这里写目录标题
- 一、并行查询相关自己置参数
- 二、并行扫描
- 2.1、并行顺序扫描
- 2.2、并行索引扫描
- 2.3、并行index-only扫描
- 2.4、并行bitmap heap扫描
- 三、并行聚合
- 四、多表关联
- 4.1、Nested loop多表关联
- 4.2、Merge join多表关联
- 4.3、Hash join多表关联
了解 Oracle 的朋友应该知道 Oracle 支持并行查询,比如 SELECT 、 UPDATE 、 DELETE大事务开启并行功能后能利用多核 CPU ,从而充分发挥硬件性能,提升大事务处理效率,PostgreSQL 在 9.6 版本前还不支持并行查询, SQ L 无法利用多核 CPU 提升性能, 9.6 版本开始支持并行查询,只是 9.6 版本的并行查询所支持的范围非常有限,例如只在顺序扫描、多表关联、聚合查询中支持并行, 10 版本增强了并行查询功能,例如增加了并行索引扫描 、并行 index-only 扫描、并行 bitmap heap 扫描等。
一、并行查询相关自己置参数
max_worker_processes(integer)
设置系统支持的最大后台进程数,默认值为 8 ,如果有备库,备库上此参数必须大于或等于主库上的 此参数配置值, 此参数调整后需重启数据库生效 。max_parallel_workers (integer)
设置系统支持的并行查询进程数,默认值为 8 ,此参数受 max_worker_processes 参数限制,设置此参数的值比 max_worker processes 值高将无效 。当调整这个参数时建议同时调整 max_parallel workers _per _gather 参数值 。max_parallel_workers_per _gather (integer)
设置允许启用的并行进程的进程数,默认值为 2 ,设置成 0 表示禁用并行查询,此参数受 max_worker_processes 参数和 max_parallel_workers 参数限制,因此并行查询的实际进程数可能比预期的少,并行查询比非并行查询消耗更多的 CPU 、 IO 、内存资源,对生产系统有一定影 响 , 使用时需考虑这方面的因素,这三个参数的配置值大小关系通常如下所示:
