思考
- smmu对外提供功能,设备驱动调用smmu 提供的api来配置页表,那其他设备是如何和smmu交互的?
- iommu 作为将不同smmu硬件的一个抽象封装,其它设备应该只能看到iommu这个封装层,那么iommu这个子系统是如何进行抽象的,抽象概念 domain group 等
- 实际开发smmu驱动是做什么?基于arm-smmu-v3.c 实现具体的硬件驱动?
应该从iommu抽象子系统入手,从上往下去分析
iommu
抽象概念与框架设计
- iommu_group:共享同一个IOMMU地址空间的一组设备
- iommu_domain:地址翻译的上下文(包含页表、地址空间标识符ASID/PASID等),一个group可以绑定到一个domain上,一个domain可以被多个group绑定
- iommu_ops:一组抽象接口,用于适配不同硬件厂商的smmu设备,如arm-smmu-v3.c中的iommu_ops实例
iommu_group
struct iommu_group {struct kobject kobj;struct kobject *devices_kobj;struct list_head devices; // 组内设备链表struct mutex mutex;struct blocking_notifier_head notifier; // 允许其它组件注册对组变化的监听,当设备被添加、移除或组状态改变时通知监听者void *iommu_data; // 私有字段void (*iommu_data_release)(void *iommu_data); // 组被销毁时释放私有字段,被销毁时会调用char *name; // 显示在sysfs中int id;struct iommu_domain *default_domain;struct iommu_domain *domain;
};
// 组内的一个设备
struct group_device {struct list_head list; // 链表节点struct device *dev; // 指向设备的指针char *name; // 设备在组中的名称
};
struct kobject kobj; // Sysfs对象,用于在/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/下创建目录
struct kobject *devices_kobj; // 设备子目录对象,用于/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/X/devices/
功能:
在sysfs中创建IOMMU组的表示
提供用户空间接口来查看和管理IOMMU组
支持组属性和设备列表的显示
struct list_head devices; // 组内设备链表
struct mutex mutex; // 保护组内数据结构的互斥锁
功能:
- devices:维护组内所有设备的链表
- mutex:确保对组内数据的并发访问安全
- 防止在遍历设备时设备被添加或移除
struct blocking_notifier_head notifier; // 阻塞通知器头
功能:
- 允许其他组件注册对组变化的监听
- 当设备被添加、移除或组状态改变时通知监听者
- 支持异步事件处理
struct iommu_domain *default_domain; // 默认域
struct iommu_domain *domain; // 当前附加的域
默认域(default_domain)
- 定义:系统为IOMMU组自动创建的基础域
- 目的:提供基本的IOMMU功能,确保设备始终有可用的域
- 类型:通常是IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA或IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY
- 生命周期:与组同生共死,组销毁时域也销毁
当前附加域(domain)
- 定义:组当前实际使用的IOMMU域
- 目的:可以是默认域,也可以是用户指定的自定义域
- 类型:可以是任何类型的IOMMU域
- 生命周期:可以动态切换,独立于默认域
iommu_domain
struct iommu_domain {unsigned type; // 域类型const struct iommu_ops *ops; unsigned long pgsize_bitmap; /* Bitmap of page sizes in use */iommu_fault_handler_t handler; // 故障处理函数指针,当IOMMU检测到访问违规时调用void *handler_token; // 上面函数的参数,故障处理相关的上下文struct iommu_domain_geometry geometry; // 定义域的地址空间几何信息struct iommu_domain_geometry {dma_addr_t aperture_start; // 可映射地址范围的起始地址dma_addr_t aperture_end; // 可映射地址范围的结束地址bool force_aperture; // 是否强制在指定范围内进行DMA};void *iova_cookie; // IOVA私有数据指针,存储IOVA管理相关的上下文信息,如地址分配器状态等
};
| 域类型 | 地址转换 | 用途 | 典型应用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA | 是 | 标准DMA操作 | 设备驱动DMA |
| IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY | 否,可以访问 | 直通模式 | 高性能场景 |
| IOMMU_DOMAIN_UNMANAGED | 手动 | 自定义管理 | 特殊需求 |
