前文:【学习笔记】Langchain基础
文章目录
- 8 [LangGraph] 实现 Building Effective Agents,各种 workflows 及 Agent
- Augmented LLM
- Prompt Chaining
- Parallelization
- Routing
- Orchestrator-Worker (协调器-工作器)
- Evaluator-optimizer (Actor-Critic)
- Agent
8 [LangGraph] 实现 Building Effective Agents,各种 workflows 及 Agent
-
video: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ZsM2zcEFa
-
code: https://github.com/chunhuizhang/llm_aigc/blob/main/tutorials/agents/langchain/advanced/building_effective_agents.ipynb
-
https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/building-effective-agents
- https://mirror-feeling-d80.notion.site/Workflow-And-Agents-17e808527b1780d792a0d934ce62bee6
- https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/workflows/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aHCDrAbH_go
- https://mirror-feeling-d80.notion.site/Workflow-And-Agents-17e808527b1780d792a0d934ce62bee6
-
AlphaEvolve: coding agent
- llm 作为核心算子实现遗传算法;
- 适用于可以自动评估的环境;& 大量脚手架类似的工作;
-
https://github.com/google-gemini/gemini-fullstack-langgraph-quickstart/tree/main
- 基于 langgraph 编排工作流实现 deepresearch
- 不同的节点用不同的 gemini models
- pro:deep,flash:width
- 基于 langgraph 编排工作流实现 deepresearch
-
sota llms (gemini 2.5 pro, openai o3) + 精心设计的 workflow(脚手架,scaffolding)能解决非常多非常复杂的问题;
- 基础模型实在是越来越powerful了

- workflows
- Create a scaffolding of predefined code paths around llm calls
- LLMs directs control flow through predefined code paths
- Agen: remove this scaffolding (LLM directs its own actions, responds to feedback)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
assert load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4o-mini')
Augmented LLM
- Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
- Augment the LLM with tools

# Schema for structured output => output schema
from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldclass SearchQuery(BaseModel):search_query: str = Field(None, description="Query that is optimized web search.")justification: str = Field(None, description="Why this query is relevant to the user's request.")# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(SearchQuery)# Invoke the augmented LLM
output = structured_llm.invoke("How does Calcium CT score relate to high cholesterol?") # SearchQuery(search_query='Calcium CT score high cholesterol relationship', justification='This query targets the relationship between calcium CT scores and cholesterol levels, which may help in understanding cardiovascular risk assessment.')
执行:structured_llm.invoke("今年高考新闻"),输出SearchQuery(search_query='2023年高考 新闻 相关报道', justification='搜索2023年高考的相关新闻,以获取该年度高考的最新动态、政策变化及新闻事件等信息,符合用户对今年高考的关注。')
# Define a tool
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:return a * b
def sigmoid(a: float) -> float:return 1./(1+np.exp(-a))
# Augment the LLM with tools
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([multiply, sigmoid])
# Invoke the LLM with input that triggers the tool call
msg = llm_with_tools.invoke("What is derivative of sigmoid(5)")
msg.tool_calls
"""
[{'name': 'sigmoid','args': {'a': 5},'id': 'call_PBKMYMxZjU0x8IP9TxMHuE8Y','type': 'tool_call'}]
"""
msg具体如下:
AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_PBKMYMxZjU0x8IP9TxMHuE8Y', 'function': {'arguments': '{"a":5}', 'name': 'sigmoid'}, 'type': 'function'}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 14, 'prompt_tokens': 194, 'total_tokens': 208, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_34a54ae93c', 'id': 'chatcmpl-BiJpUWnwANEG7bDWV9FR6mXp5vHj1', 'service_tier': 'default', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--ac1635ef-b4cd-4526-af25-f1ba23e22ed7-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'sigmoid', 'args': {'a': 5}, 'id': 'call_PBKMYMxZjU0x8IP9TxMHuE8Y', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 194, 'output_tokens': 14, 'total_tokens': 208, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}})