max_worker_processes > max_parallel_workers > max_parallel_workers p er_gather
parallel_setup_cost(floating point)
设置优化器启动并行进程的成本 ,默认为 1000 。parallel_tuple_cost(floating point)
设置优化器通过并行进程处理一行数据的成本,默认为 0.1 。mi n_pa ra I lel_ta ble_sca n_size(integer)
设置 开启并行的 条件之一 , 表 占用 空 间小于此值将不会开启并行,并行顺序扫描场景下扫描的数据大小通常等于表大小 , 默认值为 8MB 。min_parallel_index_scan_size(integer)
设置开启 并行的 条件之一,实 际上并行索引扫描不会扫描索引所有数据块,只是扫描索引相关数据块,默认值为 512kb 。force_parallel_mode (enum)
强制开启并行, 一般作为测试目的, OLTP 生产环境开启需慎重,一般不建议开启 。
postgresql.conf 配置文件设置了以下参数:
max_worker_processes = 16
max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 4 # taken from max_parallel_workers
max_parallel_worders = 8
parallel_tuple_cost = 0.1
parallel_setup+cost = 1000.0
min_parallel_table_scan_size = 8MB
min_parallel_index_scan_size = 612kb
force_parallel_mode = off
行查询进程 数 预估值由 ~ 4&. max_parallel workers_per_阴阳控制,并行进程数预估值是指优化器解析 SQL 时执行计划预计会启用的并行进程数,而实际执行查询时的并行进程数受参数 max_parallel_ workers 、 max_worker_processes 的限制,也就是说 SQL 实际获得的并行进程数不会超过这两个参数设直的值,比如 max worker_processes 参数 设直成 2, max_parallel_workers_per_gather 参数设直成 4 ,不考虑其他因素的情况下,并行查询实际的并行进程数将会是 2 ,另一方面并行进程数据会受 min_parallel_table _scan_size 参数 的影响, flf 表的大小会影响并行进程数 。 并行查询执行计划中的 Workers Planned 表示执行计划预估的并行进程 数 , Worker Launched 表示并行查询实际获得的并行进程数 。
二、并行扫描
2.1、并行顺序扫描
介绍并行顺序扫描之前先介绍顺序扫描(sequential scan),顺序扫描通常也称之为扫描,全表扫描会扫描整张表数据,当表很大时,全表扫描会占用大量CPU、内存、源,对数据库性能有较大影响,在OLTP事务型数据库系统中应当尽量避免。
首先创建一张测试表,井插入500万数据,如下所示:
create table test_big1 (id int4,name character varying(32),create_time timestamp without time zone default clock_timestamp()
);insert into test_big1(id, name)
select n, n || '_test'
from generate_series(1, 50000000) n;
一个顺序扫描的示例如下所示:
explain select *
from test_big1
where name = '1_test';

以上执行计划Seq Scan on test_bigl说明表test_bigl典型的顺序扫描执行计划,PostgreSQL中的顺序扫描在9.6
上进行了顺序扫描,这是版本开始支持并行处理,一个典
并行顺序扫描会产生多个子进程,井利用多个逻辑CPU
并行全表扫描,一个并行顺序扫描的执行计划如下所示:
explain analyze select *
from test_big1