| IOMMU_DOMAIN_BLOCKED | 拒绝访问 | 安全隔离 | 安全敏感设备 |
iommu_ops
struct iommu_ops {// 1. 能力查询bool (*capable)(enum iommu_cap); // 查询IOMMU是否支持特定功能// 2. 域管理struct iommu_domain *(*domain_alloc)(unsigned iommu_domain_type); // 分配IOMMU域void (*domain_free)(struct iommu_domain *); // 释放IOMMU域// 3. 设备管理int (*attach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 将设备附加到域void (*detach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 从域分离设备int (*add_device)(struct device *dev); // 添加设备到IOMMUvoid (*remove_device)(struct device *dev); // 从IOMMU移除设备struct iommu_group *(*device_group)(struct device *dev); // 获取设备的group 直接创建一个group// 4. 地址映射int (*map)(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova, // 映射IOVA到物理地址phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot);size_t (*unmap)(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova, // 取消地址映射size_t size, struct iommu_iotlb_gather *iotlb_gather);phys_addr_t (*iova_to_phys)(struct iommu_domain *domain, dma_addr_t iova); // IOVA转物理地址// 5. TLB管理void (*flush_iotlb_all)(struct iommu_domain *domain); // 刷新所有TLB条目void (*iotlb_sync_map)(struct iommu_domain *domain); // 同步映射TLBvoid (*iotlb_sync)(struct iommu_domain *domain, // 同步TLBstruct iommu_iotlb_gather *iotlb_gather);// 6. 域属性管理int (*domain_get_attr)(struct iommu_domain *domain, // 获取域属性enum iommu_attr attr, void *data);int (*domain_set_attr)(struct iommu_domain *domain, // 设置域属性enum iommu_attr attr, void *data);// 7. 保留区域管理void (*get_resv_regions)(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list); // 获取设备保留区域void (*put_resv_regions)(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list); // 释放保留区域void (*apply_resv_region)(struct device *dev, // 应用保留区域struct iommu_domain *domain,struct iommu_resv_region *region);// 8. 窗口管理int (*domain_window_enable)(struct iommu_domain *domain, u32 wnd_nr, // 启用域窗口phys_addr_t paddr, u64 size, int prot);void (*domain_window_disable)(struct iommu_domain *domain, u32 wnd_nr); // 禁用域窗口// 9. 设备树支持int (*of_xlate)(struct device *dev, struct of_phandle_args *args); // 设备树解析// 10. 延迟附加bool (*is_attach_deferred)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 检查是否延迟附加// 11. 设备特性管理bool (*dev_has_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f); // 检查设备是否支持特性bool (*dev_feat_enabled)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f); // 检查特性是否启用int (*dev_enable_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f); // 启用设备特性int (*dev_disable_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f); // 禁用设备特性// 12. 