一 应用端
源码路径: external\tinyalsa\pcm.c external\tinyalsa\pcm_hw.c
struct pcm *pcm_open(unsigned int card, unsigned int device,unsigned int flags, struct pcm_config *config)
{...pcm->ops = &hw_ops;pcm->fd = pcm->ops->open(card, device, flags, &pcm->data, pcm->snd_node);/*实际是调用 pcm_hw.c 的pcm_hw_open 接口 open("/dev/snd/pcmC0D0c") 打开节点*/if (pcm->ops->ioctl(pcm->data, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_INFO, &info)) {oops(&bad_pcm, errno, "cannot get info");goto fail_close;}if (pcm->ops->ioctl(pcm->data, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_HW_PARAMS, ¶ms)) {oops(&bad_pcm, errno, "cannot set hw params");goto fail_close;}/* get our refined hw_params */config->period_size = param_get_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIOD_SIZE);config->period_count = param_get_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIODS);pcm->buffer_size = config->period_count * config->period_size;if (pcm->ops->ioctl(pcm->data, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_SW_PARAMS, &sparams)) {oops(&bad_pcm, errno, "cannot set sw params");goto fail;}
}二 audio 节点 介绍
1. /dev/snd下的pcm设备节点介绍
我们 adb shell, 进入手机中,ls -al /dev/snd 看下,可以看到很多设备节点。
简化如下:
$ cd /dev/snd $ ls –l crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 8 2011-02-23 21:38 controlC0 ---> 用于声卡的控制,例如通道选择,混音,麦克风的控制等 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 4 2011-02-23 21:38 midiC0D0 ---> 用于播放midi 音频 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 7 2011-02-23 21:39 pcmC0D0c ---> 用于录音的pcm 设备 1 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 6 2011-02-23 21:56 pcmC0D0p ---> 用于播放的pcm 设备 1 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 5 2011-02-23 21:38 pcmC0D1p ---> 用于播放的pcm 设备 2 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 3 2011-02-23 21:38 seq ---> 音序器 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 2 2011-02-23 21:38 timer ---> 定时器
其中,
C0D0 代表的是声卡0 中的设备0,
pcmC0D0c 最后一个c 代表capture,
pcmC0D0p 最后一个p 代表 playback,
这些都是alsa-driver 中的命名规则。
2. /dev/snd下的pcm设备节点 创建过程分析
另外,还有一个发现,就,/dev/snd 下面所有的节点的主设备号 都是 116 ,面次设备号各不相同。
原因是因为,
在alsa 中所有的节点都是同一个主设备号,到时访问open 节点的时候就会先调用同一个主设备号的open 函数,
接着,在主设备号的open 函数中,再来分发调用,各个不同次设备号的open 函数。
2.1 CONFIG_SND_MAJOR 主设备号 116
代码可以参考 sound.c 中的代码:
主设备号注册
@\kernel\msm-3.18\include\sound\core.h
#define CONFIG_SND_MAJOR 116 /* standard configuration */ 定义主设备号@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\sound.c
static int major = CONFIG_SND_MAJOR; // 主设备号
module_param(major, int, 0444);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(major, "Major # for sound driver.");static const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = snd_open,.llseek = noop_llseek,
};static int __init alsa_sound_init(void)
{snd_major = major;snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit;if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) { // 主册一个主设备号pr_err("ALSA core: unable to register native major device number %d\n", major);return -EIO;}snd_info_minor_register();return 0;
}
2.2 snd_minors 数组分析
在 snd_register_device_for_dev 函数中,主要作用就是创建不同的次设备号节点,保存在 snd_minors[] 数组中。
其主要是在pcm.c 创建节点时被调用的。
可以发现在代码中,会根据声卡号和设备索引号,依次创建 pcmC%iD%ip 和 pcmC%iD%ic 两个设备节点的名字。
接着,调用 snd_register_device_for_dev 来创建设备节点,传入换参数就是 设备节点的名字。
