list的相关文档:list - C++ Reference
一、list的介绍及使用
list中的接口比较多,此处类似,只需要掌握如何正确的使用,然后再去深入研究背后的原理,已达到可扩展的能力。以下为list中一些常见的重要接口。我们库里的list 是一个带头双向循环链表 。
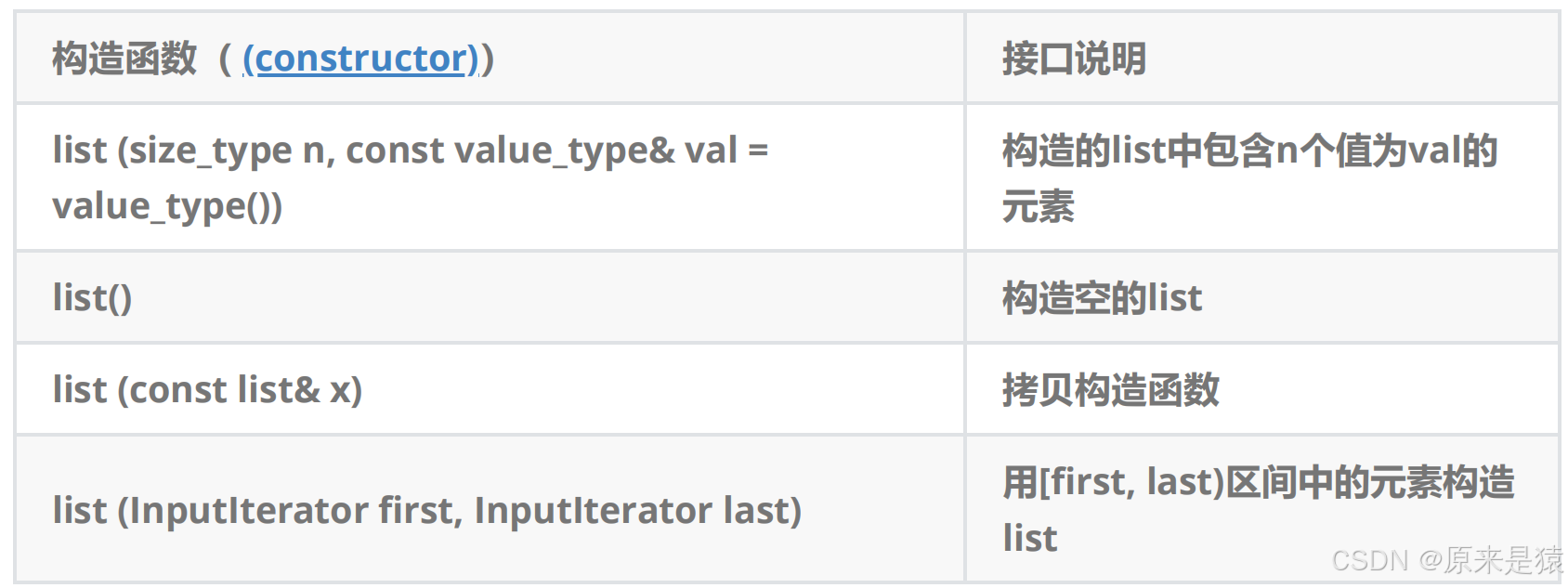
1.1 list 的构造
1.2. list 迭代器的使用
此处,大家可以暂时将迭代器理解成一个指针 , 该指针指向 list 中的某个节点 。

遍历链表 , 与vector和string 不同的是 , list 不支持 [ ] , 仅支持迭代器和范围 for 遍历链表 。