Prompt Chaining

from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from IPython.display import Image, display# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):topic: strjoke: strimproved_joke: strfinal_joke: str# Nodes
def generate_joke(state: State):"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a short joke about {state['topic']}")return {"joke": msg.content}def check_punchline(state: State):"""Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline"""# Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!"if "?" in state["joke"] or "!" in state["joke"]:return "Pass"return "Fail"def improve_joke(state: State):"""Second LLM call to improve the joke"""# wordplay: 俏皮话/双关语msg = llm.invoke(f"Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: {state['joke']}")return {"improved_joke": msg.content}def polish_joke(state: State):"""Third LLM call for final polish"""msg = llm.invoke(f"Add a surprising twist to this joke: {state['improved_joke']}")return {"final_joke": msg.content}
然后搭建workflow:
# Build workflow
workflow = StateGraph(State)# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("generate_joke", generate_joke)
workflow.add_node("improve_joke", improve_joke)
workflow.add_node("polish_joke", polish_joke)# Add edges to connect nodes
workflow.add_edge(START, "generate_joke")
workflow.add_conditional_edges("generate_joke", check_punchline, {"Fail": "improve_joke", "Pass": END}
)
workflow.add_edge("improve_joke", "polish_joke")
workflow.add_edge("polish_joke", END)# Compile
chain = workflow.compile()
Image(chain.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())可视化如下:

state = chain.invoke({"topic": "cats"})
"""
{'topic': 'cats','joke': 'Why did the cat sit on the computer?\n\nBecause it wanted to keep an eye on the mouse!'}
"""for step in chain.stream({"topic": "dogs"}):print(step)
# {'generate_joke': {'joke': "Why did the dog sit in the shade? \n\nBecause he didn't want to become a hot dog!"}}
Parallelization
LangGraph中可以并发执行一些workflow
- LLMs can sometimes work simultaneously on a task and have their outputs aggregated programmatically. This workflow, parallelization, manifests in two key variations:
- Sectioning: Breaking a task into independent subtasks run in parallel.
- Aggregator(Voting): Running the same task multiple times to get diverse outputs.

定义图:
# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):topic: strjoke: strstory: strpoem: strcombined_output: str# Nodes
def call_llm_1(state: State):"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']}")return {"joke": msg.content}def call_llm_2(state: State):"""Second LLM call to generate story"""msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a story about {state['topic']}")return {"story": msg.content}def call_llm_3(state: State):"""Third LLM call to generate poem"""msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a poem about {state['topic']}")return {"poem": msg.content}def aggregator(state: State):"""Combine the joke and story into a single output"""combined = f"Here's a story, joke, and poem about {state['topic']}!\n\n"combined += f"STORY:\n{state['story']}\n\n"combined += f"JOKE:\n{state['joke']}\n\n"combined += f"POEM:\n{state['poem']}"return {"combined_output": combined}
搭建工作流:
# Build workflow
parallel_builder = StateGraph(State)# Add nodes
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_1", call_llm_1)
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_2", call_llm_2)
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_3", call_llm_3)
parallel_builder.add_node("aggregator", aggregator)# Add edges to connect nodes
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_1")
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_2")
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_3")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_1", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_2", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_3", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("aggregator", END)
parallel_workflow = parallel_builder.compile()
可视化:display(Image(parallel_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))