@\kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\pcm.cstatic int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{pcm = device->device_data;err = snd_pcm_add(pcm);for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {int devtype = -1;switch (cidx) {case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK:sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ip", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;break;case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE:sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ic", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;break;}/* device pointer to use, pcm->dev takes precedence if* it is assigned, otherwise fall back to card's device* if possible */dev = pcm->dev;/* register pcm */err = snd_register_device_for_dev(devtype, pcm->card,pcm->device,&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx],pcm, str, dev);dev = snd_get_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device);if (dev) {err = sysfs_create_groups(&dev->kobj,pcm_dev_attr_groups);put_device(dev);}for (substream = pcm->streams[cidx].substream; substream; substream = substream->next)snd_pcm_timer_init(substream);}list_for_each_entry(notify, &snd_pcm_notify_list, list)notify->n_register(pcm);return 0;
}
在snd_register_device_for_dev() 中,会根据传入的字符串名字,创建不同的设备节点。
看 snd_register_device_for_dev() 代码前,我们来看一下snd_minors[] 这个数组。
static struct snd_minor *snd_minors[SNDRV_OS_MINORS];其结构体描述如下:
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\include\sound\core.hstruct snd_minor {int type; /* SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_XXX */ // 声卡类型: SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK 和 SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE 两种int card; /* card number */ //声卡号int device; /* device number */ // 设备号const struct file_operations *f_ops; /* file operations */ // 该节点换操作节构体void *private_data; /* private data for f_ops->open */ // 私有参数struct device *dev; /* device for sysfs */ // sys 设备节点描述符struct snd_card *card_ptr; /* assigned card instance */ //声卡结构体
};
从上面的结构体可以看出,snd_minors中 主要是包含了 card声卡下 device设备的操作方法 f_ops。
这样就很清楚了。
通过snd_minors[] 这个 数组,我人能够找到任意一个 声卡下的设备 的操作方法。
2.3 pcm设备节点创建代码
接下来,我们来分析snd_register_device_for_dev() 这个函数,
这个函数主要工作 如下:
step 1. 使用 snd_minor 指针将 要创建的声卡设备的信息保存下来
step 2. 给声卡设备分配 次设备号,如果定义了动态分配,则分配次设备号
step 3. 以次设备号为索引,将声卡设备的信息保存在 snd_minors[minor]数组中。
step 4. 通过 device_create 创建一个 主设备号 majore=116, 次设备号minor 的设备节点,节点名字就是字符串 pcmC%iD%ip 或 pcmC%iD%ic
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\sound.c
/*** snd_register_device_for_dev - Register the ALSA device file for the card* @type: the device type, SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_XXX* @card: the card instance* @dev: the device index* @f_ops: the file operations* @private_data: user pointer for f_ops->open()* @name: the device file name* @device: the &struct device to link this new device to** Registers an ALSA device file for the given card.* The operators have to be set in reg parameter.** Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.*/
int snd_register_device_for_dev(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,const struct file_operations *f_ops,void *private_data,const char *name, struct device *device)
{int minor;struct snd_minor *preg;preg = kmalloc(sizeof *preg, GFP_KERNEL);// step 1. 使用 snd_minor 指针将 要创建的声卡设备的信息保存下来preg->type = type;preg->card = card ? card->number : -1;preg->device = dev;preg->f_ops = f_ops;preg->private_data = private_data;preg->card_ptr = card;// step 2. 给声卡设备分配 次设备号,如果定义了动态分配,则分配次设备号
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_DYNAMIC_MINORSminor = snd_find_free_minor(type);
#elseminor = snd_kernel_minor(type, card, dev);if (minor >= 0 && snd_minors[minor])minor = -EBUSY;
#endif// step 3. 以次设备号为索引,将声卡设备的信息保存在 snd_minors[minor]数组中。snd_minors[minor] = preg;// step 4. 通过 device_create 创建一个 主设备号 majore=116, 次设备号minor 的设备节点,节点名字就是字符串 pcmC%iD%ip 或 pcmC%iD%icpreg->dev = device_create(sound_class, device, MKDEV(major, minor),private_data, "%s", name);return 0;
