如有问题大概率是我的理解比较片面,欢迎评论区或者私信指正。
最近了解到了一个新的改变和提高自己的方法·时刻记录不论多小的事情都记下,我目前用了4天,之前感觉一天天忙死但没啥收获,但是记录了之后知道自己的时间花在了哪里,后期该如何调整,并且可以很好缓解焦虑情绪。
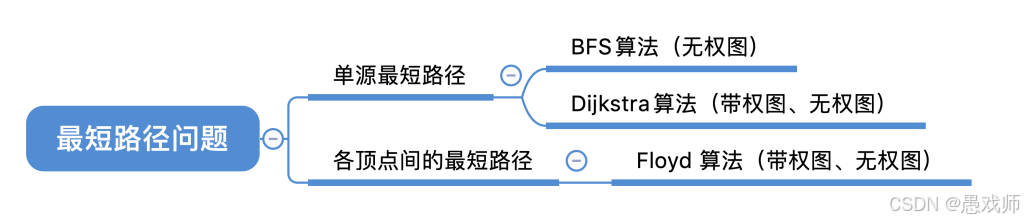
一、最小生成树(最小代价树)
1、基础概念
最小生成树基本概念:
MST的定义:权值和最小的生成树(连通所有顶点、无环、边数=顶点数-1、砍掉一条边则不连通)。
性质:权值和唯一,但树形可能不唯一(存在相同权值的边时)。
适用场景:连通图(非连通图只有生成森林)。
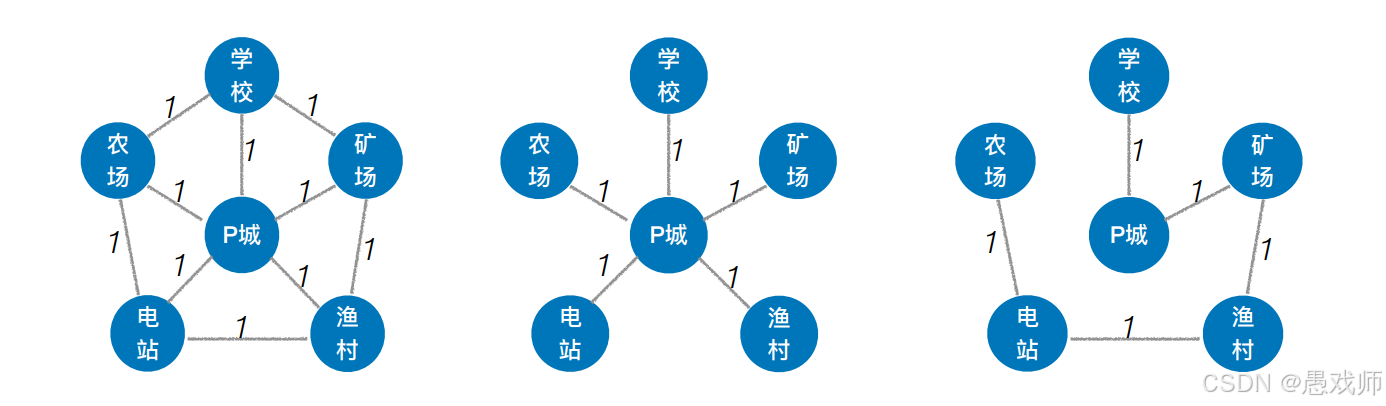
Prim算法:
核心思想:贪心策略,从单个顶点逐步扩展,每次添加与当前树连接的最小权值边对应的顶点。
实现关键:
- 维护
lowCost[]数组存储顶点到生成树的最小代价。 - 用
isJoin[]标记顶点是否已加入树(避免成环)。
时间复杂度: (适合稠密图)。
(适合稠密图)。
Kruskal算法:
核心思想:贪心策略、按边权升序选择边、避免成环。
实现关键:
边排序![]() 。
。
用并查集(Union-Find)判断边的两点是否连通。
时间复杂度:![]() (适合稀疏图)。
(适合稀疏图)。
两种算法对比:
适用场景:稠密图用Prim,稀疏图用Kruskal。
时间复杂度差异:Prim依赖顶点数,Kruskal依赖边数。
2、Prim 算法(普⾥姆)
数据结构
lowCost[]:记录各顶点加入生成树的最小代价(初始:起点为0,直连顶点为边权,非直连为∞)
isJoin[]:标记顶点是否已加入生成树(初始:仅起点为true)
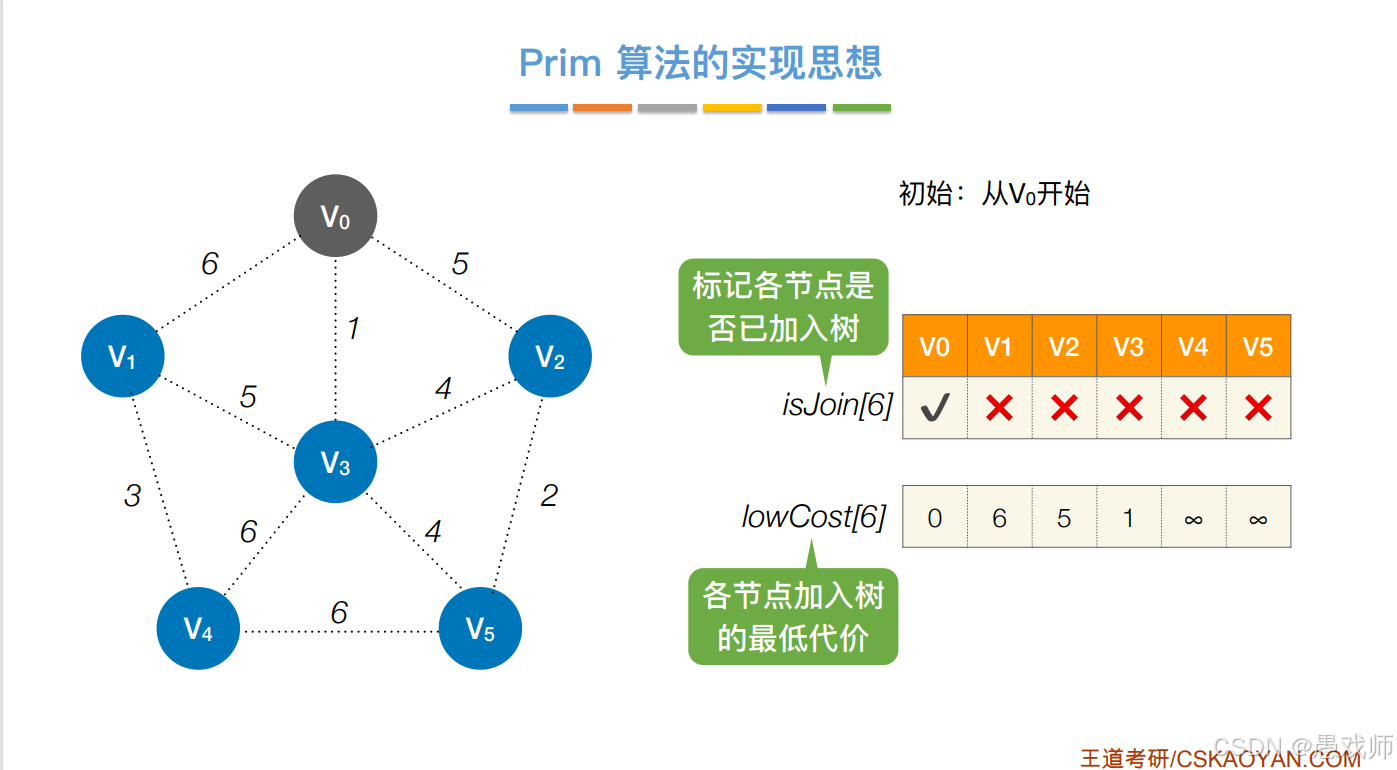
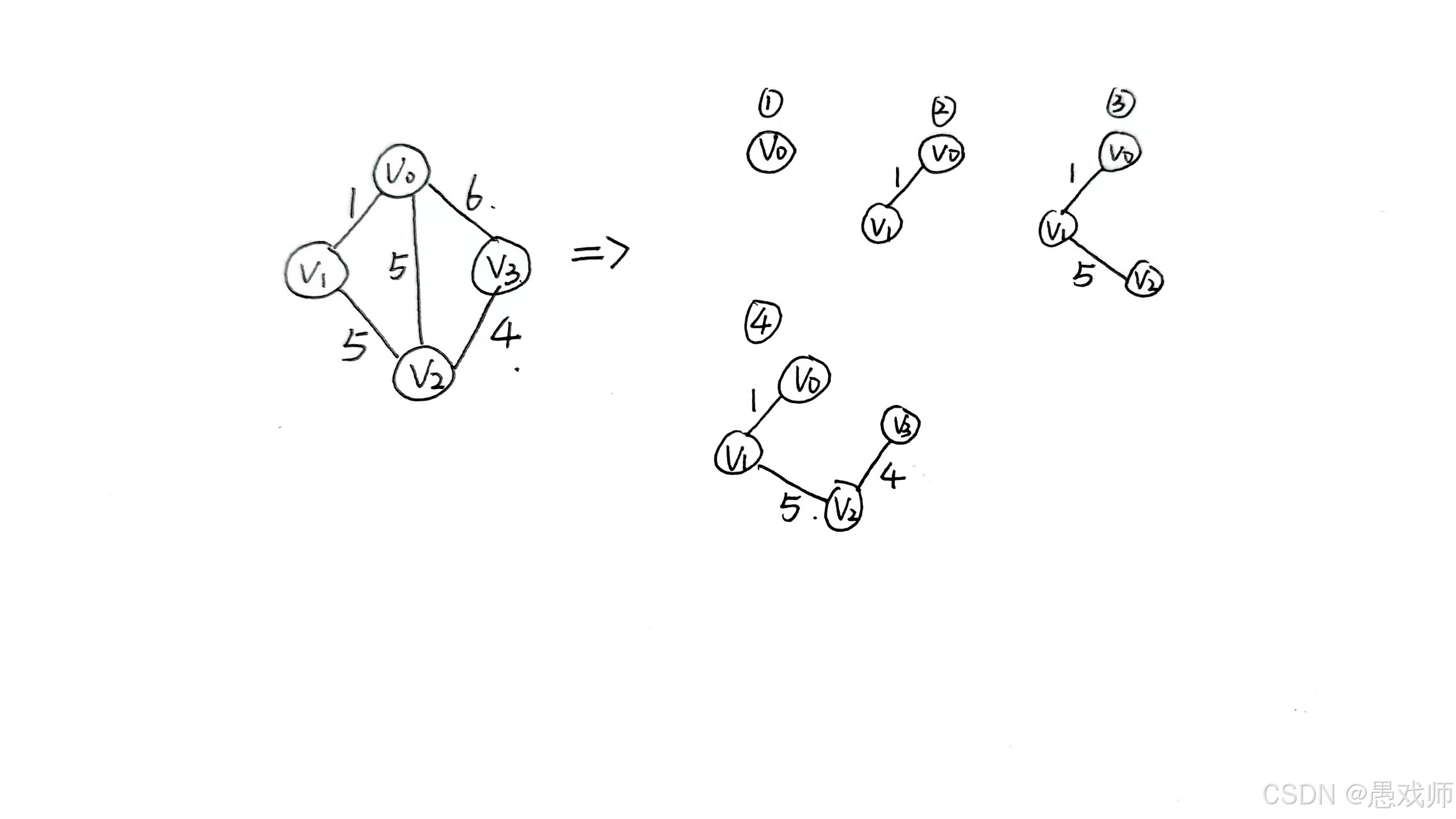
核心流程
for i in range(n-1): # 共n-1轮# 1. 扫描lowCost找最小值顶点u(未加入的顶点)u = find_min(lowCost, isJoin) isJoin[u] = True # 加入生成树# 2. 更新邻接点v的lowCostfor v in graph[u]:if not isJoin[v] and graph[u][v] < lowCost[v]:lowCost[v] = graph[u][v]时间复杂度
朴素实现:O(|V|^2)
堆优化:O(|E| log |V|)(用优先队列存(lowCost, v))
易错点
初始化错误
- 未将起点
lowCost设为0(误设为∞) - 未标记起点
isJoin=True(导致重复加入)
更新逻辑错误
- 更新邻接点时未检查
isJoin[v](已加入顶点不应更新) - 错误更新非邻接点(应只更新当前顶点的邻接点)
非连通图处理
- 未检查是否加入所有顶点(若未完成但
lowCost全为∞,说明图不连通)
权值比较错误
- 更新时用边权与旧
lowCost比较(正确:graph[u][v] < lowCost[v]) - 未处理重边(应取最小权值边)
基础模板如下:
import java.util.*;public class PrimMST {// 朴素版Prim算法实现(O(V^2))public static int prim(int[][] graph) {int n = graph.length;// 易错点1:初始化 - 未正确设置起点会导致逻辑错误int[] lowCost = new int[n]; // 各顶点加入生成树的最小代价boolean[] isJoin = new boolean[n]; // 标记顶点是否已加入生成树Arrays.fill(lowCost, Integer.MAX_VALUE);lowCost[0] = 0; // 起点最小代价设为0(易错点1.1:起点设为0)int totalCost = 0;int selectedCount = 0; // 已选顶点计数(用于检测非连通图)// 核心流程:共需选择n个顶点(包括起点)for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 1. 