四、Mapper 的动态代理
1. 引入
在上面的 CURD 例子中,我们发现:Dao 层的实现类的每一个方法仅仅是通过 SqlSession 对象的相关 API 定位到映射文件 mapper 中的 SQL 语句,真正对数据库操作的工作实际上是有 Mybatis 框架通过 mapper 中的 SQL 语句完成的,所以 Dao 层的实现类并没有做什么实质性的工作,所以,Mybatis 就可以抛开 Dao 层实现类,直接定位到 mapper 中的 SQL 语句来操作数据库,这种 Dao 层实现类的实现方式称为 Mapper 动态代理,即使用动态代理对象替换掉原来的 Dao 层实现类。
2. Mapper 动态代理特点
Mapper 动态代理方式不需要程序员去实现 Dao 层接口,接口的实现由 Mybatis 结合映射文件自动生成动态代理对象来实现的。
3. 要实现 mapper 的动态代理,需要满足如下条件:
(1) 映射文件 mapper 需要和 Dao 层接口在同一个包下面: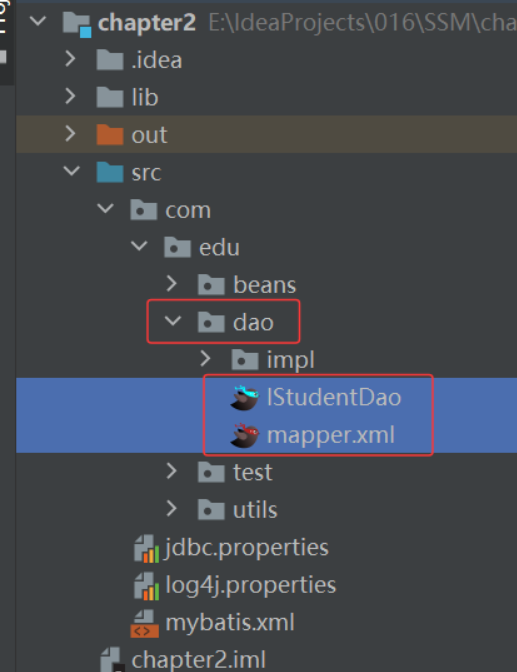
(2) 映射文件的名称需要和 Dao 层接口的名称相同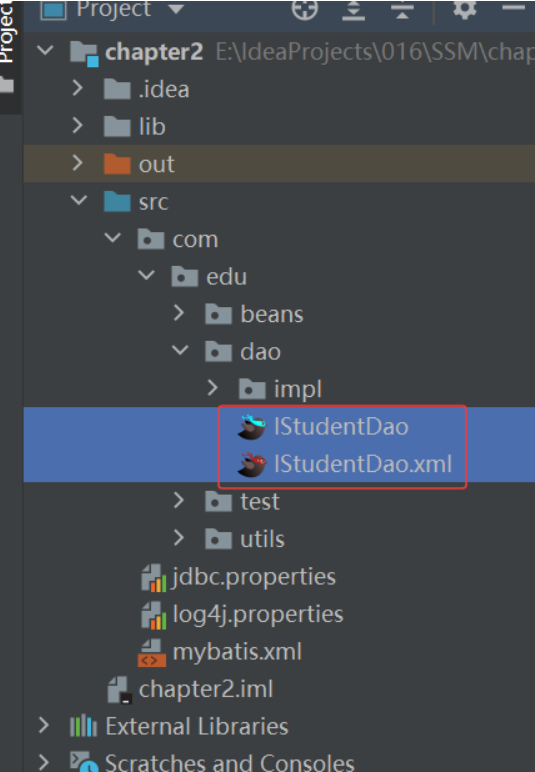
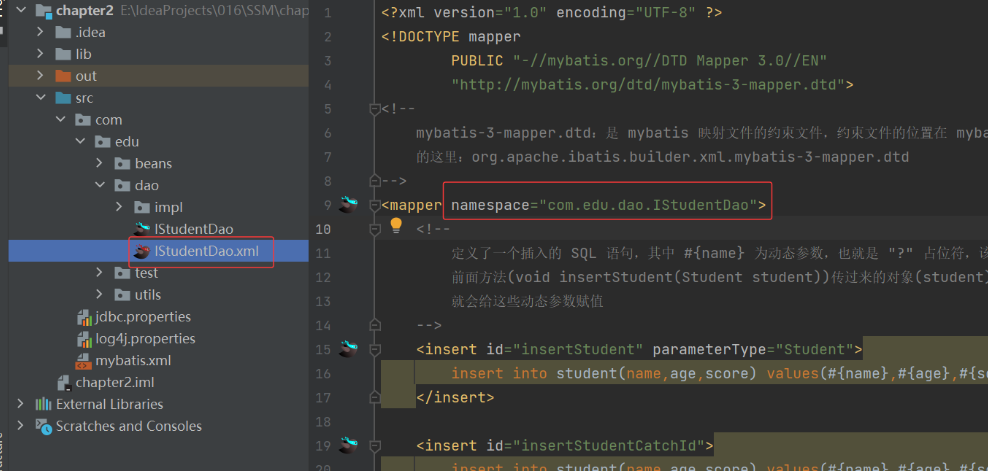
(3) 映射文件 mapper 中的 namespace 的名称必须是 Dao 层接口的全类名
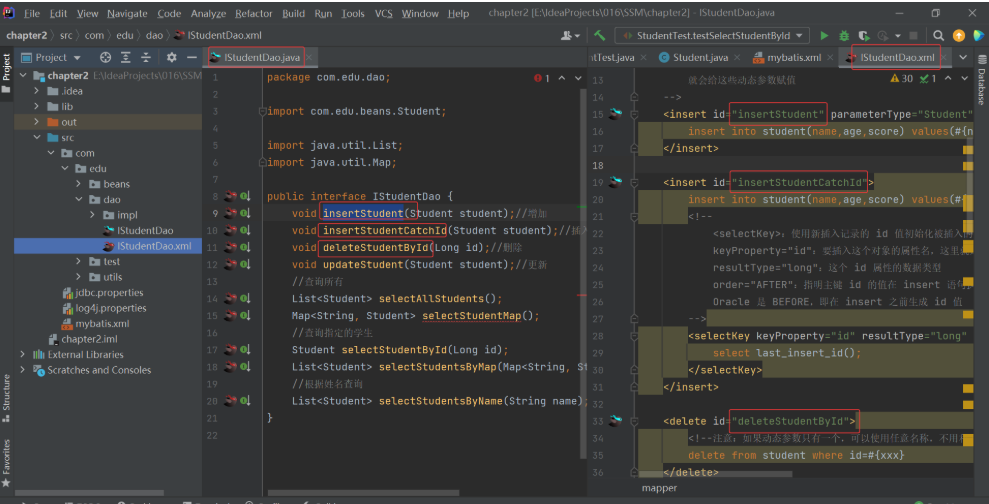
(4) 映射文件 mapper 中的 SQL 语句的 id 名称需要和 Dao 层接口的方法名相同:
(5) 删除 Dao 层的实现类
(6) 删除 Dao 层接口的 selectStudentMap() 方法以及映射文件配置,因为 Mapper 动态代理不支持 map 查询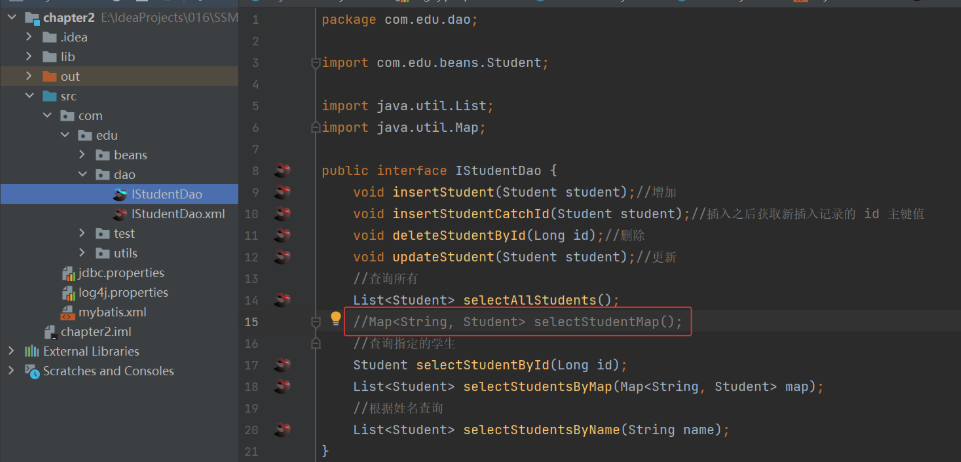
(7) 修改主配置文件 mybatis.xml 中引入 mapper 映射文件的方式:
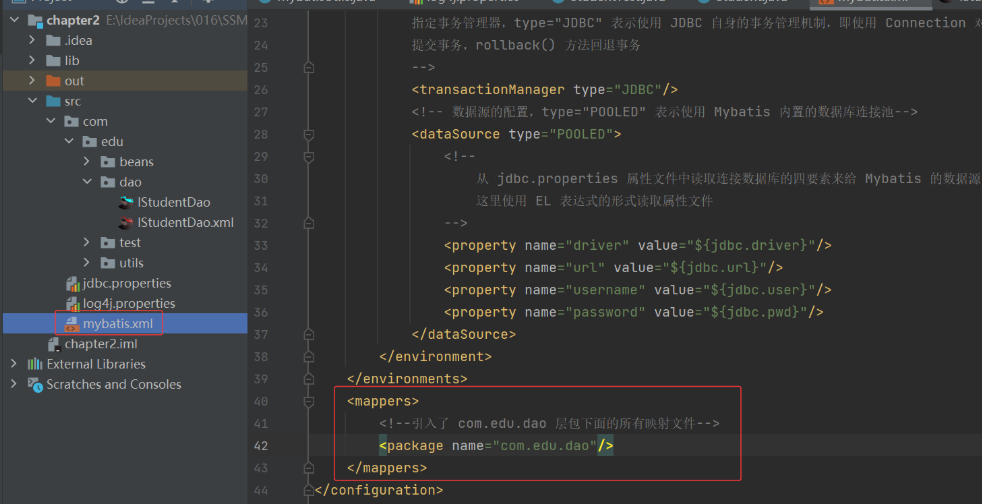
(8) 将 Student 的 tscore 属性改过来,mapper 也要改
Student.java:
package com.edu.beans;
public class Student {
private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public Student(long id, String name, int age, double score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
IStudentDao.xml 映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IStudentDao">
<!--
定义了一个插入的 SQL 语句,其中 #{name} 为动态参数,也就是 "?" 占位符,该动态参数的名称要和
前面方法(void insertStudent(Student student))传过来的对象(student)的属性同名,这样 student 对象的属性值