where name = '1_test';
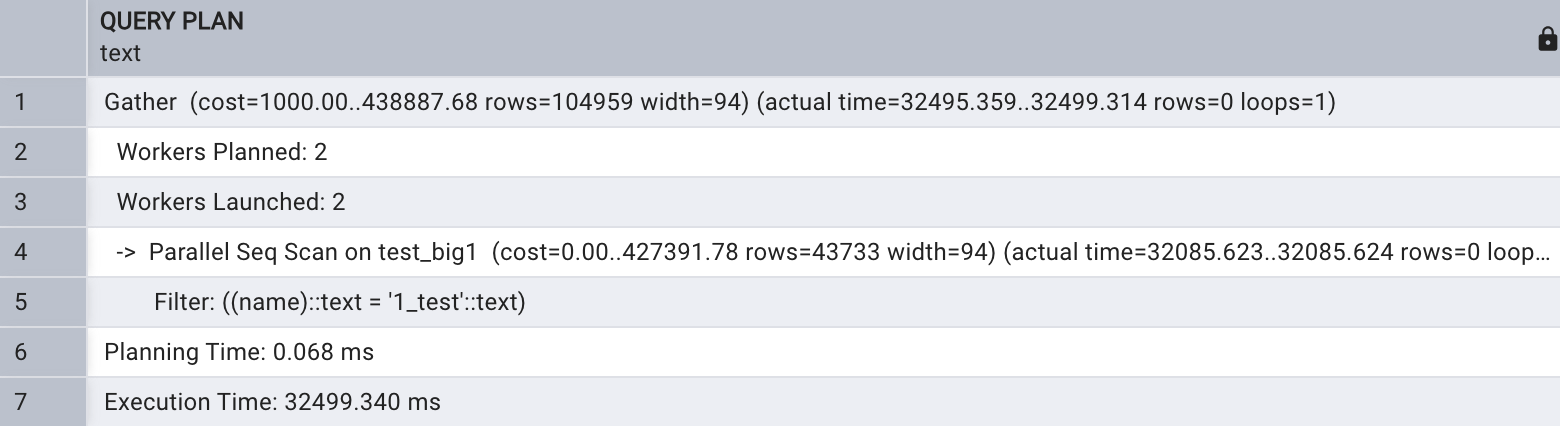
Workers Planned 表示执行计划预估的并行进程数,
Worker Launched 表示查询实际获得的并行进程数,这里 Workers Planned 和 Worker Launched值都为 4 , Parallel Seq Scan on test_ big 1 表示进行了并行顺序扫描, Planning time 表示生成执行计划的时间, Execution time 表示 SQL 实际执行时间,从以 上可 以 看出, 开启 4 个并行时 SQL 实际执行时间为 1367 毫秒。
接下来测试不开启并行的 SQL 性能,由于 max_parallel_workers_per_gather 参数设置成了 4 , 设置成 0 表示关闭并行,在会话级别设置此参数值为 0 ,如下所示 :
set max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;
不开启并行,执行计划如下所示 :
explain analyze select *
from test_big1
where name = '1_test';

不开启并行时此 SQL 执行时间为50463毫秒,开启井行查询为32499毫秒。
2.2、并行索引扫描
Index Scan using 表示 执行计划预计进行索引扫描, 索 引扫描也支持并行,称为并行索引扫描 ( Parallel index scan ), 首 先在表 test_bigl 上创建索引, 如下所示 :
create index idx_test_big1_id
on test_big1 using btree (id);
执行以下SQL,统计ID小于1千万的记录数,如下所示:
explain analyze select count(name)
from test_big1
where id < 10000000;
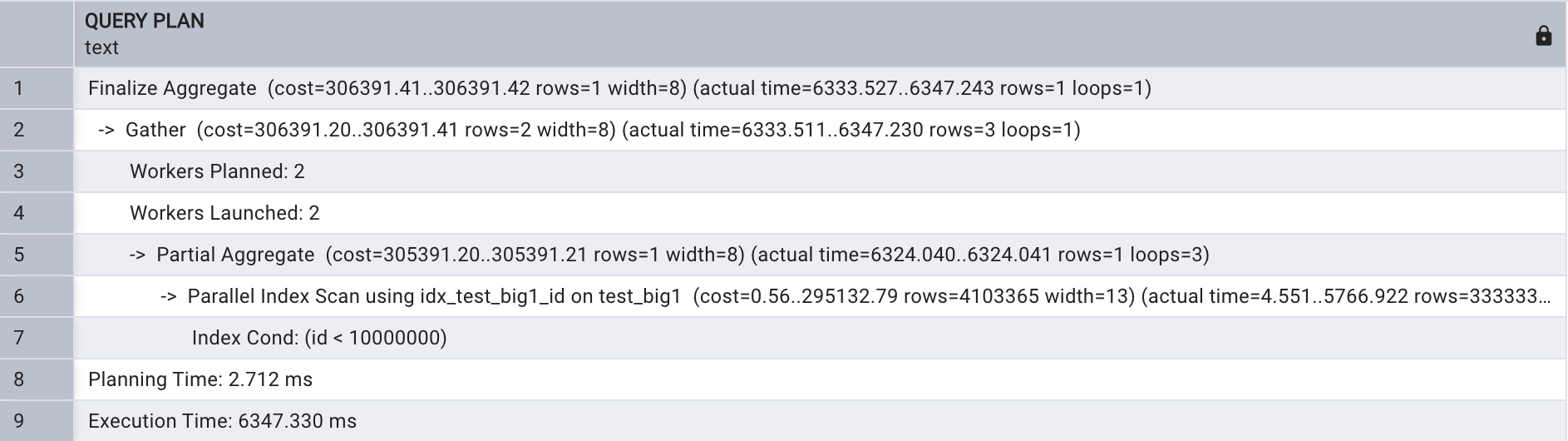
根据以上执行计划可以看出,进行了并行索引扫描,开启了2个并行进程,在会话级别关闭并行查询,如下所示:
SET max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;explain analyze select count(name)
from test_big1
where id < 10000000;
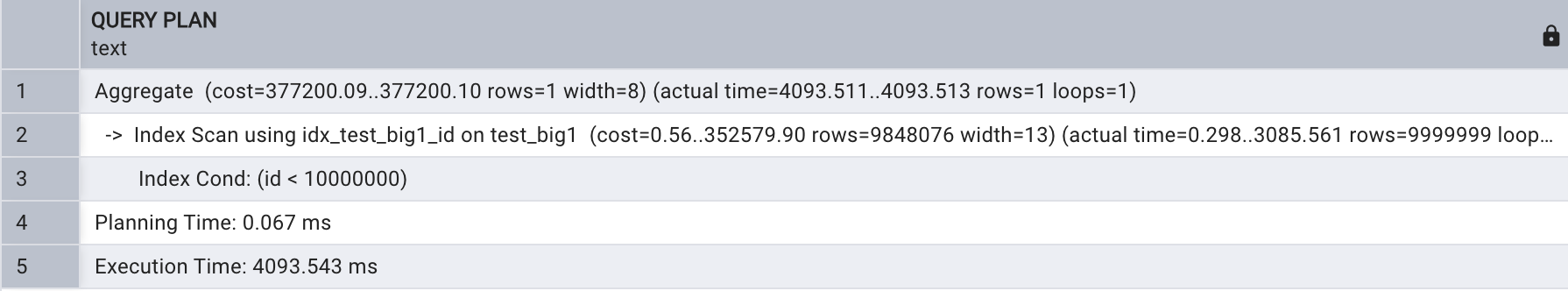
执行计划看出进行了索引扫描,没有开启并行。
2.3、并行index-only扫描
了解并行 index-only 扫描之前首先介绍下index-only扫描,顾名思义,index-only扫描是指只需扫描索引,也就是说SQL 仅根据索引就能获得所需检索 的 数据,而不需要通过索引回表查询数据 。 例如 ,使用SQL统计ID小于100万的记录数,在开始测试之前,先在会话级别关闭 并行, 如下所示:
SET max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;explain select count(*)
from test_big1
where id < 10000000;

上执行计划主要看Index Only Scan这一 行 ,由于ID宇段上建 立了索引,统计记录数不需要再回表查询其他信息,因此进行了index-only扫描,接下来使用EXPLAIN ANALYZE执行此SQL,如下所示:
explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1
where id < 10000000;

index-only 扫描支持并行,称为并行 index-only 扫描,接着测试并行 index-only扫描,在会话级别开启并行功能,如下所示 :
SET max_parallel_workers_per_gather to default;explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1
where id < 10000000;
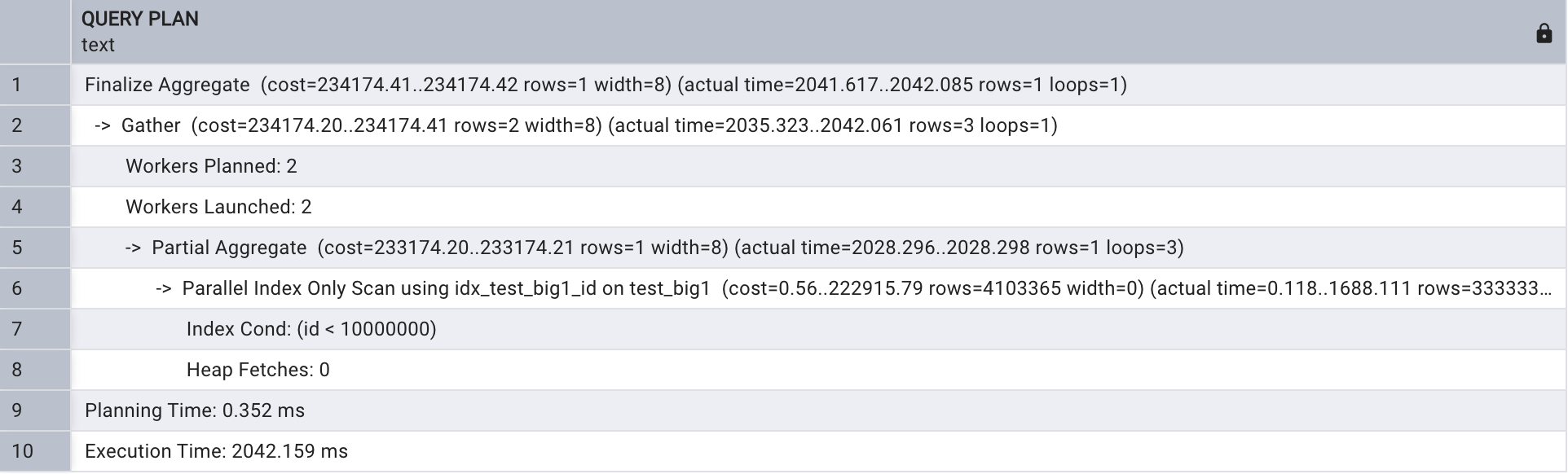
上执行计划主要看 Parallel Index Only Scan 这段 ,进行了并行 index-only 扫描。