寻找当前lowCost中的最小值顶点uint u = -1;for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {// 只考虑未加入的顶点(易错点2:已加入顶点不能重复选择)if (!isJoin[v] && (u == -1 || lowCost[v] < lowCost[u])) {u = v;}}isJoin[u] = true; // 将u加入生成树totalCost += lowCost[u];selectedCount++;// 2. 更新u的邻接点的lowCost值for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {// 易错点4:更新条件判断(必须同时满足三个条件)if (!isJoin[v] && graph[u][v] != 0 && graph[u][v] < lowCost[v]) {// 注意:graph[u][v]!=0 表示存在边(0表示无直接边)// 易错点5:权值比较(需严格小于当前值才更新)lowCost[v] = graph[u][v];}}}// 易错点3补充:检查是否加入全部顶点if (selectedCount != n) {System.out.println("图不连通!");return -1;}return totalCost;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] graph = {{0, 1, 5, 6},{1, 0, 5, 0}, // 易错点7:无向图需要对称{5, 5, 0, 4},{6, 0, 4, 0}};int cost = prim(graph);if (cost != -1) {System.out.println("最小生成树权值和: " + cost); // 正确结果:10}}
}练习1:训练Prim的二维坐标处理能力
1584. 连接所有点的最小费用 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-cost-to-connect-all-points/description/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-cost-to-connect-all-points/description/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
class Solution {public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {int n=points.length;//标记数组boolean[] isJion=new boolean[n];//最小代价数组int[] lowCost=new int[n];//初始化Arrays.fill(isJion,false);Arrays.fill(lowCost,Integer.MAX_VALUE);lowCost[0]=0;int selectedCount=0;//非连通图检测//记录最终答案int ans=0;//prim算法for(int i=0;i<n;i++){//依次将lowCost中代价最小的节点加入生成树int u=-1;//找出lowCost中代价最小的节点for(int v=0;v<n;v++){//节点未加入生成树 && (第一次·生成树的根节点 || 更小花费)if(!isJion[v] && (u==-1 || lowCost[v]<lowCost[u])){u=v;}}//加入生成树并处理isJion[u]=true;ans+=lowCost[u];selectedCount++;//更新邻接点的lowCostfor(int v=0;v<n;v++){if(!isJion[v] && cost(u,v,points)<lowCost[v]){lowCost[v]=cost(u,v,points);}}}return ans;}public int cost(int u,int v,int[][] points){return Math.abs(points[u][0]-points[v][0])+Math.abs(points[u][1]-points[v][1]);}
}3、Kruskal 算法(克鲁斯卡尔)
数据结构
边集数组:按权值排序 edges = [(weight, u, v), ...]