辅助域管理int (*aux_attach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 附加设备到辅助域void (*aux_detach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 从辅助域分离设备int (*aux_get_pasid)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev); // 获取辅助域PASID// 13. SVA (Shared Virtual Addressing) 支持struct iommu_sva *(*sva_bind)(struct device *dev, struct mm_struct *mm, // 绑定设备到进程地址空间void *drvdata);void (*sva_unbind)(struct iommu_sva *handle); // 解绑SVAint (*sva_get_pasid)(struct iommu_sva *handle); // 获取SVA的PASID// 14. 页面响应int (*page_response)(struct device *dev, // 页面请求响应struct iommu_fault_event *evt,struct iommu_page_response *msg);// 15. 支持的页面大小unsigned long pgsize_bitmap; // 支持的页面大小位图
};
iommu 子系统初始化
ARM SMMU v3 Domain 创建时机详解
1. Domain创建的触发时机
Domain的创建主要有以下几个时机:
1.1 设备探测时自动创建
dom = __iommu_domain_alloc(dev->bus, iommu_def_domain_type);
if (!dom && iommu_def_domain_type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA) {dom = __iommu_domain_alloc(dev->bus, IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA);
- 触发条件: 当设备被探测时,如果设备组没有默认domain
- 创建类型: 根据系统配置创建默认domain类型
- 回退机制: 如果默认类型创建失败,回退到DMA domain
1.2 手动创建
struct iommu_domain *iommu_domain_alloc(struct bus_type *bus)
{return __iommu_domain_alloc(bus, IOMMU_DOMAIN_UNMANAGED);
}
- 触发条件: 应用程序或驱动主动调用
- 创建类型: 通常为UNMANAGED类型
2. Domain创建流程
2.1 IOMMU核心层调用
static struct iommu_domain *__iommu_domain_alloc(struct bus_type *bus,unsigned type)
{struct iommu_domain *domain;if (bus == NULL || bus->iommu_ops == NULL)return NULL;domain = bus->iommu_ops->domain_alloc(type);if (!domain)return NULL;domain->ops = bus->iommu_ops;domain->type = type;domain->pgsize_bitmap = bus->iommu_ops->pgsize_bitmap;return domain;
}
2.2 ARM SMMU v3驱动实现
static struct iommu_domain *arm_smmu_domain_alloc(unsigned type)
{struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain;if (type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_UNMANAGED &&type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA &&type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY)return NULL;smmu_domain = kzalloc(sizeof(*smmu_domain), GFP_KERNEL);if (!smmu_domain)return NULL;if (type == IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA &&iommu_get_dma_cookie(&smmu_domain->domain)) {kfree(smmu_domain);return NULL;}mutex_init(&smmu_domain->init_mutex);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&smmu_domain->devices);spin_lock_init(&smmu_domain->devices_lock);return &smmu_domain->domain;
}
3. Domain创建时机总结
4. 关键时间点
4.1 Domain结构创建
- 时机: 设备探测或手动创建时
- 内容: 分配内存,初始化基本结构
- 状态: 此时还没有关联SMMU设备
4.2 Domain最终化
- 时机: 设备绑定到domain时
- 内容: 初始化页表,分配ASID/VMID
- 状态: 此时才真正配置硬件
4.3 页表初始化
- 时机:
arm_smmu_domain_finalise调用时 - 内容: 创建IOVA到PA的转换页表
- 状态: 此时才支持地址转换
arm-smmu-v3实例化