Routing
单个语言不够强的时候,可以根据路由将不同的输入分配给不同的LLM
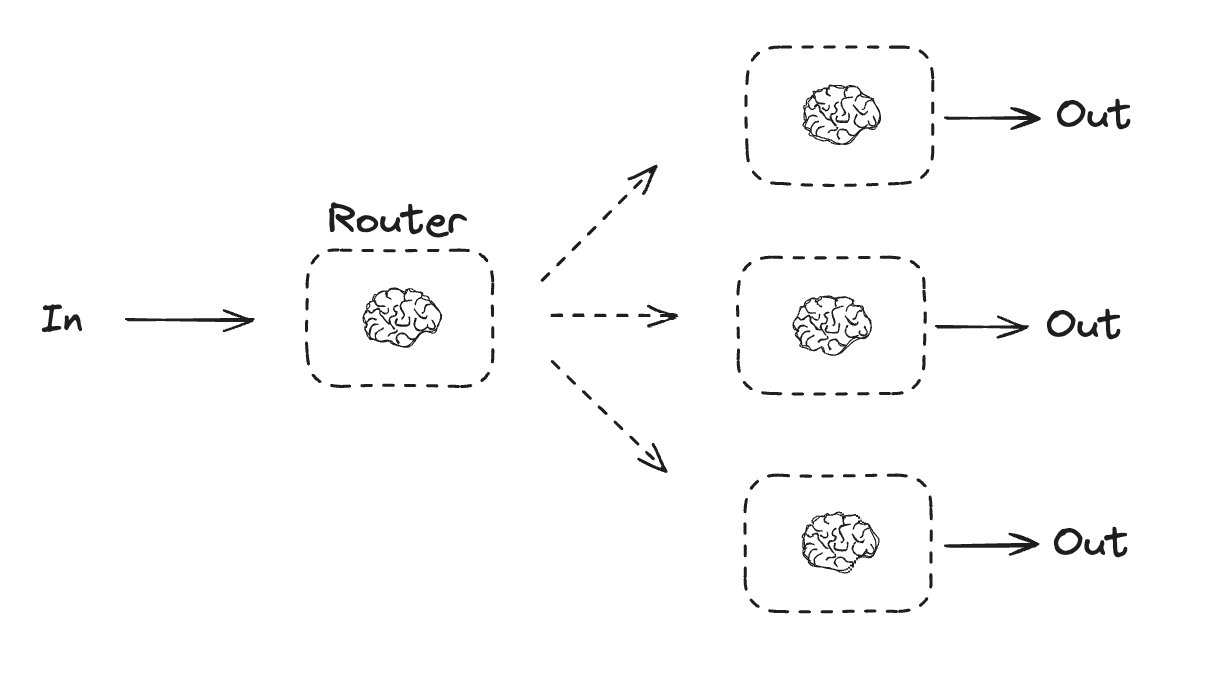
- Routing classifies an input and directs it to a specialized followup task. This workflow allows for separation of concerns, and building more specialized prompts. Without this workflow, optimizing for one kind of input can hurt performance on other inputs.
- When to use this workflow: Routing works well for complex tasks where there are distinct categories that are better handled separately, and where classification can be handled accurately, either by an LLM or a more traditional classification model/algorithm.
- distinct models (fast non-reasoning model, powerful reasoning model)
from typing_extensions import Literal
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage# Schema for structured output to use as routing logic
class Route(BaseModel):step: Literal["poem", "story", "joke"] = Field(None, description="The next step in the routing process")
# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
router = llm.with_structured_output(Route)# State
class State(TypedDict):input: strdecision: stroutput: str
定义节点:
# Nodes
def llm_call_1(state: State):"""Write a story"""result = llm.invoke(state["input"])return {"output": result.content}def llm_call_2(state: State):"""Write a joke"""result = llm.invoke(state["input"])return {"output": result.content}def llm_call_3(state: State):"""Write a poem"""result = llm.invoke(state["input"])return {"output": result.content}
定义路由:
def llm_call_router(state: State):"""Route the input to the appropriate node"""# Run the augmented LLM with structured output to serve as routing logicdecision = router.invoke([SystemMessage(content="Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request."),HumanMessage(content=state["input"]),])return {"decision": decision.step}# Conditional edge function to route to the appropriate node
def route_decision(state: State):# Return the node name you want to visit nextif state["decision"] == "story":return "llm_call_1"elif state["decision"] == "joke":return "llm_call_2"elif state["decision"] == "poem":return "llm_call_3"
搭建工作流:
# Build workflow
router_builder = StateGraph(State)# Add nodes
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_1", llm_call_1)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_2", llm_call_2)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_3", llm_call_3)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_router", llm_call_router)# Add edges to connect nodes
router_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call_router")
router_builder.add_conditional_edges("llm_call_router",route_decision,{ # Name returned by route_decision : Name of next node to visit"llm_call_1": "llm_call_1","llm_call_2": "llm_call_2","llm_call_3": "llm_call_3",},
)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_1", END)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_2", END)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_3", END)# Compile workflow
router_workflow = router_builder.compile()
可视化:display(Image(router_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))