并查集:判断连通性(初始每个顶点独立集合)
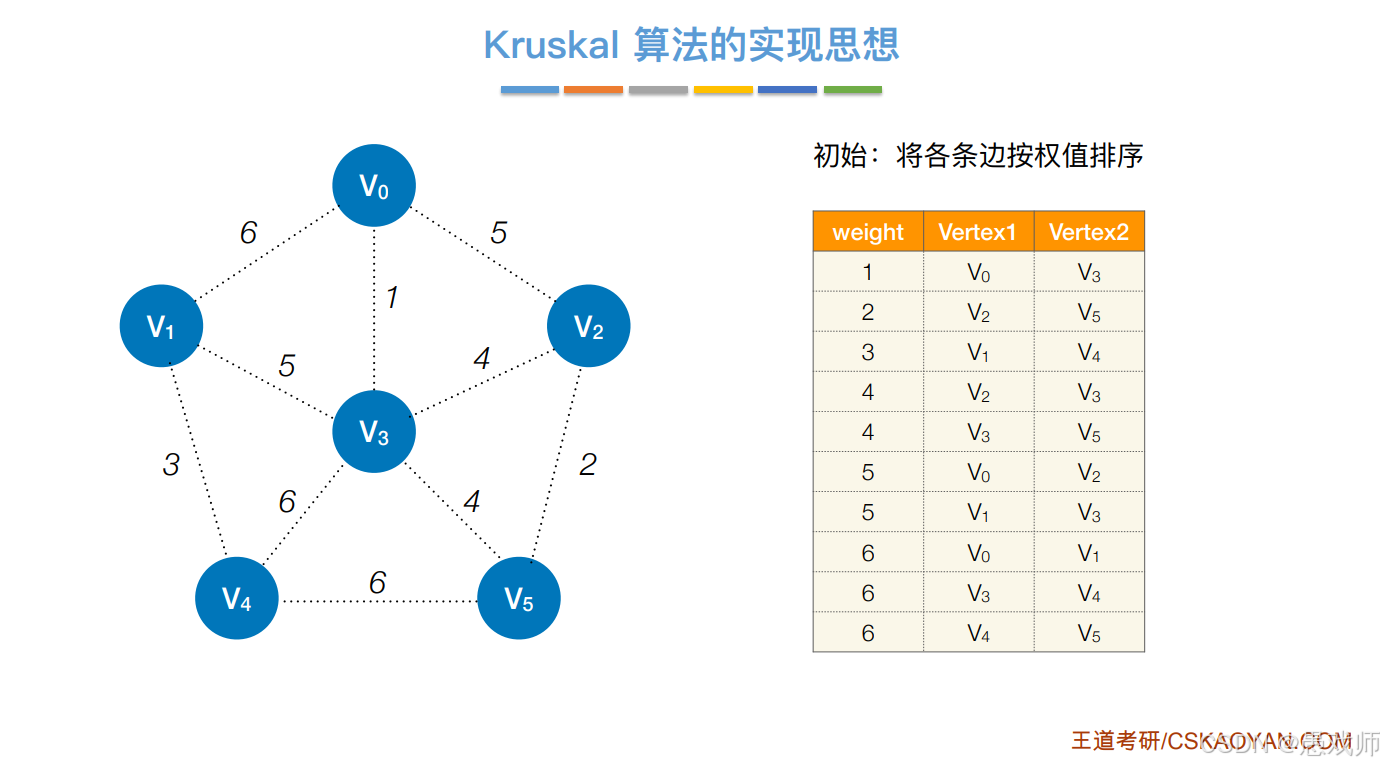
核心流程
edges.sort() # 按权值升序排序
for weight, u, v in edges:if find(u) != find(v): # 不连通union(u, v) # 合并集合add_edge(u, v) # 加入生成树if edges_added == n-1: break # 边数达标终止时间复杂度
排序:O(|E| log |E|)
并查集:每轮(近似常数)
排序遗漏
- 未对边排序直接遍历(破坏贪心策略正确性)
并查集错误
- 未初始化并查集(每个顶点应为独立集合)
- 合并后未更新父节点(需路径压缩优化)
环判断错误
- 未检查连通性直接加边(应用并查集而非DFS/BFS判环)
终止条件缺失
- 未在边数达
n-1时提前终止(多余计算)
重边处理
- 未去重直接排序(应保留最小权值重边)
import java.util.*;public class KruskalMST {// 边类static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {int src, dest, weight;public Edge(int src, int dest, int weight) {this.src = src;this.dest = dest;this.weight = weight;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Edge other) {// 易错点1:排序遗漏 - 必须按权值排序return this.weight - other.weight;}}// 并查集类static class UnionFind {int[] parent, rank;public UnionFind(int n) {parent = new int[n];rank = new int[n];// 易错点2:并查集未初始化 - 每个顶点独立集合for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {parent[i] = i; // 初始每个顶点独立成集合}}public int find(int x) {// 路径压缩优化if (parent[x] != x) {parent[x] = find(parent[x]);}return parent[x];}public void union(int x, int y) {int rootX = find(x);int rootY = find(y);if (rootX == rootY) return;// 按秩合并if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {parent[rootX] = rootY;} else if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {parent[rootY] = rootX;} else {parent[rootY] = rootX;rank[rootX]++;}}}public static List<Edge> kruskal(List<Edge> edges, int n) {// 易错点1:排序遗漏 - 必须先对边排序Collections.sort(edges);UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);List<Edge> mst = new ArrayList<>();int edgesAdded = 0;for (Edge edge : edges) {// 易错点3:环判断错误 - 必须检查连通性if (uf.find(edge.src) != uf.find(edge.dest)) {uf.union(edge.src, edge.dest);mst.add(edge);edgesAdded++;// 易错点4:终止条件缺失 - 边数达标提前终止if (edgesAdded == n - 1) break;}}// 检查是否形成完整生成树if (edgesAdded != n - 1) {System.out.println("图不连通,无法形成最小生成树");return null;}return mst;}public static void main(String[] args) {int n = 4;List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();edges.add(new Edge(0, 1, 1));edges.add(new Edge(0, 2, 5));edges.add(new Edge(0, 3, 6));edges.add(new Edge(1, 2, 5));edges.add(new Edge(2, 3, 4));// 处理重边(可选)// 易错点5:重边处理 - 保留最小权值边// 本例无重边,实际应用中需要预处理List<Edge> mst = kruskal(edges, n);if (mst != null) {System.out.println("最小生成树边集:");int totalWeight = 0;for (Edge edge : mst) {System.out.println(edge.src + " - " + edge.dest + " : " + edge.weight);totalWeight += edge.weight;}System.out.println("总权重: " + totalWeight); // 正确结果:4+2+4+4+4=18}}
}练习2:掌握Kruskal并查集实现