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);lt1.push_back(3);lt1.push_back(4);list<int>lt2 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin();while (it1 != lt1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;for (auto& e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}1.3 list modifiers
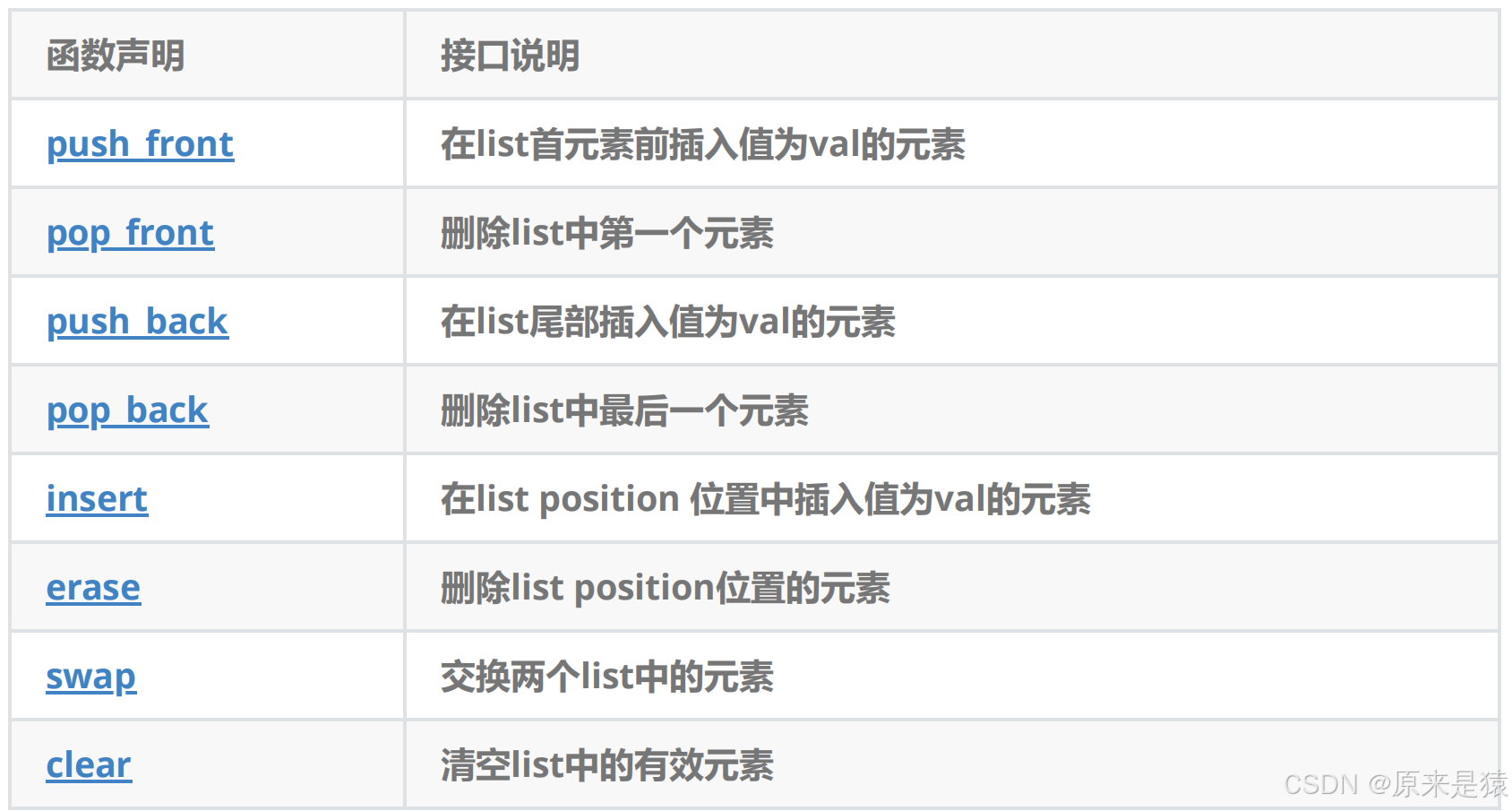
1)emplace_back 和 push_back 都能实现尾插一个数据 , 有什么区别 ?