2.4、并行bitmap heap扫描
绍并行 bitmap heap 扫描之前先了解下 Bi tmap Index 扫描和 Bitmap Heap 扫描, 当 SQL的where 条件中出现or时很有可能出现 Bitmap Index 扫描 , 如下所示 :
explain select *
from test_big1
where id = 1 or id = 2;
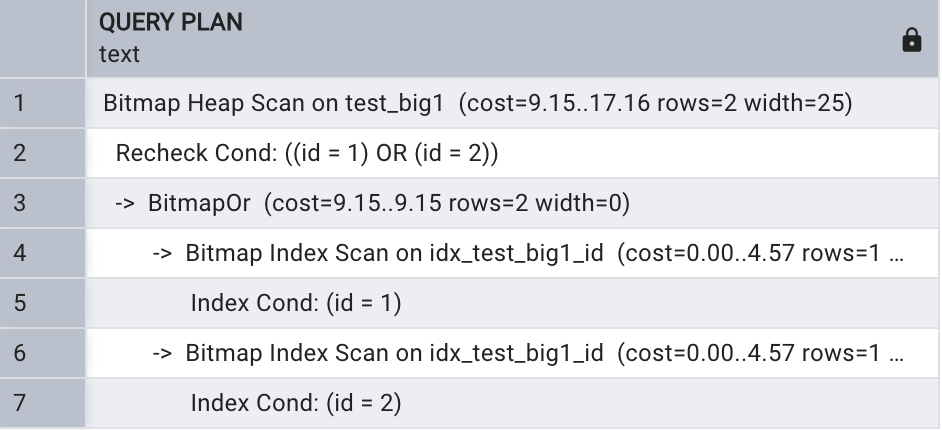
从以上执行计划看出,首先执行两次 Bitmap Index 扫描 获取索 引项,之后将 Bitmap Index扫描获取的结果合起来回表查 询 ,这时在表test_bigl 上进行了Bitmap Heap 扫描 。
Bitmap Heap 扫描也支持并行,执行以下 SQL ,在查询条件中将 ID 的选择范围扩大。
explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1
where id < 1000000 or id > 49000000;
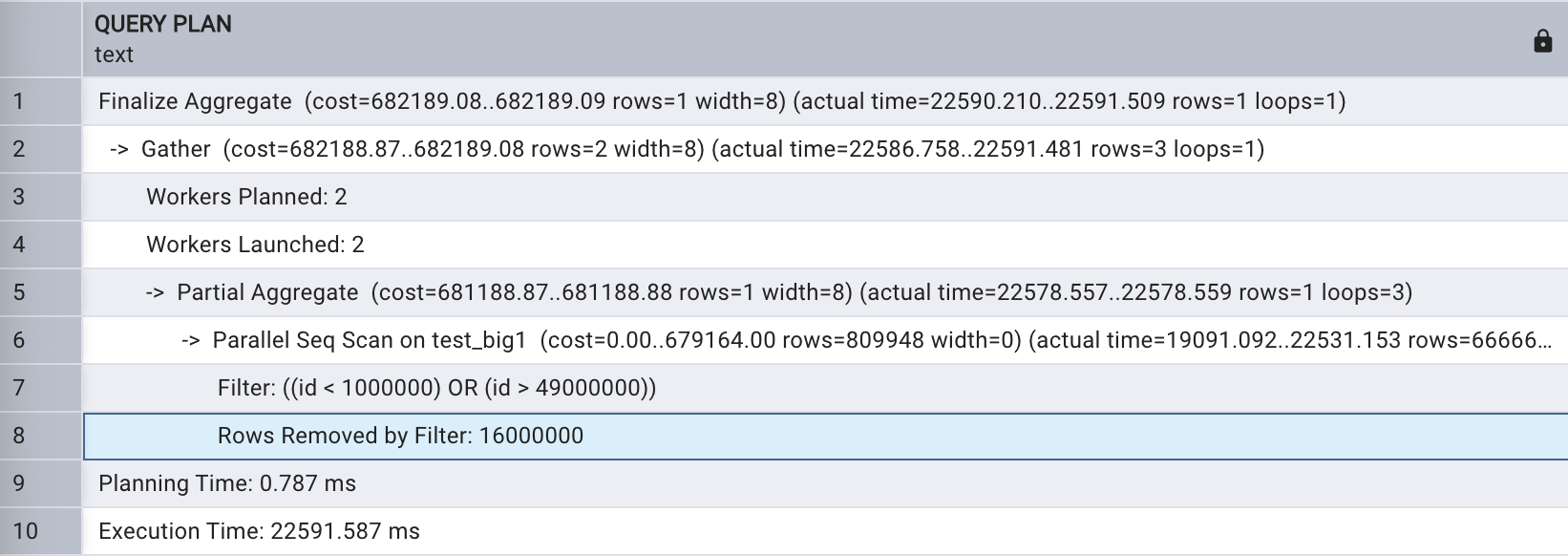
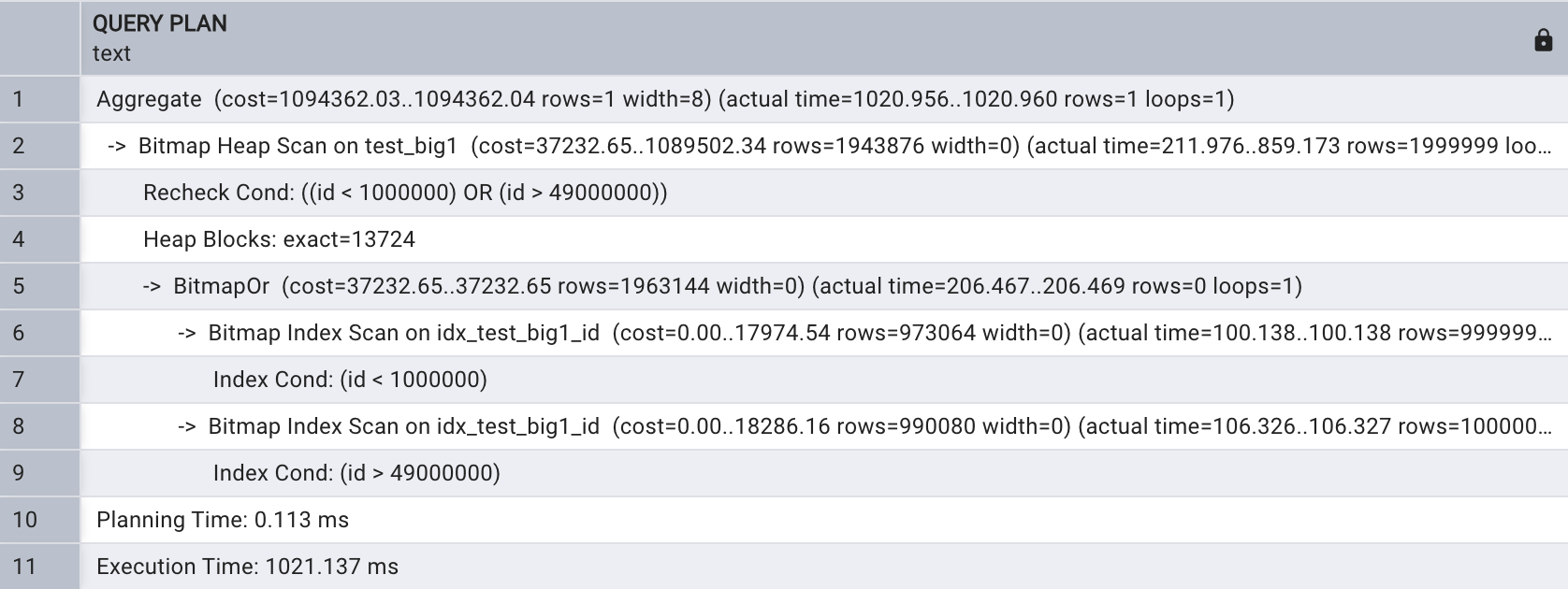
会话级关闭并行查询,如下所示:
set max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1
where id < 1000000 or id > 49000000;
三、并行聚合
合操作是指使用 count() 、 sum() 等聚合函数 的 SQL ,以下执行 count ()函数统计表记录总数,执行计划如下所示 :
explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1;

从以上执行计划 看 出, 首先进行 Part i al Aggregate , 开 启了 四个 并 行进程, 最后进行Finalize Aggregate。
这个例子充分验证 了聚合查询 count ()能 够支持并行 , 为 了 初 步测试并行性能,在会话级别关闭并行查询,如下所示 :