然后可以测试一个案例:
state = router_workflow.invoke({"input": "Write me a joke about cats"})
for step in router_workflow.stream({"input": "Write me a joke about cats"}):print(step)
输出:
{'llm_call_router': {'decision': 'joke'}}
{'llm_call_2': {'output': 'Why was the cat sitting on the computer?\n\nBecause it wanted to keep an eye on the mouse!'}}
再来一个案例:
for step in router_workflow.stream({"input": "Write me a poem about cats"}):print(step)
输出:
{'llm_call_router': {'decision': 'poem'}}
{'llm_call_3': {'output': 'In sunlit corners, shadows play, \nWhere whispers of the feline sway, \nWith graceful poise and silent tread, \nThe world’s a kingdom, theirs to thread. \n\nA tapestry of fur like night, \nWith emerald eyes that pierce the light, \nThey leap as if on dreams they dance, \nIn elegant arcs, a fleeting glance. \n\nA soft purr hums, a gentle song, \nA lullaby where hearts belong, \nWith velvet paws on wooden floors, \nThey weave their magic, open doors. \n\nEach flick of tail, a tale to tell, \nOf mischief, grace, and worlds that dwell \nIn boxes, sunbeams, every fold, \nAdventures vast, and secrets bold. \n\nThey curl like commas, snug and warm, \nIn every lap, their soft charm forms, \nA soothing presence, quiet, wise, \nWith knowing hearts and ageless sighs. \n\nOh, creatures of the night and day, \nIn your soft wisdom, we find our way, \nWith tender gazes, you understand, \nThe joys and sorrows of this land. \n\nSo here’s to cats, our quaintest friends, \nWith every whisker, affection lends, \nIn their elusive, gentle grace, \nWe find a home, a purr-fect place.'}}
Orchestrator-Worker (协调器-工作器)
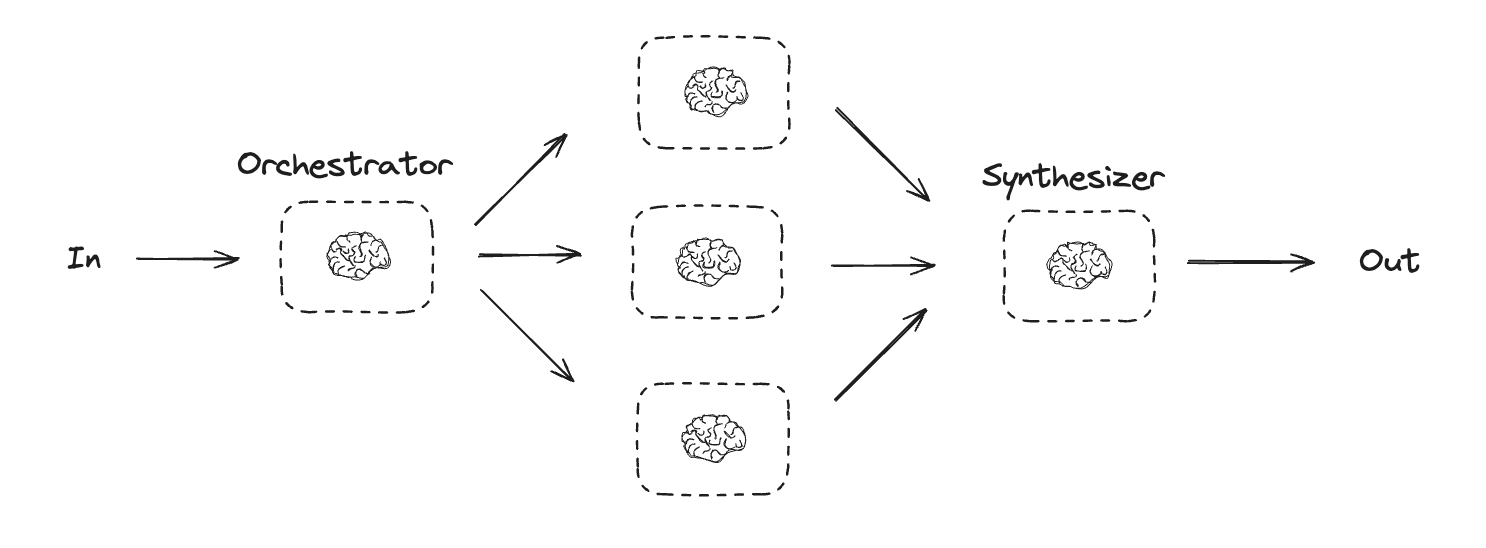
- an orchestrator breaks down a task and delegates each sub-task to workers.
- In the orchestrator-workers workflow, a central LLM dynamically breaks down tasks, delegates them to worker LLMs, and synthesizes their results.
- When to use this workflow: This workflow is well-suited for complex tasks where you can’t predict the subtasks needed (in coding, for example, the number of files that need to be changed and the nature of the change in each file likely depend on the task). Whereas it’s topographically similar, the key difference from parallelization is its flexibility—subtasks aren’t pre-defined, but determined by the orchestrator based on the specific input.
from typing import Annotated, List
import operator# Schema for structured output to use in planning
class Section(BaseModel):name: str = Field(description="Name for this section of the report.",)description: str = Field(description="Brief overview of the main topics and concepts to be covered in this section.",)class Sections(BaseModel):sections: List[Section] = Field(description="Sections of the report.",)
# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
planner = llm.with_structured_output(Sections)
from langgraph.constants import Send# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):topic: str # Report topicsections: list[Section] # List of report sectionscompleted_sections: Annotated[list, operator.add] # All workers write to this key in parallelfinal_report: str # Final report# Worker state
class WorkerState(TypedDict):section: Sectioncompleted_sections: Annotated[list, operator.add]
# Nodes
def orchestrator(state: State):"""Orchestrator that generates a plan for the report"""# Generate queriesreport_sections = planner.invoke([SystemMessage(content="Generate a plan for the report."),HumanMessage(content=f"Here is the report topic: {state['topic']}"),])return {"sections": report_sections.sections}
def llm_call(state: WorkerState):"""Worker writes a section of the report"""# Generate sectionsection = llm.invoke([SystemMessage(content="Write a report section following the provided name and description. Include no preamble for each section. Use markdown formatting."),HumanMessage(content=f"Here is the section name: {state['section'].name} and description: {state['section'].description}"),])# Write the updated section to completed sectionsreturn {"completed_sections": [section.content]}
def synthesizer(state: State):"""Synthesize full report from sections"""# List of completed sectionscompleted_sections = state["completed_sections"]# Format completed section to str to use as context for final sectionscompleted_report_sections = "\n\n---\n\n".join(completed_sections)return {"final_report": completed_report_sections}
# Conditional edge function to create llm_call workers that each write a section of the report
def assign_workers(state: State):"""Assign a worker to each section in the plan"""# Kick off section writing in parallel via Send() APIreturn [Send("llm_call", {"section": s}) for s in state["sections"]]
最后搭建工作流:
# Build workflow
orchestrator_worker_builder = StateGraph(State)# Add the nodes
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("orchestrator", orchestrator)
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("llm_call", llm_call)
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("synthesizer", synthesizer)# Add edges to connect nodes
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge(START, "orchestrator")
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_conditional_edges("orchestrator", assign_workers, ["llm_call"]
)
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge("llm_call", "synthesizer")
orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge("synthesizer", END)# Compile the workflow
orchestrator_worker = orchestrator_worker_builder.compile()# Show the workflow
display(Image(orchestrator_worker.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))