}
2.4 pcm设备节点创建open 过程分析
前面讲了pcm设备节点的创建过程,接下来我们来看下如何打开的。
先看下如下代码,在 snd_fops 文件操作节构全中,包含了 snd_open方法 。
在init 代码中,是通过 register_chrdev(major, “alsa”, &snd_fops) 来将 major=116 的主设备号 和 snd_fops绑定在一起。
也就是说,凡是打开 设备节点major 为 116 的节点时,都会调用该 snd_fop 的open方法 snd_open()。
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\sound.cstatic const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = snd_open,.llseek = noop_llseek,
};
static int __init alsa_sound_init(void)
{snd_major = major;snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit;if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) {pr_err("ALSA core: unable to register native major device number %d\n", major);return -EIO;}snd_info_minor_register();return 0;
}
在 snd_open() 方法中,整个过程为:
step 1:获取次设备号
step 2:初始化一个 snd_minor 类型的指针, 和file_operations 类型的操作方法指针
step 3:根据设备的次设备号,从 snd_minors[minor]数组中获取对应设备的snd_minor 结构体信息
step 4:解析出该设备的 操作方法
step 5:替换文件的操作方法
step 6:调用open 方法
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\sound.c
static int snd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{// step 1: 获取次设备号unsigned int minor = iminor(inode);// step 2:初始化一个 snd_minor 类型的指针, 和file_operations 类型的操作方法指针struct snd_minor *mptr = NULL;const struct file_operations *new_fops;// step 3:根据设备的次设备号,从 snd_minors[minor]数组中获取对应设备的snd_minor 结构体信息。mptr = snd_minors[minor];// step 4:解析出该设备的 操作方法new_fops = fops_get(mptr->f_ops);// step 5: 替换文件的操作方法replace_fops(file, new_fops);// step 6: 调用open 方法if (file->f_op->open)err = file->f_op->open(inode, file);return err;
}
2.5 pcm设备节点 file_operations 介绍
前面,我们说了pcm设备节点的 open() 方法的调用流程,
不知道你有没有好奇心,是否想进去看下它做了啥呢? 哈哈。
在前面的代码中,fops 是在 snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx] 中传递过来的。
/* register pcm */err = snd_register_device_for_dev(devtype, pcm->card,pcm->device,&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx],pcm, str, dev);
我们看下 snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx] 中的定义:
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\pcm_native.cconst struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {{ // SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK.owner = THIS_MODULE,.write = snd_pcm_write,.aio_write = snd_pcm_aio_write,.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_playback_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,},{ // SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE.owner = THIS_MODULE,.read = snd_pcm_read,.aio_read = snd_pcm_aio_read,.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_capture_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,}
};
可以看出,在 snd_pcm_f_ops 数组中,主要就是定义了 playback 和 capture 的各个操作方法。
2.6 pcm设备节点 snd_pcm_playback_open() 代码分析
我们以 playback 来分析下 其open 方法: snd_pcm_playback_open()
其主要工作 为:
step 1: 通过nonseekable_open函数,告诉内核,当前文件open 时,是不可 llseek 定位的
step 2: 获得 snd_minor 结构体中的 privdata 私有数据,其中保存了声卡的相关信息
step 3: 调用 snd_pcm_open() open 函数,传参为 pcm 和 SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE;
static int snd_pcm_playback_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{struct snd_pcm *pcm;// step 1: 通过nonseekable_open函数,告诉内核,当前文件open 时,是不可 llseek 定位的int err = nonseekable_open(inode, file);// step 2: 获得 snd_minor 结构体中的 privdata 私有数据,其中保存了声卡的相关信息pcm = snd_lookup_minor_data(iminor(inode),SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK);-------->+ private_data = mreg->private_data;+ return private_data;<-------// step 3: 调用 snd_pcm_open() open 函数,err = snd_pcm_open(file, pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK);return err;
}
2.7 snd_pcm_open() 代码分析
主要工作如下:
- 将 pcm->card 和 file 添加链表
- 构造当前进程对应的等待队列 wait