1584. 连接所有点的最小费用 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-cost-to-connect-all-points/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-cost-to-connect-all-points/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
class Solution {public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {//极端if(points.length==0 || points==null)return 0;//边List<Eadge> eadges=new ArrayList<>();//并查集UnionFind uf=new UnionFind(points.length);//终止条件int selectedCount=0;int ans=0;//初始化边for(int v=0;v<points.length;v++){for(int u=v+1;u<points.length;u++){eadges.add(new Eadge(v,u,cost(v,u,points)));}}//排序Collections.sort(eadges);for(Eadge e:eadges){//判断连通性if(uf.find(e.s)!=uf.find(e.e)){uf.union(e.s,e.e);selectedCount++;ans+=e.weight;}//终止if(selectedCount==points.length-1)break;}return ans;}public int cost(int u,int v,int[][] points){return Math.abs(points[u][0]-points[v][0])+Math.abs(points[u][1]-points[v][1]);}
}//边类
class Eadge implements Comparable<Eadge>{int s;int e;int weight;public Eadge(int s,int e,int weight){this.s=s;this.e=e;this.weight=weight;}//重写比较·升序@Overridepublic int compareTo(Eadge other) {return this.weight - other.weight;}
}//并查集类class UnionFind {//双亲数组·记录当前下标节点的双亲节点下标int[] parent;//rank数组·union优化int[] rank;//初始化public UnionFind(int n){parent=new int[n];rank=new int[n];Arrays.fill(rank,0);//初始·每个节点都是独立集合for(int i=0;i<n;i++){parent[i]=i;}}//查找·路径优化public int find(int x){//终止条件·根节点的父节点是自己本身if(parent[x]!=x){parent[x]=find(parent[x]);}return parent[x];}//合并·高度压缩(小树并大树上)public void union(int x,int y){//找根int v=find(x);int u=find(y);if(v==u)return ;//同一个集合不需要合并//检查秩if(rank[v]<rank[u]){parent[v]=u;}else if(rank[v]>rank[u]){parent[u]=v;}else{parent[v]=u;rank[v]++;}}}
4、综合练习·考察MST关键边的理解
1489. 找到最小生成树里的关键边和伪关键边 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-critical-and-pseudo-critical-edges-in-minimum-spanning-tree/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-critical-and-pseudo-critical-edges-in-minimum-spanning-tree/description/
二、最短路径
基础
1. 算法适用场景
| 算法 | 无权图 | 带权图 | 负权边 | 负权回路 | 单源/多源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFS | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 单源(无权图) |
| Dijkstra | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 单源(带权图) |
| Floyd | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 多源(任意两点) |
2. 核心原理
-
BFS:层序遍历,距离=层数(权值视为1)。
-
Dijkstra:贪心策略,每次选距离起点最近的未访问点,更新邻接点。
-
Floyd:动态规划,
A[k][i][j] = min(A[k-1][i][j], A[k-1][i][k] + A[k-1][k][j])。
3. 时间复杂度
| 算法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| BFS | O(|V| + |E|) | O(|V|) |
| Dijkstra(基础) | O(|V|²) | O(|V|) |
| Floyd | O(|V|³) | O(|VBFS |
BFS
问题1:“为什么DFS不适合?权值不等时为何BFS失效?”(为何BFS适合解决无权图单源最短路径(每条边权值为1,路径长度=边数))