就会给这些动态参数赋值
-->
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
insert into student(name,age,score) values(#{name},#{age},#{score})
</insert>
<insert id="insertStudentCatchId">
insert into student(name,age,score) values(#{name},#{age},#{score})
<!--
<selectKey>:使用新插入记录的 id 值初始化被插入的对象,即初始化方法参数 student,它的属性有:
keyProperty="id":要插入这个对象的属性名,这里就是指给方法参数 Student 的 id 属性赋值
resultType="long":这个 id 属性的数据类型
order="AFTER":指明主键 id 的值在 insert 语句执行时的生成时机,MySQL 是 AFTER,即在 insert 之后生成 id 值,
Oracle 是 BEFORE,即在 insert 之前生成 id 值
-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="long" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id();
</selectKey>
</insert>
<delete id="deleteStudentById">
<!--注意:如果动态参数只有一个,可以使用任意名称,不用和方法参数同名,例如这里的 #{xxx} 而不是 #{id}-->
delete from student where id=#{xxx}
</delete>
<update id="updateStudent">
<!--这里除了 #{id} 是旧值,其他都是新值-->
update student set name=#{name},age=#{age},score=#{score} where id=#{id}
</update>
<!--
resultType="Student":将返回结果集中的每一条记录封装成 Student 类型,这里要给出全类名,我们已经在主配置文件配置了
别名,就可以写别名
-->
<select id="selectAllStudents" resultType="Student">
select * from student
</select>
<!--
<resultMap>:完成表字段到 JavaBean 属性的映射,从而可以将查询结果封装成 JavaBean 对象,它的属性:
id="studentMap":resultMap 的 id 名称
type="Student":查询记录封装成的 JavaBean 类型
-->
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="Student">
<!--完成表字段到 JavaBean 属性的映射-->