同样给两个例子:
state = orchestrator_worker.invoke({"topic": "Create a report on LLM scaling laws"})from IPython.display import Markdown
# Markdown(state["final_report"])# for step in orchestrator_worker.stream({"topic": "Create a report on LLM scaling laws"}):
# print(step)
Evaluator-optimizer (Actor-Critic)

- In the evaluator-optimizer workflow, one LLM call generates a response while another provides evaluation and feedback in a loop.
- When to use this workflow: This workflow is particularly effective when we have clear evaluation criteria, and when iterative refinement provides measurable value. The two signs of good fit are, first, that LLM responses can be demonstrably improved when a human articulates their feedback; and second, that the LLM can provide such feedback. This is analogous to the iterative writing process a human writer might go through when producing a polished document.
定义图:
# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):joke: strtopic: strfeedback: strfunny_or_not: str# Schema for structured output to use in evaluation
class Feedback(BaseModel):grade: Literal["funny", "not funny"] = Field(description="Decide if the joke is funny or not.",)feedback: str = Field(description="If the joke is not funny, provide feedback on how to improve it.",)# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
evaluator = llm.with_structured_output(Feedback)def llm_call_generator(state: State):"""LLM generates a joke"""if state.get("feedback"):msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']} but take into account the feedback: {state['feedback']}")else:msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']}")return {"joke": msg.content}def llm_call_evaluator(state: State):"""LLM evaluates the joke"""grade = evaluator.invoke(f"Grade the joke {state['joke']}")return {"funny_or_not": grade.grade, "feedback": grade.feedback}# Conditional edge function to route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator
def route_joke(state: State):"""Route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator"""if state["funny_or_not"] == "funny":return "Accepted"elif state["funny_or_not"] == "not funny":return "Rejected + Feedback"
搭建工作流:
# Build workflow
optimizer_builder = StateGraph(State)# Add the nodes
optimizer_builder.add_node("llm_call_generator", llm_call_generator)
optimizer_builder.add_node("llm_call_evaluator", llm_call_evaluator)# Add edges to connect nodes
optimizer_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call_generator")
optimizer_builder.add_edge("llm_call_generator", "llm_call_evaluator")
optimizer_builder.add_conditional_edges("llm_call_evaluator",route_joke,{ # Name returned by route_joke : Name of next node to visit"Accepted": END,"Rejected + Feedback": "llm_call_generator",},
)# Compile the workflow
optimizer_workflow = optimizer_builder.compile()display(Image(optimizer_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))