答案:DFS可能探索非最短路径;权值不等时路径长度≠边数,需Dijkstra算法。
问题2:代码中的三个核心数组
d[]:记录源点到各顶点的最短距离(初始化为∞)。visited[]:标记顶点是否被访问(初始化为false)。path[]:记录路径前驱(初始化为-1)。
if (!visited[w]) {d[w] = d[u] + 1; // 更新距离path[w] = u; // 记录前驱visited[w] = TRUE;EnQueue(Q, w);
}问题3:“BFS与Dijkstra在权值为1时的关系?”
答案:BFS是Dijkstra在无权图中的特例(优先级队列退化为普通队列)。
问题4:若图非连通,部分顶点d[]保持∞,如何处理?
方法:遍历所有顶点,对未访问顶点再次调用BFS。
问题5:
“如何输出完整路径?”→ 用path[]回溯。
“若需记录多条最短路径?”→ 将path[]改为存储链表。
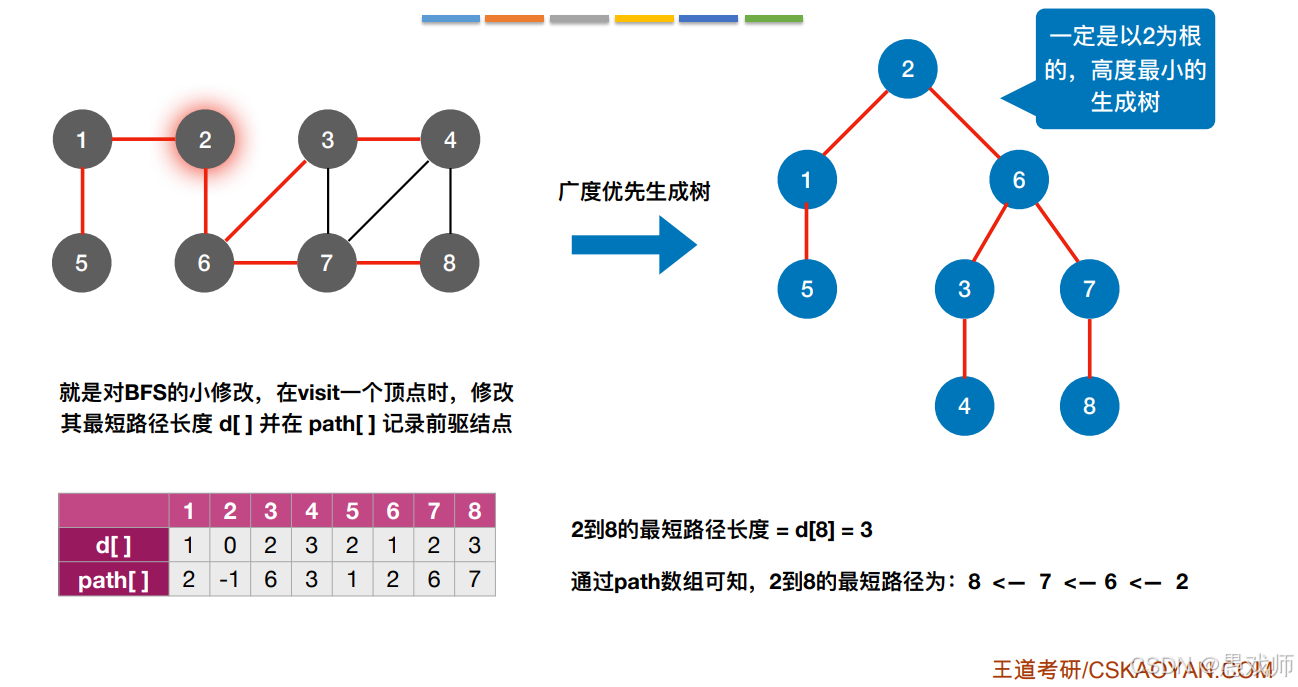
基础代码实现:
import java.util.*;public class BFSShortestPath {private List<List<Integer>> graph; // 邻接表存储图结构private int[] dist; // 存储源点到各顶点的最短距离private int[] parent; // 存储最短路径的前驱节点private boolean[] visited; // 访问标记数组public void bfsMinDistance(int start) {// 使用graph的大小(包含索引0)int n = graph.size();dist = new int[n];parent = new int[n];visited = new boolean[n];// 初始化Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);Arrays.fill(parent, -1);Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();dist[start] = 0;visited[start] = true;queue.offer(start);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int u = queue.poll();// 安全遍历(防止空指针)if (graph.get(u) != null) {for (int w : graph.get(u)) {if (!visited[w]) {dist[w] = dist[u] + 1;parent[w] = u;visited[w] = true;queue.offer(w);}}}}}// 重建最短路径public List<Integer> getPath(int target) {LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();for (int v = target; v != -1; v = parent[v]) {path.addFirst(v);}return path;}// 图初始化public static void main(String[] args) {BFSShortestPath bfs = new BFSShortestPath();int vertexCount = 8; // 顶点数量int arraySize = vertexCount + 1; // 数组大小=顶点数+1// 创建包含索引0~8的图(共9个位置)bfs.graph = new ArrayList<>(arraySize);for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {bfs.graph.add(new ArrayList<>());}// 添加图的边(索引1~8对应顶点1~8)bfs.graph.get(1).add(2); bfs.graph.get(2).add(1);bfs.graph.get(1).add(5); bfs.graph.get(5).add(1);bfs.graph.get(2).add(6); bfs.graph.get(6).add(2);bfs.graph.get(6).add(3); bfs.graph.get(3).add(6);bfs.graph.get(6).add(7); bfs.graph.get(7).add(6);bfs.graph.get(3).add(4); bfs.graph.get(4).add(3);bfs.graph.get(7).add(8); bfs.graph.get(8).add(7);bfs.bfsMinDistance(2); // 从顶点2(索引2)开始System.out.println("从2到8的最短距离: " + bfs.dist[8]);System.out.println("路径: " + bfs.getPath(8)); // [2, 6, 7, 8]}
}练习:1091. 二进制矩阵中的最短路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-in-binary-matrix/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-in-binary-matrix/