set max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;explain analyze select count(*)
from test_big1;
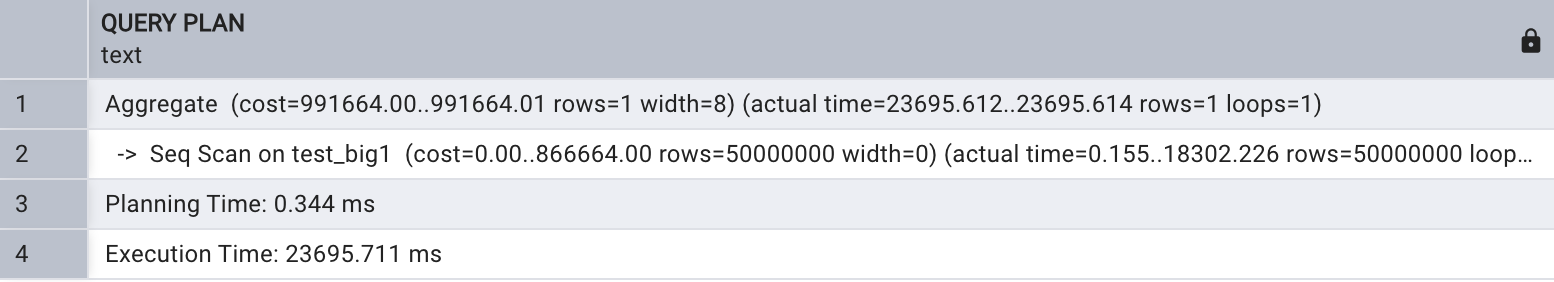
不同并行进程数下的全表扫描执行时间:

四、多表关联
4.1、Nested loop多表关联
多表关联 Nested loop 实际上是一个嵌套循环, 伪代码如下所示 :
for (i = 0; i < length(outer); i++)for (j = 0; j < length(inner); j++)if (outer[i] == inner[j])output(outer[i], inner[j]);
接着 测试 Nested loop 多表关联场景 下使用到并行扫描 的情况,创建一张 test_small 小表,如下所示 :
create table test_small(id int4,name character varying(32)
);insert into test_small(id, name)
select n, n || '_small'
from generate_series(1, 800000) n;
ANALYZE 命令用于收集表上的统计信息,使优化器能够获得更准确的执行计划,两表关联执行计划如下所示 :
explain analyze select test_small.name
from test_big1, test_small
where test_big1.id = test_small.id and test_small.id < 10000;
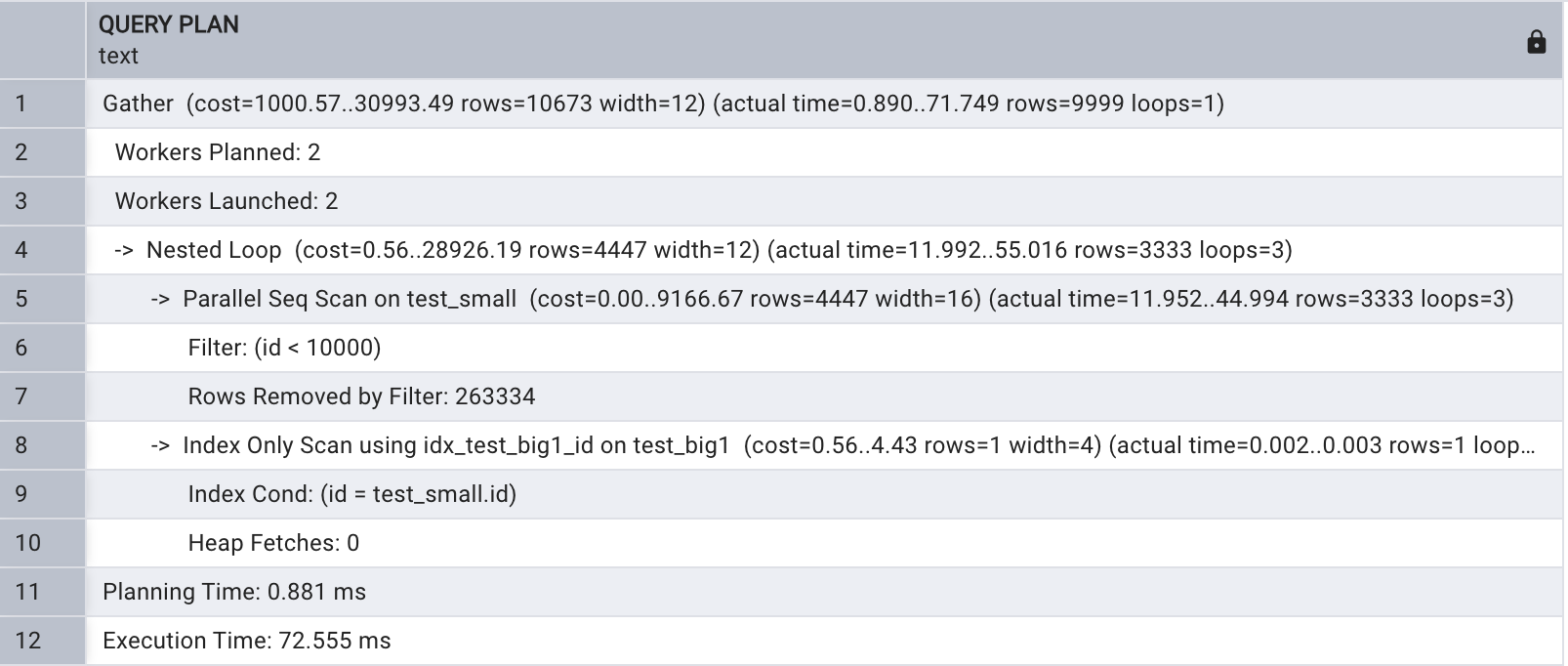
从以上执行计划可以 看出,首先在表 test_bigl 上进行 了 Index Only 扫描,用于检索 id 小于 10000 的记录,之后两表进行 Nested loop 关联同时在表 test_small I 上进行了并行 Bitmap Heap 扫描,用于检索 id 小于 10000 的记 录。