- 将wait 保存在 pcm->open_wait 中
- 上锁
- 在while(1) 中打开文件,如果失败就退出
- 在阻塞模式下,设置SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO会导致read/write函数返回EAGAIN
我们此返回 -EAGAIN 说明是正常的,数据还没写完 - 设置当前进和为可被中断
- 调度,让更高优先及的任务得到处理,或者让其他任务得到处理
- 等待调度到来,继续写播放数据
@ \kernel\msm-3.18\sound\core\pcm_native.cstatic int snd_pcm_open(struct file *file, struct snd_pcm *pcm, int stream)
{int err;wait_queue_t wait;// 1. 将 pcm->card 和 file 添加链表err = snd_card_file_add(pcm->card, file);if (!try_module_get(pcm->card->module)) {err = -EFAULT;goto __error2;}// 2. 构造当前进程对应的等待队列 waitinit_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);// 3. 将wait 保存在 pcm->open_wait 中add_wait_queue(&pcm->open_wait, &wait);// 4. 上锁mutex_lock(&pcm->open_mutex);while (1) {// 5. 在while(1) 中打开文件,如果失败就退出err = snd_pcm_open_file(file, pcm, stream);if (err >= 0)break;// 6. 在阻塞模式下,设置SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO会导致read/write函数返回EAGAIN// 我们此返回 -EAGAIN 说明是正常的if (err == -EAGAIN) {if (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) { // 如果是非阻塞模式下,则直接退出,在非阻塞模式下,write或read返回-1,errno为EAGAIN,表示相应的操作还没执行完成。err = -EBUSY;break;}} elsebreak;// 7. 设置当前进和为可被中断set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);mutex_unlock(&pcm->open_mutex);// 8. 调度,让更高优先及的任务得到处理,或者让其他任务得到处理schedule();// 9. 等待调度到来,继续写播放数据mutex_lock(&pcm->open_mutex);if (pcm->card->shutdown) {err = -ENODEV;break;}if (signal_pending(current)) {err = -ERESTARTSYS;break;}}remove_wait_queue(&pcm->open_wait, &wait);mutex_unlock(&pcm->open_mutex);return err;
}
接下往下看snd_pcm_open_file
static int snd_pcm_open_file(struct file *file,struct snd_pcm *pcm,int stream)
{struct snd_pcm_file *pcm_file;struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;int err;err = snd_pcm_open_substream(pcm, stream, file, &substream);if (err < 0)return err;pcm_file = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm_file), GFP_KERNEL);if (pcm_file == NULL) {snd_pcm_release_substream(substream);return -ENOMEM;}pcm_file->substream = substream;if (substream->ref_count == 1)substream->pcm_release = pcm_release_private;file->private_data = pcm_file;return 0;
}继续跟踪snd_pcm_open_substream
int snd_pcm_open_substream(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int stream,struct file *file,struct snd_pcm_substream **rsubstream)
{struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;int err;err = snd_pcm_attach_substream(pcm, stream, file, &substream);if (err < 0)return err;if (substream->ref_count > 1) {*rsubstream = substream;return 0;}err = snd_pcm_hw_constraints_init(substream);if (err < 0) {pcm_dbg(pcm, "snd_pcm_hw_constraints_init failed\n");goto error;}err = substream->ops->open(substream);if (err < 0)goto error;substream->hw_opened = 1;err = snd_pcm_hw_constraints_complete(substream);if (err < 0) {pcm_dbg(pcm, "snd_pcm_hw_constraints_complete failed\n");goto error;}*rsubstream = substream;return 0;error:snd_pcm_release_substream(substream);return err;
}substream->ops->open(substream);会调用创建PCM注册的ops
int soc_new_pcm(struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *rtd, int num)
{....../* ASoC PCM operations */if (rtd->dai_link->dynamic) {rtd->ops.open = dpcm_fe_dai_open;rtd->ops.hw_params = dpcm_fe_dai_hw_params;rtd->ops.prepare = dpcm_fe_dai_prepare;rtd->ops.trigger = dpcm_fe_dai_trigger;rtd->ops.hw_free = dpcm_fe_dai_hw_free;rtd->ops.close = dpcm_fe_dai_close;rtd->ops.pointer = soc_pcm_pointer;} else {rtd->ops.open = soc_pcm_open;rtd->ops.hw_params = soc_pcm_hw_params;rtd->ops.prepare = soc_pcm_prepare;rtd->ops.trigger = soc_pcm_trigger;rtd->ops.hw_free = soc_pcm_hw_free;rtd->ops.close = soc_pcm_close;rtd->ops.pointer = soc_pcm_pointer;}......