class Solution {//移动数组int[][] dir=new int[][]{{-1,1},{0,1},{1,1},{-1,0},{1,0},{-1,-1},{0,-1},{1,-1}};public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {//起始判断if(grid[0][0]==1)return -1;int n=grid.length;//路径距离int[][] dist=new int[n][n];//路径节点int[][][] path=new int[n][n][2];//标记数组boolean[][] visited=new boolean[n][n];//初始化for(int i=0;i<n;i++){Arrays.fill(dist[i],Integer.MAX_VALUE);}Deque<int[]> deque=new ArrayDeque<>();//起始节点入队deque.add(new int[]{0,0});visited[0][0]=true;dist[0][0]=1;path[0][0]=new int[]{-1,-1};while(!deque.isEmpty()){//出队int[] node=deque.poll();//处理int x=node[0],y=node[1];if(x==n-1 && y==n-1){PrintPath(grid,path);return dist[x][y];}//邻居入队for(int i=0;i<8;i++){int newx=x+dir[i][0];int newy=y+dir[i][1];//边界if(newx<0 || newx>=n || newy<0 || newy>=n)continue;//符合条件的邻居if(!visited[newx][newy] && grid[newx][newy]==0){deque.add(new int[]{newx,newy});dist[newx][newy]=dist[x][y]+1;visited[newx][newy]=true;path[newx][newy]=new int[]{x,y};}}}return -1;}//输出路径public void PrintPath(int[][] grid,int[][][] path){int n=grid.length;int x=path[n-1][n-1][0];int y=path[n-1][n-1][1];System.out.print("("+ (n-1) +", "+(n-1) +")"+"<-");while(x!=-1 && y!=-1){System.out.print("("+ x +", "+y +")"+"<-");int[] node=path[x][y];x=node[0];y=node[1];}}}为了更加直观,添加了路径打印
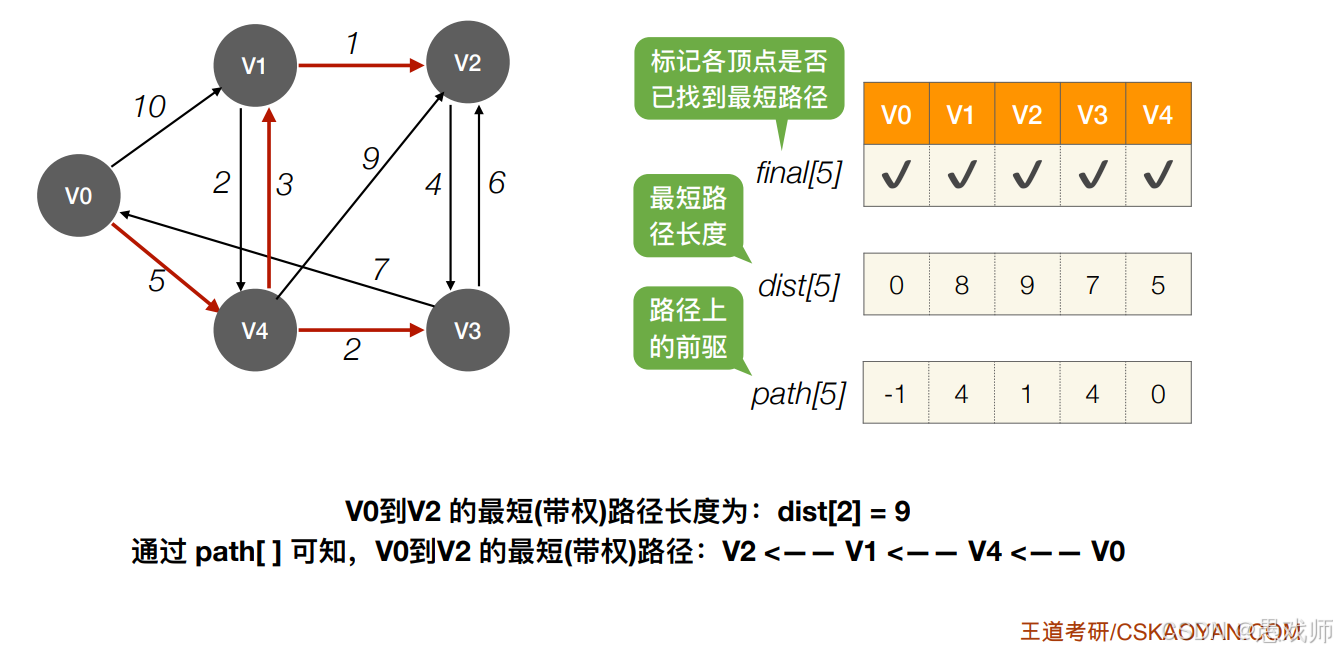
Dijkstra
重点理解更新过程与负权图的局限性
1. 初始化阶段
易错:漏掉不可达顶点的初始化
正确:dist[V] = ∞, path[V] = -1
难点:源点到自身(dist[V0]=0)和直接邻接点的处理
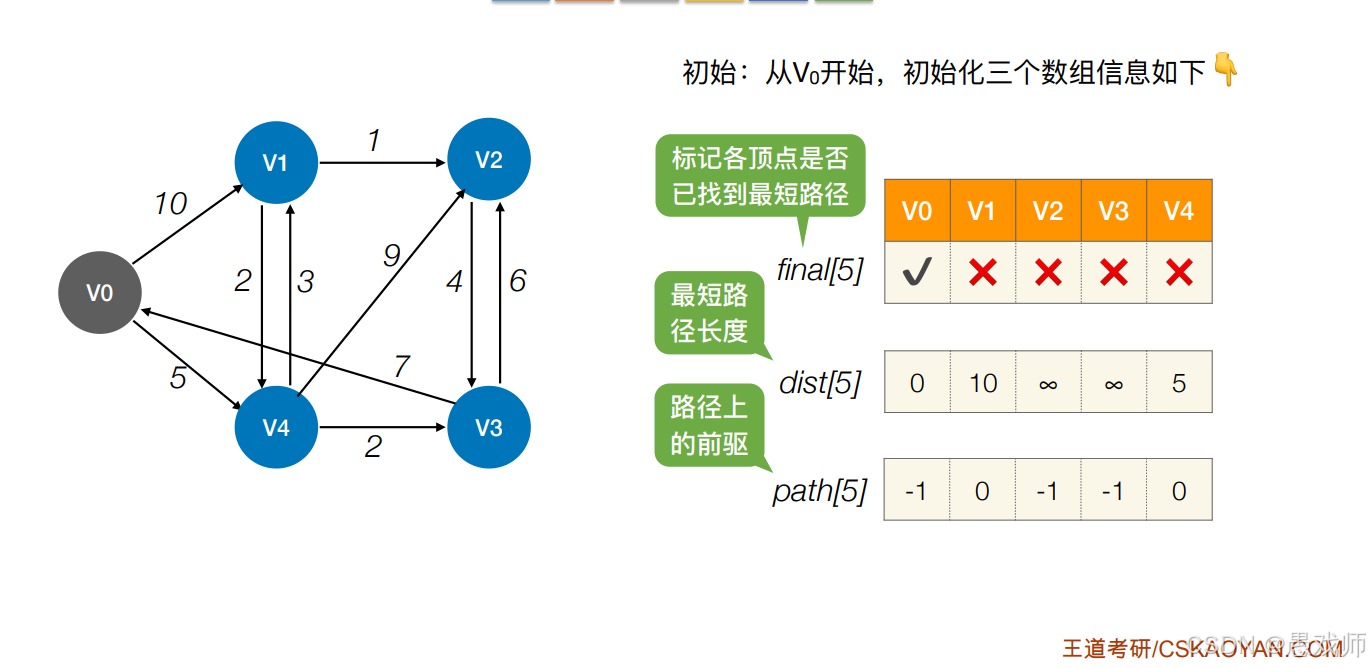
2. 顶点选择(每轮循环)
-
易错:选择已确定顶点(
final[i]=true的顶点不应再选) -
难点:当存在多个相同
dist值时,选择任意一个均可(需说明)
3. 更新邻接点
-
核心公式:
若 dist[i] + arcs[i][j] < dist[j],则更新 dist[j] 和 path[j] -
易错:
-
未检查
final[j]==false -
忽略不可达顶点(∞参与计算)
-
-
难点:理解"松弛操作"本质(通过新顶点缩短路径)
4. 负权图问题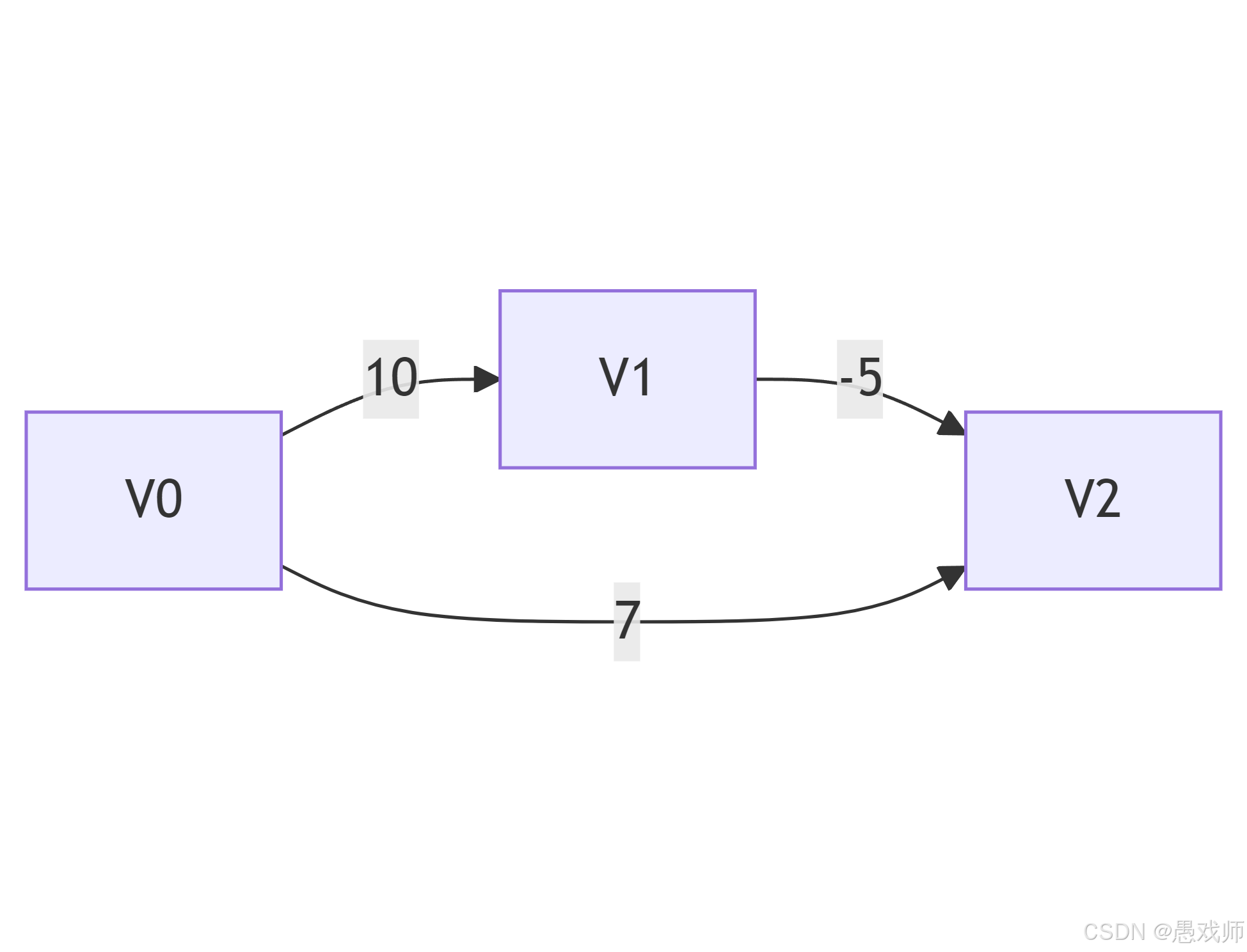
负权值的破坏性:
当存在负权边(如 V₁→V₂ 权值为 -5),已标记为 final=true的节点可能被更短路径推翻
算法路径:V₀→V₂(dist=7)
实际更优路径:V₀→V₁→V₂(10 + (-5) = 5)
但 V₂ 被提前标记为 final=true,导致无法更新:
import java.util.Arrays;public class DijkstraAlgorithm {// 使用邻接矩阵存储图(易错点1:需确保矩阵对称性)private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 表示无穷大public static void dijkstra(int[][] graph, int source) {int n = graph.length;int[] dist = new int[n]; // 最短路径长度数组int[] path = new int[n]; // 前驱节点数组(易错点2:需记录路径)boolean[] finalSet = new boolean[n]; // 已确定最短路径的顶点集// 初始化三个核心数组(关键点1)Arrays.fill(dist, INF);Arrays.fill(path, -1);dist[source] = 0; // 源点到自身距离为0// 主循环:执行n-1轮(关键点2)for (int count = 0; count < n - 1; count++) {// 步骤1:找当前dist最小的未确定节点int u = -1;int minDist = INF;for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {if (!finalSet[v] && dist[v] <= minDist) { // 易错点3:注意等号minDist = dist[v];u = v;}}if (u == -1) break; // 所有顶点已处理完finalSet[u] = true; // 标记为已确定// 步骤2:更新邻接点(关键点3)for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {// 易错点4:需同时检查4个条件if (!finalSet[v] &&graph[u][v] != INF &&dist[u] != INF &&dist[u] + graph[u][v] < dist[v]) {dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v];path[v] = u; // 记录前驱节点}}}// 打印结果(示例)printSolution(dist, path, source);}private static void printSolution(int[] dist, int[] path, int source) {System.out.println("源点: " + source);System.out.println("顶点\t距离\t路径");for (int i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t", i, dist[i]);printPath(path, i);System.out.println();}}// 递归打印路径(关键点4)private static void printPath(int[] path, int current) {if (current == -1) return;printPath(path, path[current]);System.out.print(current + " ");}public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] graph = {{0, 10, INF, INF, 5},{INF, 0, 1, INF, 2},{INF, INF, 0, 4, INF},{7, INF, 6, 0, INF},{INF, 3, 9, 2, 0}};dijkstra(graph, 0);}
}练习:
743. 网络延迟时间 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
class Solution {public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {//异常判断if(times.length==0 || times==null || k>n)return -1;//构建图int[][] g=new int[n][n];final int INF =Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){Arrays.fill(g[i],INF);//g[x][y]==INF 无边}for(int[] t:times){int x=t[0]-1,y=t[1]-1;g[x][y]=t[2];}//初始化boolean[] used=new boolean[n];//used[x]==true 存在x到源点最短距离int[] dist=new int[n];//dist[x] 源点到x最短距离Arrays.fill(dist,INF);dist[k-1]=0;int[] path=new int[n];Arrays.fill(path,-1);//计算其他n-1个节点的distfor(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){//找最短距离的邻居(第一轮是初始节点)int u=-1;for(int v=0;v<n;v++){if(!used[v] && (u==-1 || dist[v]<dist[u]))u=v;}used[u]=true;//更新distfor(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(!used[j] && g[u][j]!=INF & dist[u]!=INF && dist[u]+g[u][j]<dist[j]){dist[j]=dist[u]+g[u][j];path[j]=u;}}}//直观演示// Print(path,dist,k-1);int ans=Arrays.stream(dist).max().getAsInt();return ans==INF? -1:ans;}public void Print(int[] path,int[] dist,int source){System.out.println("源点: " + source);System.out.println("顶点\t距离\t路径");for (int i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t", i, dist[i]);printPath(path, i);System.out.println();}}public void printPath(int[] path,int curr){if(curr==-1)return ;printPath(path,path[curr]);System.out.print(curr+"->");}
}Floyd
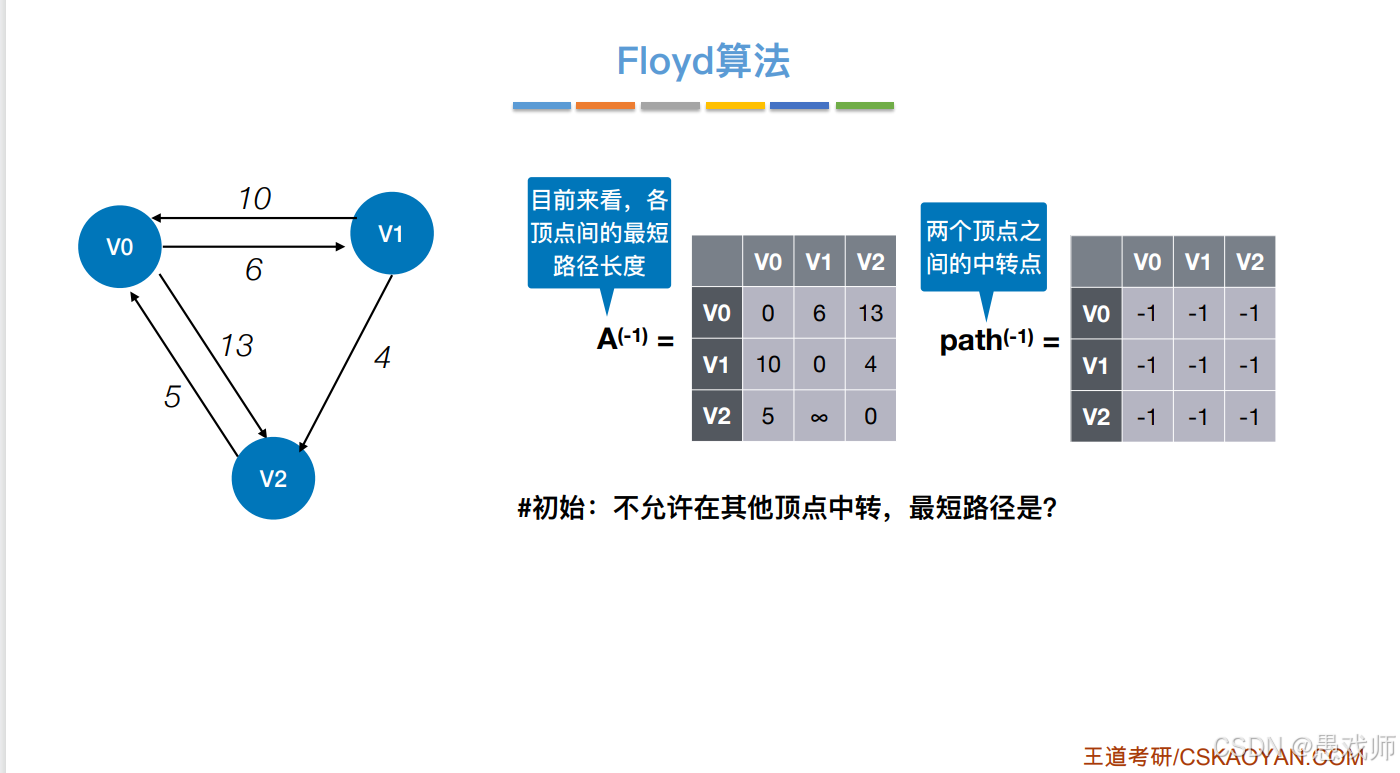
1、算法思想(建立直观理解)
通过逐步增加中转点,动态更新所有顶点之间的最短路径。
初始化:假设一张地图有多个城市(顶点),先记录所有城市间直达的路径长度(没有直达记为无穷大)。
动态中转:逐个考虑每个城市作为中转站(比如先允许通过城市A中转,再允许通过A和B中转,以此类推)。
检查优化:对于每一对城市(比如X到Y),检查如果从X先到中转站K,再从K到Y,总距离是否比当前已知的X到Y路径更短。
如果更短:更新X到Y的最短路径为 X->K->Y 的路径,并记录这个中转站K;否则:保持原有路径。
完成:当所有城市都作为中转站被考虑过后,最终得到任意两城市间的最短路径。
想象你要为所有城市之间规划最短快递路线。Floyd的做法是:
-
第一轮:只允许快递从起点直达终点。
-
第二轮:允许快递在城市A中转一次(比如
上海->A->广州可能比上海->广州更快)。 -
第三轮:允许在城市A和B中转,依此类推...