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;class Pos
{
public:Pos(int row,int col):_row(row),_col(col){}
private:int _row;int _col;
};int main()
{list<Pos> lt;Pos p1(1, 1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(Pos(2, 2));lt.push_back({3,3});lt.emplace_back(p1);lt.emplace_back(Pos(2, 2));//lt.emplace_back({ 3,3 });lt.emplace_back(3, 3);return 0;
}补充 : 单参数的构造函数 , 支持隐式类型转化


2)删除指定元素
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;int x;cin >> x;auto it = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);if (it != lt1.end()){lt1.erase(it);}for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}1.4 Operations

1)merge : 合并

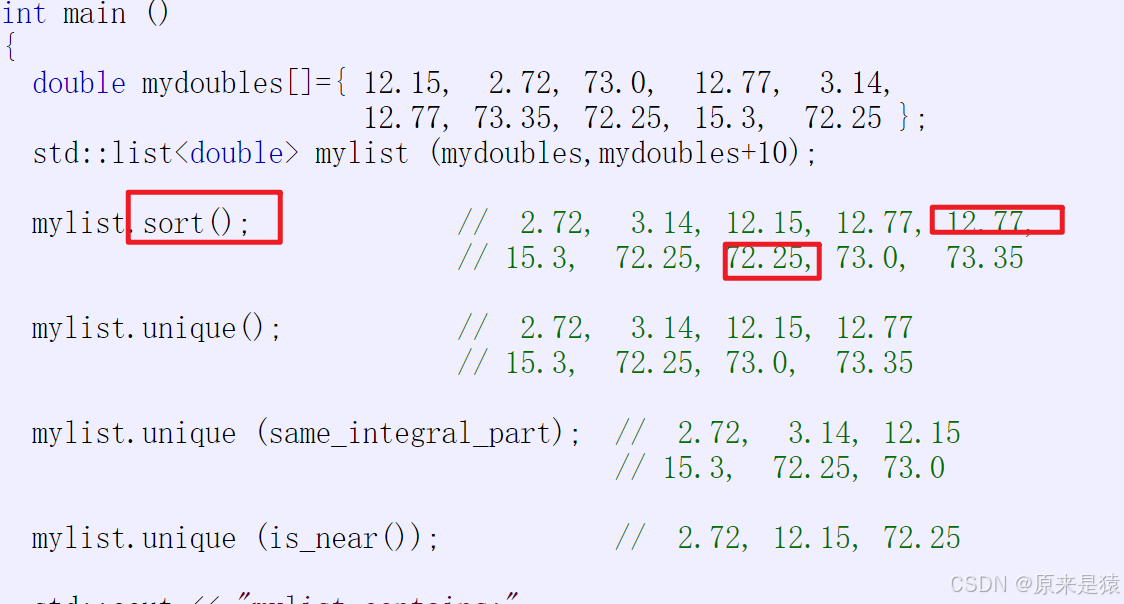
2)unique : 去重 , 前提:有序
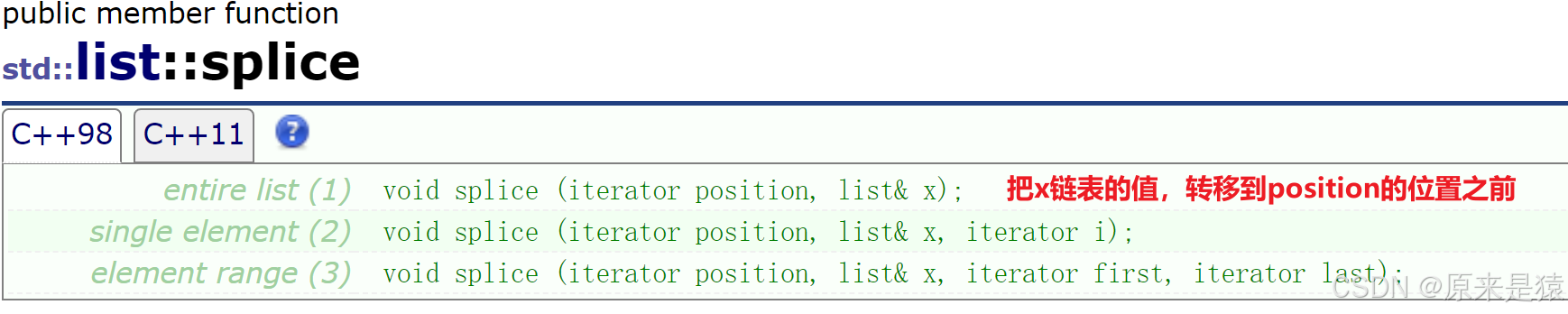
3)splice : 把一个链表的值转移到另一个链表
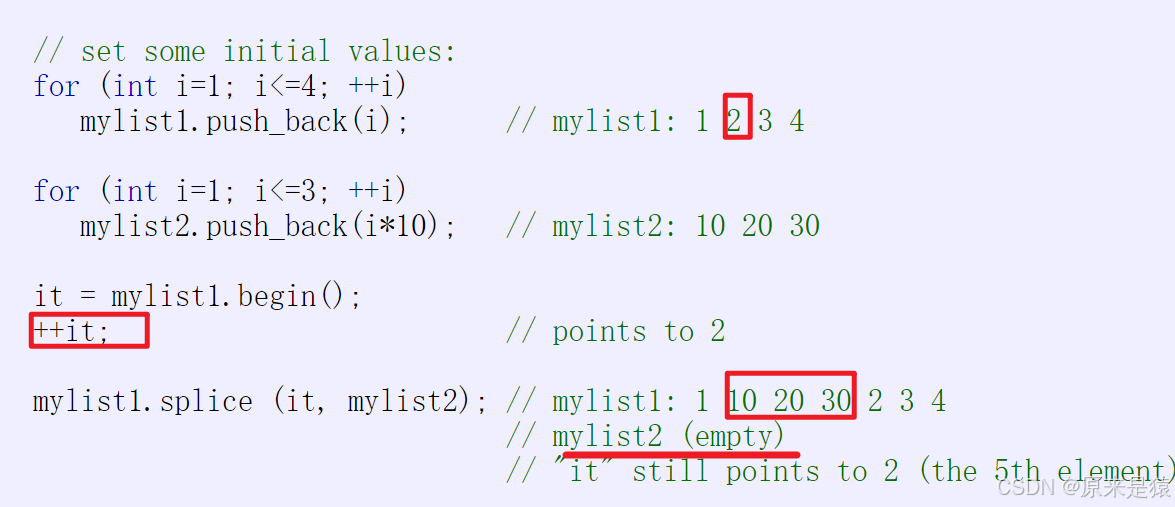
可以用来实现类似LRU(最近最少使用)的算法:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;//LRU
int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;int x;while (cin >> x){auto pos = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);if (pos != lt1.end()){lt1.splice(lt1.begin(), lt1, pos);}for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