4.2、Merge join多表关联
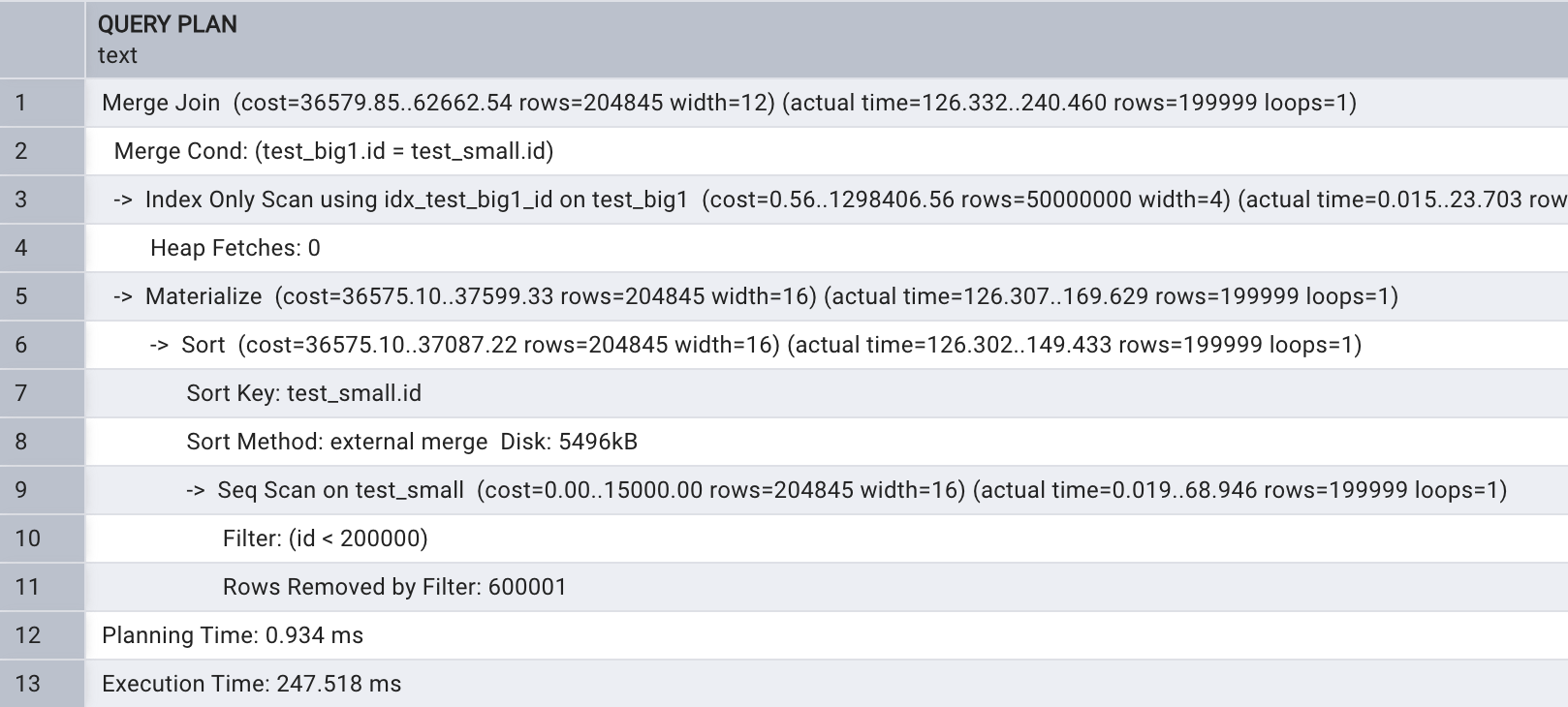
Merge join 多表关联首先将两个表进行排序,之后进行关联宇段匹配 , Merge join 示例如下所示:
explain analyze select test_small.name
from test_big1, test_small
where test_big1.id = test_small.id
and test_small.id < 200000;
4.3、Hash join多表关联
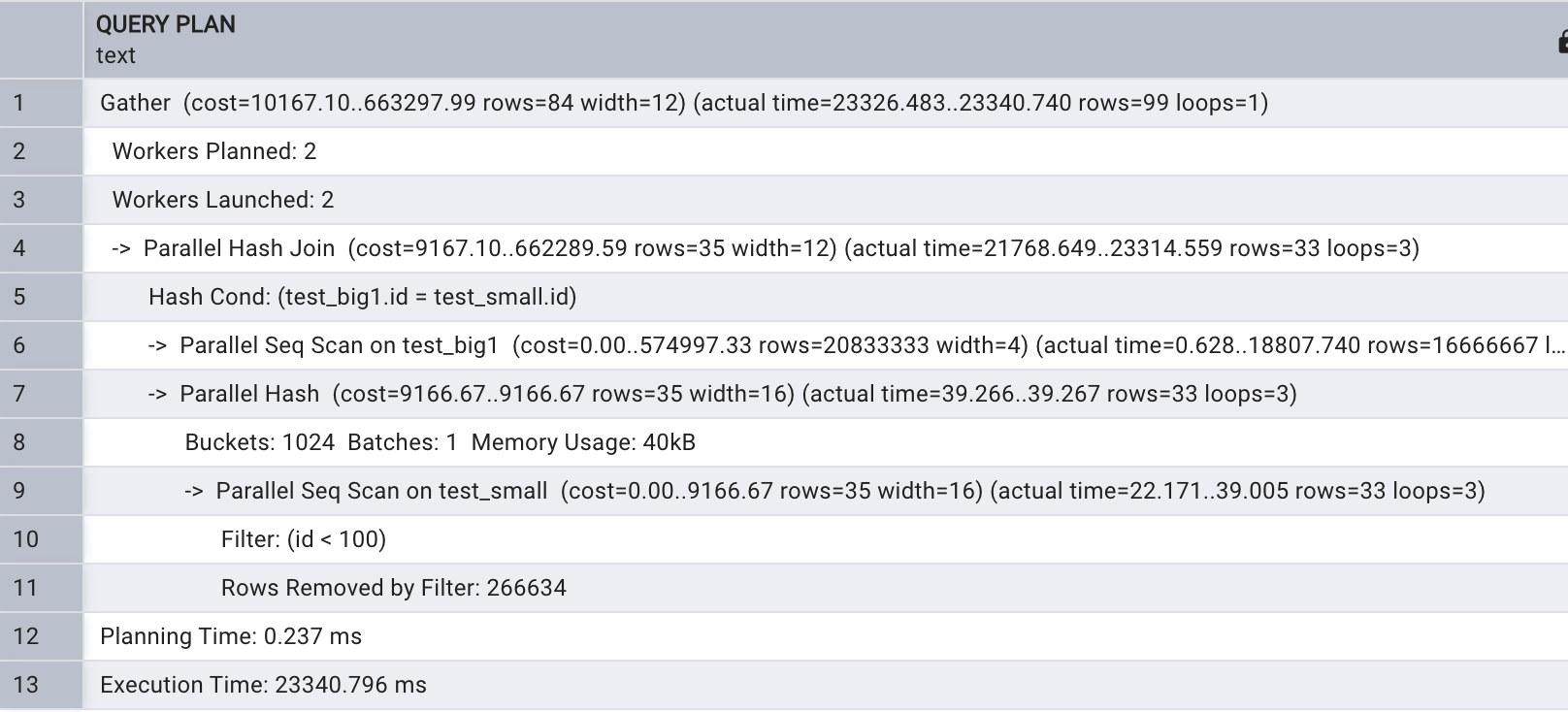
ostgreSQL 多表关联也支持 Hash join , 当关联宇段没有索引情况下两表关联通常会进行 Hash join ,接 下 来查看 Hash join 的执行计划 ,先将两张表上 的索引删除,同时关闭并行,如下所示:
drop index idx_test_big1_id;drop index idx_test_small_id;explain analyze select test_small.name
from test_big1 join test_small
on test_big1.id = test_small.id and test_small.id < 100;

)



![SQLI-labs[Part 2]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/SQLI-labs[Part 2])

![[硬件电路-194]:NPN三极管、MOS-N, IGBT比较](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[硬件电路-194]:NPN三极管、MOS-N, IGBT比较)

后半)
 用户手册)

![Vue模板中传递对象或数组时,避免直接使用字面量[]和{}](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/Vue模板中传递对象或数组时,避免直接使用字面量[]和{})




)
)
