopology.getAllPipelinedRegions()方法源码:
public Iterable<DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion> getAllPipelinedRegions() {//继续调用LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil.computePipelinedRegions()final Set<Set<LogicalVertex>> regionsRaw =LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil.computePipelinedRegions(verticesSorted);final Set<DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion> regions = new HashSet<>();for (Set<LogicalVertex> regionVertices : regionsRaw) {regions.add(new DefaultLogicalPipelinedRegion(regionVertices));}return regions;
}LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil.computePipelinedRegions()方法源码:
public static Set<Set<LogicalVertex>> computePipelinedRegions(final Iterable<? extends LogicalVertex> topologicallySortedVertices) {//继续调用final Map<LogicalVertex, Set<LogicalVertex>> vertexToRegion =PipelinedRegionComputeUtil.buildRawRegions(topologicallySortedVertices,LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil::getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults);// Since LogicalTopology is a DAG, there is no need to do cycle detection nor to merge// regions on cycles.return uniqueVertexGroups(vertexToRegion);
}在PipelinedRegionComputeUtil的buildRawRegions()方法中,首先遍历所有JobVertex节点,调用LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil的getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults()方法判断上下游节点是否连接关系是可以合并的,若可合并,且上下游节点不在一个Region,则直接合并。
PipelinedRegionComputeUtil.buildRawRegions()方法源码:
static <V extends Vertex<?, ?, V, R>, R extends Result<?, ?, V, R>>Map<V, Set<V>> buildRawRegions(final Iterable<? extends V> topologicallySortedVertices,final Function<V, Iterable<R>> getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults) {final Map<V, Set<V>> vertexToRegion = new IdentityHashMap<>();//遍历所有JobVertex节点// iterate all the vertices which are topologically sortedfor (V vertex : topologicallySortedVertices) {//把节点加入当前RegionSet<V> currentRegion = new HashSet<>();currentRegion.add(vertex);vertexToRegion.put(vertex, currentRegion);//调用LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil的getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults()方法判断上下游节点是否连接关系是可以合并的// Each vertex connected through not mustBePipelined consumingConstraint is considered// as a// single region.for (R consumedResult : getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults.apply(vertex)) {final V producerVertex = consumedResult.getProducer();final Set<V> producerRegion = vertexToRegion.get(producerVertex);if (producerRegion == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Producer task "+ producerVertex.getId()+ " failover region is null"+ " while calculating failover region for the consumer task "+ vertex.getId()+ ". This should be a failover region building bug.");}//若可合并,且上下游节点不在一个Region,则直接合并// check if it is the same as the producer region, if so skip the merge// this check can significantly reduce compute complexity in All-to-All// PIPELINED edge caseif (currentRegion != producerRegion) {currentRegion =VertexGroupComputeUtil.mergeVertexGroups(currentRegion, producerRegion, vertexToRegion);}}}return vertexToRegion;
}其中判断是否可以合并的方法为LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil的getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults()方法,判断是根据本JobVertex节点与上游IntermediateDataSet数据集的连接关系的ResultPartitionType,来判断是否可以Pipeline连接。
private static Iterable<LogicalResult> getMustBePipelinedConsumedResults(LogicalVertex vertex) {List<LogicalResult> mustBePipelinedConsumedResults = new ArrayList<>();//获取本JobVertex与所有上游IntermediateDataSet数据集的连接关系for (LogicalResult consumedResult : vertex.getConsumedResults()) {//根据本JobVertex与上游IntermediateDataSet数据集的连接关系的ResultPartitionType判断是否可以Pipeline连接if (consumedResult.getResultType().mustBePipelinedConsumed()) {mustBePipelinedConsumedResults.add(consumedResult);}}return mustBePipelinedConsumedResults;
}当把ExecutionGraph划分好LogicalPipelinedRegionComputeUtil并转换为SchedulingPipelinedRegion后,JobMaster将依次为每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion向Flink的ResourceManager申请cpu内存资源,进行计算资源调度。
4.结语
至此,ExecutionGraph生成的完整源码已解析完毕,本文解析了ExecutionGraph的ExecutionJobVertex节点、ExecutionVertex节点、IntermediateResult数据集、IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区与封装Task执行信息的Execution的创建;解析了ExecutionJobVertex节点与前置的IntermediateResult数据集的连接,及SchedulingPipelinedRegion的划分。本专栏的下篇博文将继续从Flink JobMaster 依次为每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行计算资源调度分配,来继续解析Flink的完整源码。













:Vue3响应式编程中this绑定机制与解决方案)

的使用——以NDVI去水体为例)