}2.8 soc_pcm端的open() 代码分析
MTK平台是dynamic 调用FE的open,该接口作用有:
1.获取路由信息,计算当前FE绑定的BE
2.分别Open BE和FE pcm
static int dpcm_fe_dai_open(struct snd_pcm_substream *fe_substream)
{struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *fe = asoc_substream_to_rtd(fe_substream);struct snd_soc_dapm_widget_list *list;int ret;int stream = fe_substream->stream;snd_soc_dpcm_mutex_lock(fe);fe->dpcm[stream].runtime = fe_substream->runtime;ret = dpcm_path_get(fe, stream, &list);if (ret < 0)goto open_end;/* calculate valid and active FE <-> BE dpcms */dpcm_process_paths(fe, stream, &list, 1);ret = dpcm_fe_dai_startup(fe_substream);if (ret < 0)dpcm_fe_dai_cleanup(fe_substream);dpcm_clear_pending_state(fe, stream);dpcm_path_put(&list);
open_end:snd_soc_dpcm_mutex_unlock(fe);return ret;
}继续看函数dpcm_fe_dai_startup
其中 dpcm_be_dai_startup 会调用BE端 __soc_pcm_open(be, be_substream);
/* start the DAI frontend */
ret = __soc_pcm_open(fe, fe_substream);
static int dpcm_fe_dai_startup(struct snd_pcm_substream *fe_substream)
{struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *fe = asoc_substream_to_rtd(fe_substream);int stream = fe_substream->stream, ret = 0;dpcm_set_fe_update_state(fe, stream, SND_SOC_DPCM_UPDATE_FE);ret = dpcm_be_dai_startup(fe, stream);if (ret < 0)goto be_err;dev_dbg(fe->dev, "ASoC: open FE %s\n", fe->dai_link->name);/* start the DAI frontend */ret = __soc_pcm_open(fe, fe_substream);if (ret < 0)goto unwind;fe->dpcm[stream].state = SND_SOC_DPCM_STATE_OPEN;dpcm_runtime_setup_fe(fe_substream);dpcm_runtime_setup_be_format(fe_substream);dpcm_runtime_setup_be_chan(fe_substream);dpcm_runtime_setup_be_rate(fe_substream);ret = dpcm_apply_symmetry(fe_substream, stream);unwind:if (ret < 0)dpcm_be_dai_startup_unwind(fe, stream);