一个例子:
for step in optimizer_workflow.stream({"topic": "Cats"}):print(step)
# {'llm_call_generator': {'joke': 'Why was the cat sitting on the computer?\n\nBecause it wanted to keep an eye on the mouse!'}}
# {'llm_call_evaluator': {'funny_or_not': 'funny', 'feedback': ''}}
Agent
- Environment 接受 Action 返回 feedback


import numpy as np
from langchain_core.tools import tool# Define tools
@tool
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""Multiply a and b.Args:a: first floatb: second float"""return a * b@tool
def add(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""Adds a and b.Args:a: first floatb: second float"""return a + b@tool
def subtract(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""subtract a from b.Args:a: first floatb: second float"""return a - b@tool
def divide(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""Divide a and b.Args:a: first floatb: second float"""return a / b@tool
def sigmoid(a: float) -> float:"""sigmoid(a)Args: a: first float"""return 1./(1+np.exp(-a))# Augment the LLM with tools
tools = [add, subtract, multiply, divide, sigmoid]
tools_by_name = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage, ToolMessage# Nodes
def llm_call(state: MessagesState):"""LLM decides whether to call a tool or not"""return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke([SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful assistant tasked with performing arithmetic on a set of inputs.")]+ state["messages"])]}def tool_node(state: dict):"""Performs the tool call"""result = []for tool_call in state["messages"][-1].tool_calls:tool = tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]]observation = tool.invoke(tool_call["args"])result.append(ToolMessage(content=observation, tool_call_id=tool_call["id"]))return {"messages": result}# Conditional edge function to route to the tool node or end based upon whether the LLM made a tool call
def should_continue(state: MessagesState) -> Literal["environment", END]:"""Decide if we should continue the loop or stop based upon whether the LLM made a tool call"""messages = state["messages"]last_message = messages[-1]# If the LLM makes a tool call, then perform an actionif last_message.tool_calls:return "Action"# Otherwise, we stop (reply to the user)return END# Build workflow
agent_builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)# Add nodes
agent_builder.add_node("llm_call", llm_call)
agent_builder.add_node("environment", tool_node)# Add edges to connect nodes
agent_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call")
agent_builder.add_conditional_edges("llm_call",should_continue,{# Name returned by should_continue : Name of next node to visit"Action": "environment",END: END,},
)
agent_builder.add_edge("environment", "llm_call")# Compile the agent
agent = agent_builder.compile()# Show the agent
display(Image(agent.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png()))

看一个例子:
# Invoke
messages = [HumanMessage(content="calculate derivative of sigmoid(5)")]
messages = agent.invoke({"messages": messages})
for m in messages["messages"]:m.pretty_print()
具体的输出结果:
================================ Human Message =================================calculate derivative of sigmoid(5)
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:sigmoid (call_yhe0L1h0iirYx86Oc4tGbHHm)Call ID: call_yhe0L1h0iirYx86Oc4tGbHHmArgs:a: 5
================================= Tool Message =================================0.9933071490757153
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:multiply (call_eepwJz1ggN5uMOU3hCNOir1V)Call ID: call_eepwJz1ggN5uMOU3hCNOir1VArgs:a: 0.9933071490757153b: 0.006692850924284857
================================= Tool Message =================================0.006648056670790157
================================== Ai Message ==================================The derivative of the sigmoid function at \( \text{sigmoid}(5) \) is approximately \( 0.00665 \).
:连接外部世界(中) - 向量嵌入与向量数据库)
)













:让AI自主行动 - 初探LangChain4j中的智能体(Agents))