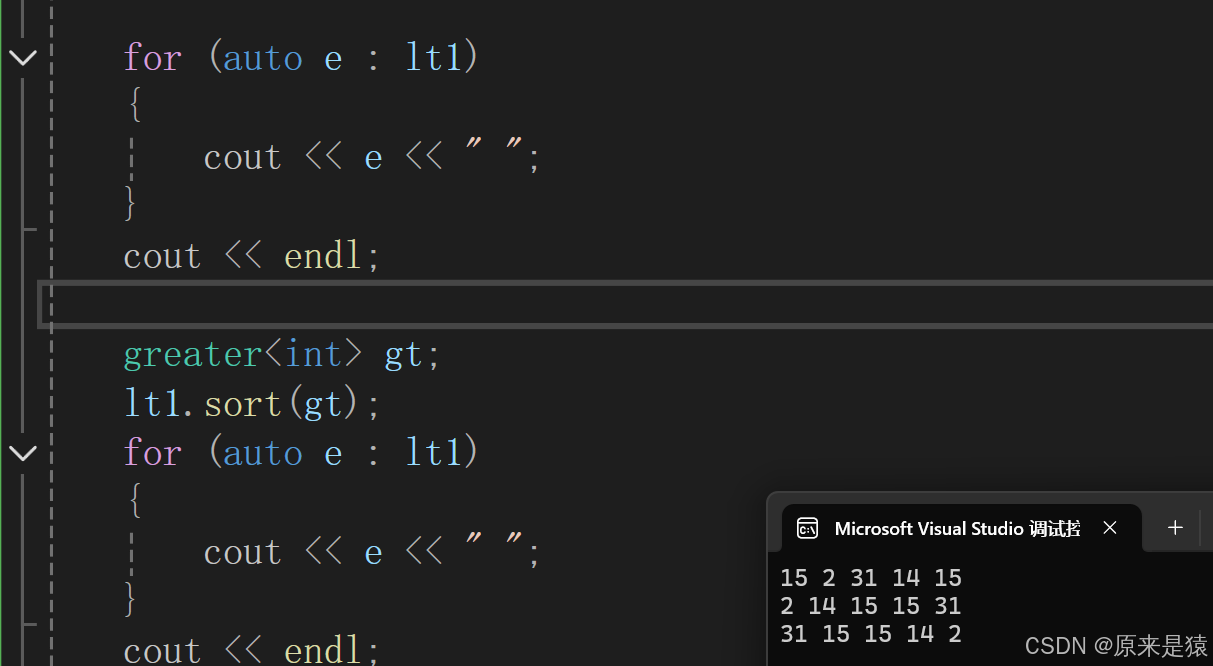
}4)sort : 排序


#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 15,2,31,14,15 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt1.sort();for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;greater<int> gt;lt1.sort(gt);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
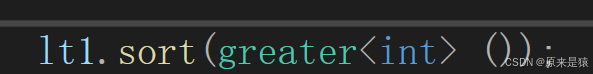
为了简化,我们一般按照下面的写法 ,传仿函数 :
为什么库里面有sort , list 还要实现一个sort , 难道不会是多次一举吗?
我们可以看到 , 不是list 不想用 , 是list 根本用不了 。 这就和迭代器的功能分类有关了。
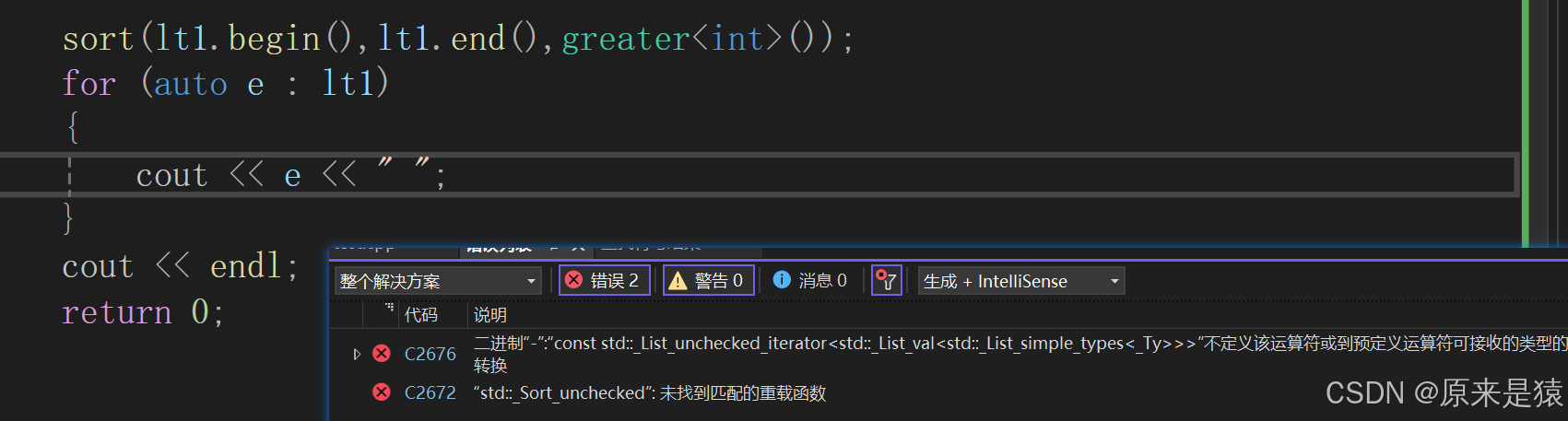
虽然,算法库的sort 是一个模板,但是也很明显的告诉了你 , 传的要是随机迭代器 。

二、list 底层
模板不支持分离成两个文件 , 这里我们仅创建 list.h
list 的底层很深刻的体现了封装的优点:
- 三者的角色分工
- 节点(Node) - 数据的 "容器" : 存储实际的数据,以及连接其他节点的指针(前向和后向指针)
- 迭代器(Iterator) - 数据的 "导航员" : 提供访问节点数据的统一方式,屏蔽底层节点的实现细节
- list 类 - 整个链表的 "管理者" : 负责整体的创建、销毁、插入、删除等操作,维护链表的完整性
-
封装的意义
-
分离关注点
- 节点只关心数据存储和连接
- 迭代器只关心如何访问数据
- list 类只关心整体管理
- 这样每个部分可以独立修改,不会互相影响
- 隐藏实现细节
- 用户不需要知道节点如何定义
- 不需要知道迭代器如何移动
- 只需要调用 list 提供的接口即可
- 统一访问方式
- 无论是 list、vector 还是其他容器,都可以用类似的迭代器方式访问
- 使得算法可以通用(如 sort、find 等)
- 提高安全性
- 防止用户直接操作节点指针导致的错误
- 迭代器会自动处理边界检查等问题
-
2.1 list 节点类
1. ( 惯例 ) 如果成员变量 和 成员函数 全部是公有的 , 一般用 struct 。既有公有 又有 私有 , 则用class