ARM SMMU v3的实例化流程体现了Linux内核中抽象框架的设计模式:平台驱动注册 → 2. 设备探测 → 3. 硬件初始化 → 4. 抽象层注册 → 5. 总线集成。平台驱动注册,然后内核启动时根据设备数创建platform_device,然后device_initcall阶段会注册platform_driver,然后会触发driver_attach最终触发probe函数来进行设备探测和初始化
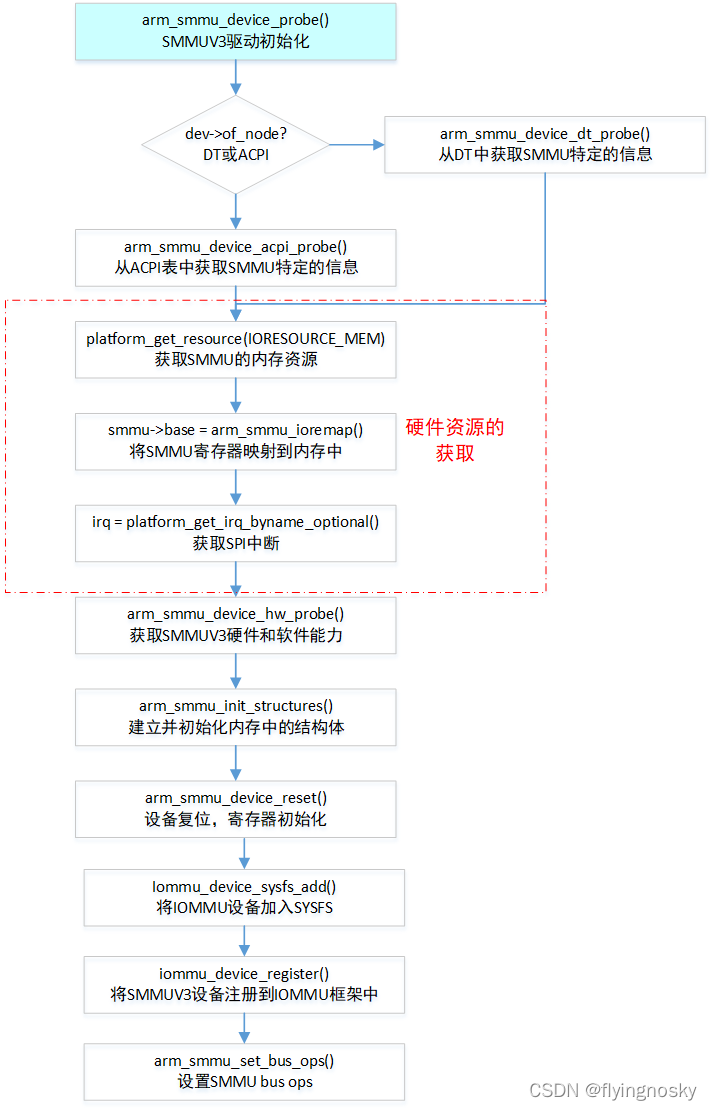
设备探测和初始化
内存分配和设备结构初始化
分配 arm_smmu_device 结构体
设置设备指针
根据设备树或ACPI进行探测
硬件资源获取
获取MMIO寄存器区域
映射寄存器地址空间
获取中断资源(combined、eventq、priq、gerror)
硬件探测和初始化 arm_smmu_device_hw_probe
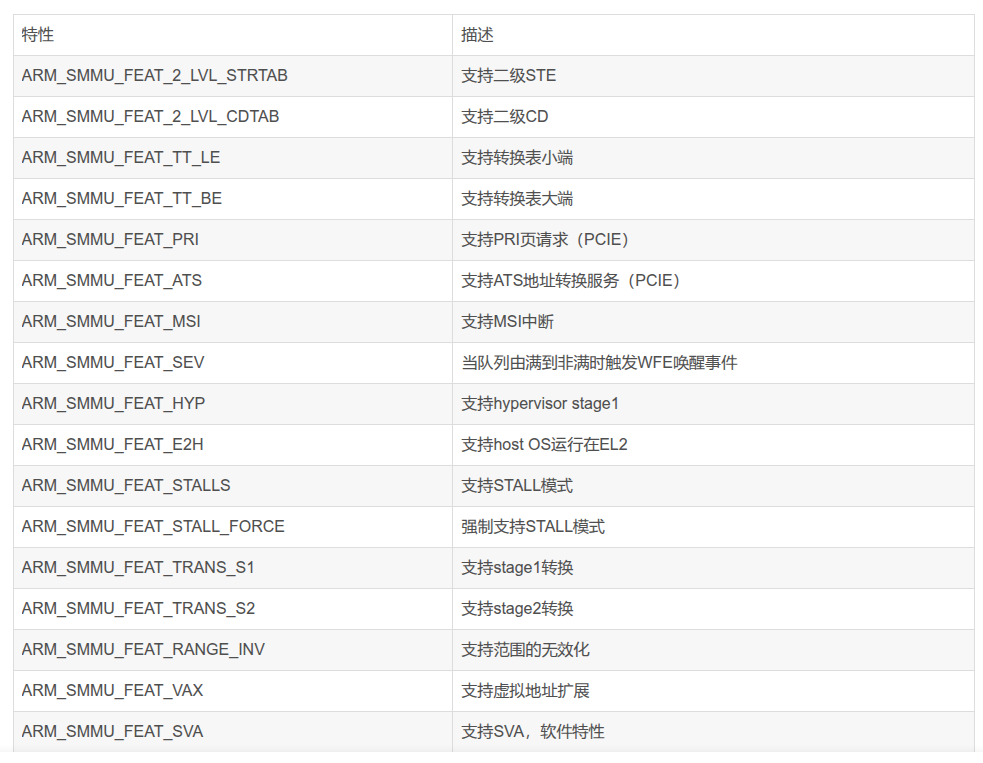
arm_smmu_init_structures(): 初始化内存中的数据结构
arm_smmu_init_queues 队列初始化
- CMDQ:接收用户命令的队列
- EVTQ:接收SMMU硬件的事件队列
- PRIQ:优先级队列,处理页面请求接口事件队列
arm smmu v3 队列机制
arm_smmu_init_strtab 流表初始化 设备到domain的映射
注册到IOMMU核心框架
iommu_device_sysfs_add(): 添加sysfs接口
iommu_device_set_ops(): 设置操作函数
iommu_device_register(): 注册IOMMU设备
总线设备初始化
为PCI、AMBA、Platform总线设置IOMMU操作
将所有总线对应的iommu_ops 都设置为arm_smmu_ops,然后调用iommu_bus_init->bus_for_each_dev 为bus上的每个设备进行add_iommu_group->iommu_probe_device->ops->add_device
最后调用arm_smmu_add_device进行添加设备到group中
- 设备初始化
验证设备: 检查设备是否支持IOMMU操作
创建master结构: 为设备分配 arm_smmu_master 结构体
建立关联: 将设备与SMMU设备关联起来 - Stream ID管理
SID验证: 检查设备的Stream ID是否在SMMU支持的范围内
二级表初始化: 如果支持二级流表,确保相应的二级表已初始化 - IOMMU组管理
获取IOMMU组: 调用 iommu_group_get_for_dev() 为设备分配IOMMU组
设备链接: 将设备链接到IOMMU设备
arm_smmu_device和arm_smmu_master
关系建立过程
设备发现: 系统发现一个需要IOMMU保护的设备 (dev)
SMMU查找: 通过设备树或ACPI找到对应的SMMU硬件 (smmu)
Master创建: 为设备创建一个master结构,建立设备和SMMU的关联
配置初始化: 在master中设置设备的SID、ATS等配置
实际应用场景
一个SMMU: 管理多个设备,每个设备有自己的master一个设备: 对应一个master,连接到特定的SMMU地址转换: 设备发起DMA请求时,SMMU根据master中的配置进行地址转换这种设计实现了一对多的关系:一个SMMU可以管理多个设备,每个设备通过自己的master与SMMU交互。
dev smmudev domain
多个dev组成一个group ,一个group对应有其domain,表示其地址转换上下文
smmudev和domain关联
dev绑定到domain时机
ARM SMMU v3 页表初始化详解
1. 页表初始化的位置
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise(struct iommu_domain *domain)
{int ret;unsigned long ias, oas;enum io_pgtable_fmt fmt;struct io_pgtable_cfg pgtbl_cfg;struct io_pgtable_ops *pgtbl_ops;int (*finalise_stage_fn)(struct arm_smmu_domain *,struct io_pgtable_cfg *);struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = to_smmu_domain(domain);struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;// ... 配置页表格式和参数 ...pgtbl_ops = alloc_io_pgtable_ops(fmt, &pgtbl_cfg, smmu_domain);if (!pgtbl_ops)return -ENOMEM;// ... 调用具体的stage初始化函数 ...smmu_domain->pgtbl_ops = pgtbl_ops;return 0;
}
2. 页表操作结构
struct io_pgtable_ops *pgtbl_ops;
这个结构包含了所有页表操作函数:
map: IOVA到PA的映射unmap: 解除映射iova_to_phys: IOVA到PA的转换
3. 页表格式选择
根据domain类型选择不同的页表格式:
switch (smmu_domain->stage) {case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1:ias = (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_VAX) ? 52 : 48;ias = min_t(unsigned long, ias, VA_BITS);oas = smmu->ias;fmt = ARM_64_LPAE_S1; // Stage-1页表格式finalise_stage_fn = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1;break;case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_NESTED:case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S2:ias = smmu->ias;oas = smmu->oas;fmt = ARM_64_LPAE_S2; // Stage-2页表格式finalise_stage_fn = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s2;break;default:return -EINVAL;}
4. Stage-1页表初始化
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,struct io_pgtable_cfg *pgtbl_cfg)
{int ret;int asid;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;// 分配ASIDasid = arm_smmu_bitmap_alloc(smmu->asid_map, smmu->asid_bits);if (asid < 0)return asid;// 分配上下文描述符cfg->cdptr = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS << 3,&cfg->cdptr_dma,GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_ZERO);if (!cfg->cdptr) {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to allocate context descriptor\n");ret = -ENOMEM;goto out_free_asid;}// 配置上下文描述符cfg->cd.asid = (u16)asid;cfg->cd.ttbr = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.ttbr[0]; // 页表基地址cfg->cd.tcr = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.tcr; // 转换控制寄存器cfg->cd.mair = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.mair[0]; // 内存属性return 0;
}
5. Stage-2页表初始化
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s2(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,struct io_pgtable_cfg *pgtbl_cfg)
{int vmid;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s2_cfg;// 分配VMIDvmid = arm_smmu_bitmap_alloc(smmu->vmid_map, smmu->vmid_bits);if (vmid < 0)return vmid;// 配置Stage-2参数cfg->vmid = (u16)vmid;cfg->vttbr = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s2_cfg.vttbr; // Stage-2页表基地址cfg->vtcr = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s2_cfg.vtcr; // Stage-2转换控制return 0;
}
6. IOVA到PA转换的页表操作
6.1 映射操作
static int arm_smmu_map(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot)
{struct io_pgtable_ops *ops = to_smmu_domain(domain)->pgtbl_ops;return ops->map(ops, iova, paddr, size, prot);
}
6.2 解除映射操作
static size_t arm_smmu_unmap(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,size_t size, struct iommu_iotlb_gather *gather)
{struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = to_smmu_domain(domain);struct io_pgtable_ops *ops = smmu_domain->pgtbl_ops;return ops->unmap(ops, iova, size, gather);
}
6.3 IOVA到PA转换
static phys_addr_t
arm_smmu_iova_to_phys(struct iommu_domain *domain, dma_addr_t iova)
{struct io_pgtable_ops *ops = to_smmu_domain(domain)->pgtbl_ops;if (!ops)return 0;return ops->iova_to_phys(ops, iova);
}
ARM SMMU v3 页表架构图
页表初始化调用链