直到所有城市都可作为中转站,最终得到全局最优路线。
关键:
-
能处理任意两点间的最短路径(单源/多源都适用)。
-
支持带权图(包括负权边,但不能有负权环路)。
-
本质是动态规划,通过三重循环实现(外层控制中转点)。
可以去看看这个博主的讲解,很直观:
图-最短路径-Floyd(弗洛伊德)算法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili![]() https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19k4y1Q7Gj?spm_id_from=333.788.videopod.sections&vd_source=4b89f462036a892baf8931104a1f36b1
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19k4y1Q7Gj?spm_id_from=333.788.videopod.sections&vd_source=4b89f462036a892baf8931104a1f36b1
注意:视频的path数组初始化和本文所采用的初始化方式不同(本文参考王道教材),但大体算法思路一致,可以参考。
算法演示:
Floyd-Warshall All-Pairs Shortest Path![]() https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Floyd.html
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Floyd.html
2、代码实现·明确易错点和难点
距离矩阵 dist
定义与初始化
int[][] dist = new int[n][n];-
含义:
dist[i][j]表示从顶点i到顶点j的当前已知最短路径长度 -
初始化:
-
如果
i == j,则dist[i][j] = 0(顶点到自身距离为0) -
如果存在边
i→j,则dist[i][j] = weight(i, j)(边的权重) -
如果不存在边
i→j,则dist[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE(表示无穷大)
-
更新原理(动态规划核心)
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}-
物理意义:检查通过中间点
k的路径是否比当前路径更短 -
状态转移方程:
-
动态规划思想:当考虑允许通过顶点
k中转时,更新所有i→j的路径
路径矩阵 path
定义与初始化
int[][] path = new int[n][n];-
含义:
path[i][j]记录从i到j的最短路径上的第一个中转点 -
初始化:
-
path[i][j] = -1表示没有中转点(直接相连) -
path[i][j] = k表示路径i→j需要经过中转点k
-
更新原理
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {path[i][j] = k; // 记录中转点
}-
关键点:当发现通过
k中转的路径更短时,记录这个关键中转点 -
路径重建原理:路径信息是递归存储的:
-
要获取
i→j的完整路径,需要:-
找到
path[i][j] = k -
递归查找
i→k的路径 -
递归查找
k→j的路径
-
-
路径重建算法
void printPath(int i, int j, int[][] path) {if (path[i][j] == -1) {System.out.print(j + " "); // 直接连接return;}int k = path[i][j];printPath(i, k, path); // 前半段路径printPath(k, j, path); // 后半段路径
}import java.util.Arrays;public class FloydAlgorithm {public static void floyd(int[][] graph) {int n = graph.length;// 初始化距离矩阵(存储最短路径长度)int[][] dist = new int[n][n];// 初始化路径矩阵(存储中转点)int[][] path = new int[n][n];// 易错点1:正确初始化矩阵for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {dist[i][j] = graph[i][j]; // 复制原始图// 难点1:路径矩阵初始化// -1表示没有中转点(直接相连)path[i][j] = -1;}}// 核心三重循环// 易错点2:循环顺序必须是k->i->jfor (int k = 0; k < n; k++) { // 考虑每个顶点作为中转点for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 遍历所有起点// 难点2:跳过无效路径提升性能if (dist[i][k] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) continue;for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { // 遍历所有终点// 跳过不可达路径if (dist[k][j] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) continue;// 发现更短路径// 易错点3:避免整数溢出long newDist = (long) dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];if (newDist < dist[i][j]) {dist[i][j] = (int) newDist;path[i][j] = k; // 记录中转点}}}}// 打印最终结果printSolution(dist, path);}// 递归打印路径(难点3:路径回溯)private static void printPath(int[][] path, int i, int j) {if (path[i][j] == -1) {System.out.print(" → " + j);return;}printPath(path, i, path[i][j]); // 前半段路径printPath(path, path[i][j], j); // 后半段路径}private static void printSolution(int[][] dist, int[][] path) {int n = dist.length;System.out.println("距离矩阵:");for (int[] row : dist) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));}System.out.println("\n路径矩阵:");for (int[] row : path) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));}System.out.println("\n详细路径:");for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (i != j && dist[i][j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {System.out.print(i + "→" + j + ": " + i);printPath(path, i, j);System.out.println(" (长度: " + dist[i][j] + ")");}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 示例图(使用MAX_VALUE表示无穷大)int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int[][] graph = {{0, 6, 13},{10, 0, 4},{5, INF, 0}};floyd(graph);}
}3、练习1334. 阈值距离内邻居最少的城市 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-city-with-the-smallest-number-of-neighbors-at-a-threshold-distance/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-city-with-the-smallest-number-of-neighbors-at-a-threshold-distance/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china
class Solution {public int findTheCity(int n, int[][] edges, int distanceThreshold) {//极端条件if(edges==null || edges.length==0)return 0;int INF=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;//构建图int[][] g=new int[n][n];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){Arrays.fill(g[i],INF);}for(int[] e:edges){int x=e[0],y=e[1];g[x][y]=e[2];g[y][x]=e[2];//无向图}//距离数组int[][] dist=new int[n][n];//路径数组·存中转点int[][] path=new int[n][n];//初始化for(int i=0;i<n;i++){Arrays.fill(path[i],-1);}for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(i==j)dist[i][j]=0;else dist[i][j]=g[i][j];}}//floy流程for(int i=0;i<n;i++){//中转点for(int s=0;s<n;s++){//源点if(dist[s][i]==INF)continue;//源点无法到达中转点for(int e=0;e<n;e++){//终点if(dist[i][e]==INF)continue;//中转点无法到达终点//更新dist与path·发现通过中转点有更小的路径就更新int curr=dist[s][i]+dist[i][e];if(curr<dist[s][e]){dist[s][e]=curr;path[s][e]=i;}}}}//结果int max_index=-1;int min_city=INF/2;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int count=0;for(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(dist[i][j]<=distanceThreshold)count++;}if(count<=min_city){min_city=count;max_index=i;//i是递增的}}// printSolution(dist,path);//可视化return max_index;}// 递归打印路径private static void printPath(int[][] path, int i, int j) {if (path[i][j] == -1) {System.out.print(" → " + j);return;}printPath(path, i, path[i][j]); // 前半段路径printPath(path, path[i][j], j); // 后半段路径}private static void printSolution(int[][] dist, int[][] path) {int n = dist.length;System.out.println("距离矩阵:");for (int[] row : dist) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));}System.out.println("\n路径矩阵:");for (int[] row : path) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));}System.out.println("\n详细路径:");for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (i != j && dist[i][j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {System.out.print(i + "→" + j + ": " + i);printPath(path, i, j);System.out.println(" (长度: " + dist[i][j] + ")");}}}}
}4、细节处理
无穷大(∞)的处理
代码中需用足够大的数表示∞,注意避免运算溢出。
Floyd与Dijkstra的区别?
Floyd:解决所有顶点对最短路径,支持负权边,时间复杂度O(|V|³)。
Dijkstra:解决单源最短路径,不支持负权边,时间复杂度O(|V|²)。
为何Floyd能处理负权边,但不支持负权回路?
负权边可通过中转优化路径。
负权回路导致路径长度无限降低,无确定最短路径。
如何用Floyd检测负权回路?
检查最终距离矩阵A的对角线:若存在A[i][i] < 0,则顶点i在负权回路中。
空间复杂度优化?
使用单个矩阵滚动更新(无需保留所有阶段矩阵),空间复杂度O(|V|²)。






——SDRAM回环测试)




JVM(一))