2. 如果把节点类放公有 , 不是会不安全 ? 能被任意修改 ?
节点类虽然是公开的 , 但是 是隐形的封装 , 对 list 才有用 , 在使用 list 的接口的时候 , 其实我们并不会知道它底层是双向带头链表 , 也不知道成员变量的具体变量名(不同平台的变量名会不同),所以是安全的 , 在list 的增删查改的时候 , 会高频的调用list 的节点,所以直接放成struct
//惯例
//全部是公用,一般用structtemplate<class T>struct list_node{T _data;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;list_node(const T& x = T()):_data(x), _prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr){}};缺省值给匿名对象 , 因为类型是不确定的 , 给字面量 不合适 。
2.2 list 迭代器
1. 原生指针已经不够用了 ;所以list 的迭代器是 类封装指针 , 重载运算符 , 模拟指针行为 。
2. 使用struct , 因为需要频繁访问内部成员 , 不建议用访问限定符限制 。
3. 容器迭代器设计思路体现了封装 :屏蔽底层实现细节,屏蔽各容器结构差异 , 本质封装底层细节 和 差异 ,提供统一的访问方式 。
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}//返回局部对象就不能再使用引用返回了Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};
2.3 list 类
1)insert:
返回 iterator ;由于不需要扩容 , 所以不存在迭代器失效的问题
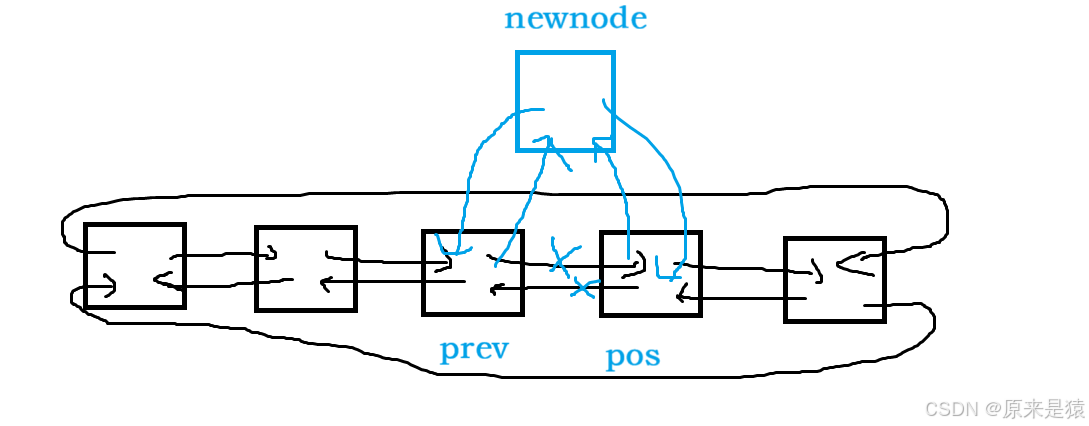
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curnewnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;prev->_next = newnode;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}复用insert 实现头插和尾插 :
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}
2)erase :