ASID和VMID
ASID 是 Address Space ID 的缩写,用于在ARM SMMU v3的Stage-1 (S1) 转换中标识不同的地址空间。
VMID 是 Virtual Machine ID 的缩写,用于在ARM SMMU v3的Stage-2 (S2) 转换中标识不同的虚拟机。
对比
| 特性 | ASID | VMID |
|---|---|---|
| 转换阶段 | Stage-1 (S1) | Stage-2 (S2) |
| 转换类型 | IOVA → IPA | IPA → PA |
| 标识对象 | 进程/地址空间 | 虚拟机 |
| 使用场景 | 进程隔离 | 虚拟机隔离 |
我来详细解释 alloc_io_pgtable_ops 分配的 pgtbl_ops 中函数定义的位置:
Ran tool
Read file: drivers/iommu/io-pgtable.c
现在让我查看ARM 64位LPAE页表的初始化函数:
Ran tool
Read file: drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c
现在让我查看具体的页表操作函数定义:
Read file: drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c
现在让我查看具体的页表操作函数实现:
Read file: drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c
现在让我查看unmap和iova_to_phys函数的实现:
Read file: drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c
现在我来详细解释 alloc_io_pgtable_ops 分配的 pgtbl_ops 中函数定义的位置:
alloc_io_pgtable_ops 分配的 pgtbl_ops 函数定义位置
1. 分配流程
struct io_pgtable_ops *alloc_io_pgtable_ops(enum io_pgtable_fmt fmt,struct io_pgtable_cfg *cfg,void *cookie)
{struct io_pgtable *iop;const struct io_pgtable_init_fns *fns;if (fmt >= IO_PGTABLE_NUM_FMTS)return NULL;fns = io_pgtable_init_table[fmt];if (!fns)return NULL;iop = fns->alloc(cfg, cookie);if (!iop)return NULL;iop->fmt = fmt;iop->cookie = cookie;iop->cfg = *cfg;return &iop->ops;
}
2. 初始化表映射
static const struct io_pgtable_init_fns *
io_pgtable_init_table[IO_PGTABLE_NUM_FMTS] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_IOMMU_IO_PGTABLE_LPAE[ARM_32_LPAE_S1] = &io_pgtable_arm_32_lpae_s1_init_fns,[ARM_32_LPAE_S2] = &io_pgtable_arm_32_lpae_s2_init_fns,[ARM_64_LPAE_S1] = &io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns,[ARM_64_LPAE_S2] = &io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s2_init_fns,[ARM_MALI_LPAE] = &io_pgtable_arm_mali_lpae_init_fns,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IOMMU_IO_PGTABLE_ARMV7S[ARM_V7S] = &io_pgtable_arm_v7s_init_fns,
#endif
};
3. ARM 64位LPAE初始化函数
struct io_pgtable_init_fns io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns = {.alloc = arm_64_lpae_alloc_pgtable_s1,.free = arm_lpae_free_pgtable,
};
4. 页表操作函数赋值
data->iop.ops = (struct io_pgtable_ops) {.map = arm_lpae_map,.unmap = arm_lpae_unmap,.iova_to_phys = arm_lpae_iova_to_phys,};
5. 具体函数定义位置
5.1 arm_lpae_map 函数
static int arm_lpae_map(struct io_pgtable_ops *ops, unsigned long iova,phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int iommu_prot)
{struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data = io_pgtable_ops_to_data(ops);arm_lpae_iopte *ptep = data->pgd;int ret, lvl = ARM_LPAE_START_LVL(data);arm_lpae_iopte prot;/* If no access, then nothing to do */if (!(iommu_prot & (IOMMU_READ | IOMMU_WRITE)))return 0;if (WARN_ON(iova >= (1ULL << data->iop.cfg.ias) ||paddr >= (1ULL << data->iop.cfg.oas)))return -ERANGE;prot = arm_lpae_prot_to_pte(data, iommu_prot);ret = __arm_lpae_map(data, iova, paddr, size, prot, lvl, ptep);/** Synchronise all PTE updates for the new mapping before there's* a chance for anything to kick off a table walk for the new iova.*/wmb();return ret;
}
5.2 arm_lpae_unmap 函数
static size_t arm_lpae_unmap(struct io_pgtable_ops *ops, unsigned long iova,size_t size, struct iommu_iotlb_gather *gather)
{struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data = io_pgtable_ops_to_data(ops);arm_lpae_iopte *ptep = data->pgd;int lvl = ARM_LPAE_START_LVL(data);if (WARN_ON(iova >= (1ULL << data->iop.cfg.ias)))return 0;return __arm_lpae_unmap(data, gather, iova, size, lvl, ptep);
}
5.3 arm_lpae_iova_to_phys 函数
static phys_addr_t arm_lpae_iova_to_phys(struct io_pgtable_ops *ops,unsigned long iova)
{struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data = io_pgtable_ops_to_data(ops);arm_lpae_iopte pte, *ptep = data->pgd;int lvl = ARM_LPAE_START_LVL(data);do {/* Valid IOPTE pointer? */if (!ptep)return 0;/* Grab the IOPTE we're interested in */ptep += ARM_LPAE_LVL_IDX(iova, lvl, data);pte = READ_ONCE(*ptep);/* Valid entry? */if (!pte)return 0;/* Leaf entry? */if (iopte_leaf(pte, lvl, data->iop.fmt))goto found_translation;/* Take it to the next level */ptep = iopte_deref(pte, data);} while (++lvl < ARM_LPAE_MAX_LEVELS);/* Ran out of page tables to walk */return 0;found_translation:iova &= (ARM_LPAE_BLOCK_SIZE(lvl, data) - 1);return iopte_to_paddr(pte, data) | iova;
}
6. 函数调用链
7. 文件位置总结
| 函数 | 定义位置 | 文件 |
|---|---|---|
alloc_io_pgtable_ops | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable.c:28 | 通用页表分配器 |
io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:1072 | ARM LPAE初始化函数 |
arm_64_lpae_alloc_pgtable_s1 | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:789 | S1页表分配 |
arm_lpae_alloc_pgtable | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:744 | LPAE页表分配 |
arm_lpae_map | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:478 | 地址映射函数 |
arm_lpae_unmap | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:651 | 地址解映射函数 |
arm_lpae_iova_to_phys | drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c:664 | 地址转换查询函数 |
8. 核心实现特点
- 模块化设计: 不同页表格式有不同的初始化函数
- 函数指针赋值: 在页表分配时动态赋值操作函数
- ARM LPAE实现: 所有ARM LPAE相关的页表操作都在
io-pgtable-arm.c中 - 通用接口: 通过
io_pgtable_ops结构体提供统一的页表操作接口
这种设计使得ARM SMMU v3可以使用标准的ARM LPAE页表格式,同时保持了良好的模块化和可扩展性。

)|SVM-KKT条件的数学理解)
模型添加教学)




)









:以编程方式使用 sqLite,4 个函数,以及 sqLite 移植,合并编译)