be_err:dpcm_set_fe_update_state(fe, stream, SND_SOC_DPCM_UPDATE_NO);if (ret < 0)dev_err(fe->dev, "%s() failed (%d)\n", __func__, ret);return ret;
}2.9 __soc_pcm_open 代码分析
该接口功能如下:
1. soc_pcm_components_open(substream); 调用component drv ops的open
2.snd_soc_link_startup(substream); 调用dai_link的rtd->dai_link->ops->startup(substream);
3.snd_soc_dai_startup调用cpu和codec 的dai->driver->ops->startup(substream, dai);
static int __soc_pcm_open(struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *rtd,struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{struct snd_soc_component *component;struct snd_soc_dai *dai;int i, ret = 0;snd_soc_dpcm_mutex_assert_held(rtd);for_each_rtd_components(rtd, i, component)pinctrl_pm_select_default_state(component->dev);ret = snd_soc_pcm_component_pm_runtime_get(rtd, substream);if (ret < 0)goto err;ret = soc_pcm_components_open(substream);if (ret < 0)goto err;ret = snd_soc_link_startup(substream);if (ret < 0)goto err;/* startup the audio subsystem */for_each_rtd_dais(rtd, i, dai) {ret = snd_soc_dai_startup(dai, substream);if (ret < 0)goto err;}/* Dynamic PCM DAI links compat checks use dynamic capabilities */if (rtd->dai_link->dynamic || rtd->dai_link->no_pcm)goto dynamic;/* Check that the codec and cpu DAIs are compatible */soc_pcm_init_runtime_hw(substream);soc_pcm_update_symmetry(substream);ret = soc_hw_sanity_check(substream);if (ret < 0)goto err;soc_pcm_apply_msb(substream);/* Symmetry only applies if we've already got an active stream. */for_each_rtd_dais(rtd, i, dai) {ret = soc_pcm_apply_symmetry(substream, dai);if (ret != 0)goto err;}
dynamic:snd_soc_runtime_activate(rtd, substream->stream);ret = 0;
err:if (ret < 0) {soc_pcm_clean(rtd, substream, 1);dev_err(rtd->dev, "%s() failed (%d)", __func__, ret);}return ret;
}整体流程图如下:
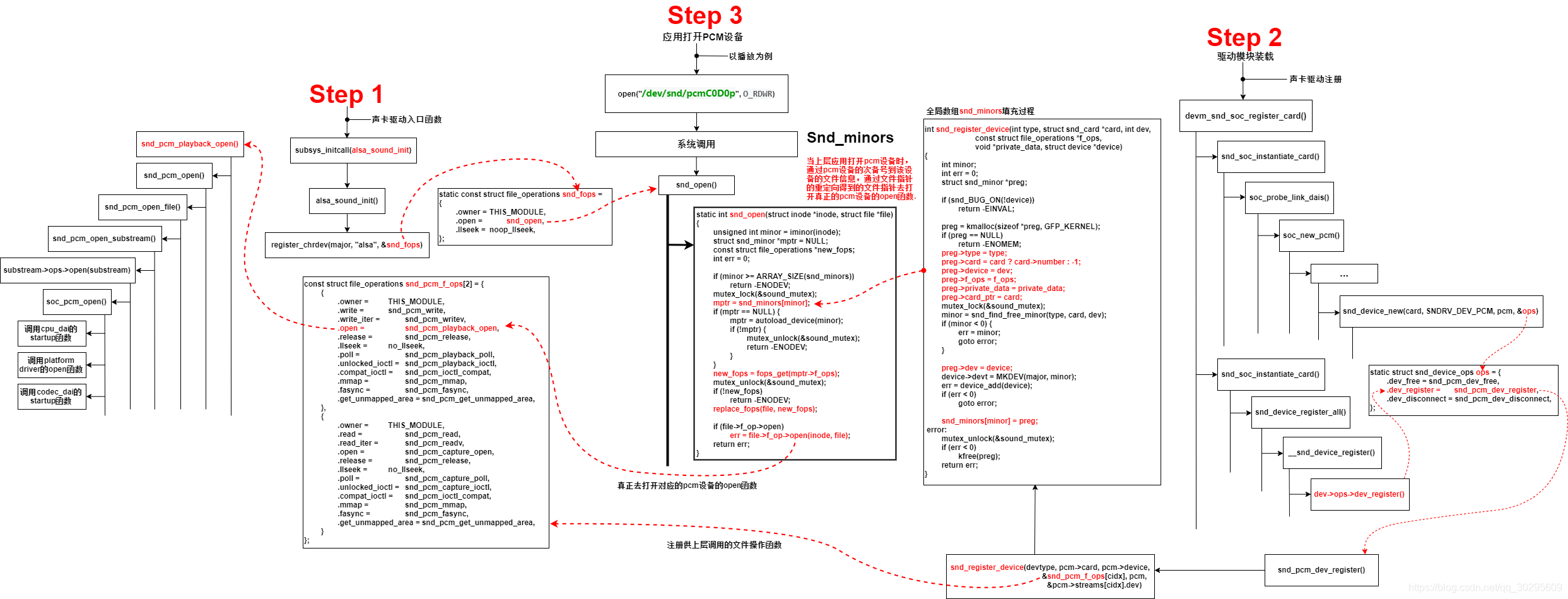
)
)













)

 Linux 基础使用和程序部署)
)