list 的迭代器失效 : 迭代器失效即 迭代器所指向的节点无效 , 即该节点被删除了 。 因为 list 的底层结构为带头节点的双向循环链表 , 因此再 list 中 进行插入时 是 不会导致 list 的迭代器失效的 , 只有在删除时才会失效 , 并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器 , 其他迭代器不会受到影响 。
注意 : 删除唯独不能删除哨兵位的头结点 !!!
iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* del = pos._node;Node* prev = del->_prev;Node* next = del->_next;//prev del nextprev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete del;return iterator(next);}复用erase 实现头删 和 尾删 :
void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}3) 析构
~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}clear 是清理资源 , 但是结构依旧保持 。 (注意 : list 的erase 会导致迭代器失效的问题 , 需要更新一下迭代器 。 ) 析构 不仅清理资源 , 同时会把头结点给删除了 。
4)拷贝构造 :
//拷贝构造//lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}5)赋值重载:
//赋值重载
//lt2 = lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{swap(lt);return *this;
}void swap(list<T>& tmp)
{std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
}6)所有代码:list.h
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>namespace LF
{//惯例
//全部是公用,一般用structtemplate<class T>struct list_node{T _data;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;list_node(const T& x = T()):_data(x), _prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr){}};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}//返回局部对象就不能再使用引用返回了Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}};//template<class T>//struct list_const_iterator//{// typedef list_node<T> Node;// typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;// Node* _node;// list_const_iterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {}// const T& operator*()// {// return _node->_data;// }// const T* operator->()// {// return &_node->_data;// }// Self& operator++()// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// Self& operator--()// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// Self operator++(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_next;// return tmp;// }// Self operator--(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_prev;// return tmp;// }// bool operator!=(const Self& s)// {// return _node != s._node;// }//};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public://typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;//typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;}list(){empty_init();}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}//n个val构造list(size_t n, const T& val = T()){empty_init();for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(val);}}//拷贝构造//lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}//赋值重载//lt2 = lt3list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}void swap(list<T>& tmp){std::swap(_head, tmp._head);}//void push_back(const T& x)//{// Node* new_node = new Node(x);// Node* tail = _head->_prev;// new_node->_next = _head;// new_node->_prev = tail;// _head->_prev = new_node;// tail->_next = new_node;//}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curnewnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;prev->_next = newnode;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* del = pos._node;Node* prev = del->_prev;Node* next = del->_next;//prev del nextprev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete del;return iterator(next);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}private:Node* _head;};
}
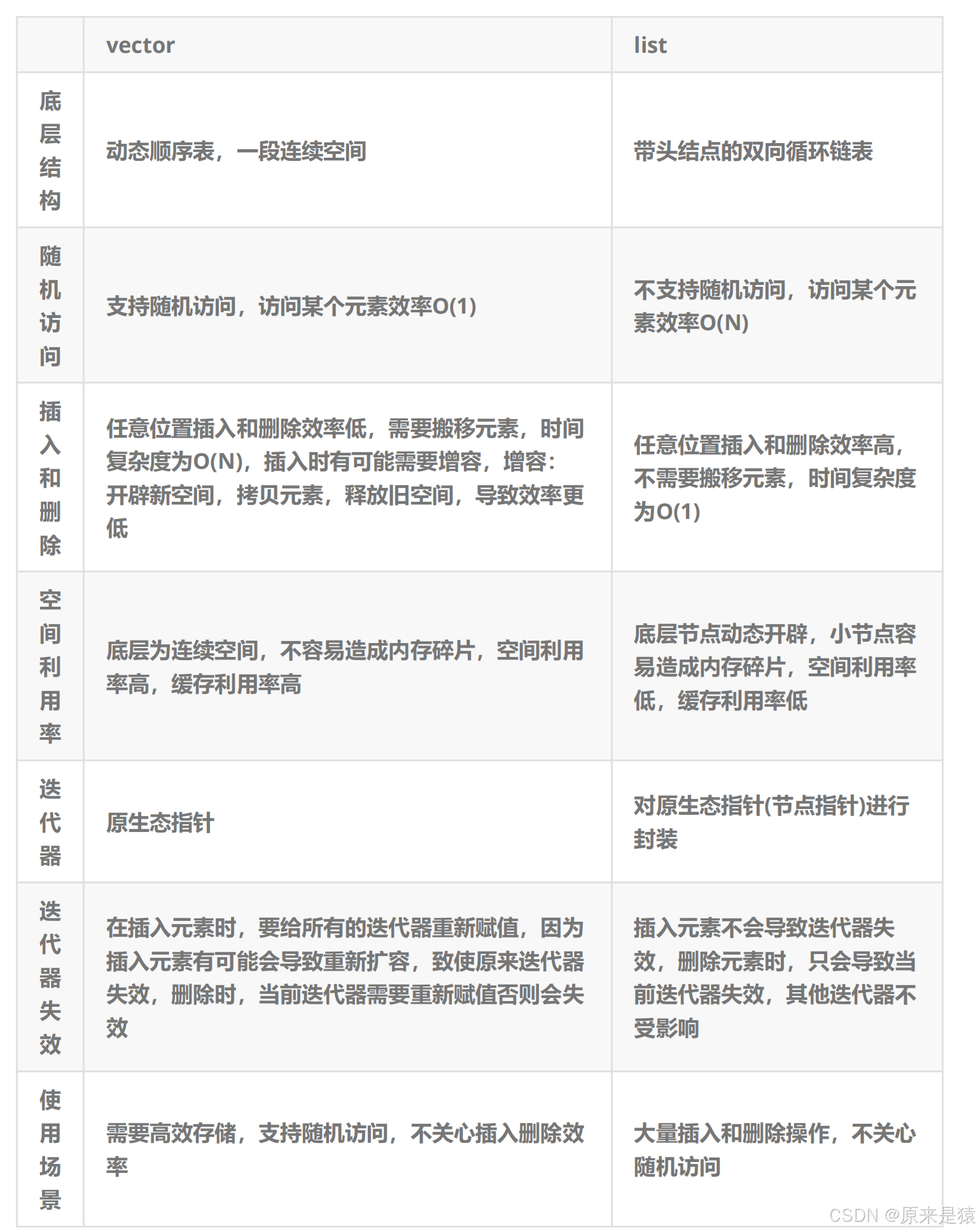
2.4 list 和 vector的对比
vector 与 list 都是 STL中非常重要的序列式容器 , 由于两个容器的底层结构不同 , 导致其特性以及应用场景不同 , 其主要不同如下 :




![C study notes[3]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/C study notes[3])

—组合模式)
安全检查)


)