<!--<id>表示主键字段,column="id"是表的字段名,property="id"是 JavaBean 的属性名-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!--其他的非主键字段的映射使用 <result> 标签-->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<result column="score" property="score"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentById" resultMap="studentMap">
select id,name,age,score from student where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<select id="selectStudentsByMap" resultType="Student">
select * from student where name=#{map.name} and age = #{map.age}
</select>
<!-- <select id="selectStudentsByName" resultType="Student">
select * from student where name like concat('%',#{xxx},'%')
</select>-->
<select id="selectStudentsByName" resultType="Student">
<!--注意:'%' 和 #{xxx} 之间有一个空格-->
select * from student where name like '%' #{xxx} '%'
</select>
</mapper>
(9) 在测试类 StudentTest 中通过 SqlSession 的 getMapper() 方法获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象来测试
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import com.edu.dao.IStudentDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class StudentTest {
private SqlSession session;
private IStudentDao studentDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
studentDao = session.getMapper(IStudentDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test //被 @Test 注解的方法为测试方法,可以有多个这样的方法
public void testInsertStudent(){
studentDao.insertStudent(new Student("张三",21,98.5));
session.commit();//动态代理对象只会根据映射文件中的 SQL 标签去执行 SQL 语句,并不会提交事务,需要我们自己提交
}
@Test
public void testInsertStudentCatchId(){
Student student = new Student("王五",21,98.5);
System.out.println("插入数据前,student=" + student);
studentDao.insertStudentCatchId(student);
System.out.println("插入数据后,student=" + student);
session.commit();//动态代理对象只会根据映射文件中的 SQL 标签去执行 SQL 语句,并不会提交事务,需要我们自己提交
}
@Test
public void testDeleteStudentById(){
studentDao.deleteStudentById(4L);
session.commit();//动态代理对象只会根据映射文件中的 SQL 标签去执行 SQL 语句,并不会提交事务,需要我们自己提交
}
@Test
public void testUpdateStudent(){
Student student = new Student(3,"小王",21,98.5);
studentDao.updateStudent(student);
session.commit();//动态代理对象只会根据映射文件中的 SQL 标签去执行 SQL 语句,并不会提交事务,需要我们自己提交
}
@Test
public void testSelectAllStudents(){
List<Student> students = studentDao.selectAllStudents();
for (Student student :
students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById(){
Student student = studentDao.selectStudentById(3L);
System.out.println(student);
}
@Test
public void testSelectStudentsByMap(){
Map<String,Student> map = new HashMap<>();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("晓晓");
student.setAge(21);
map.put("map", student);
List<Student> students = studentDao.selectStudentsByMap(map);
for (Student stu :
students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectStudentsByName(){
List<Student> students = studentDao.selectStudentsByName("晓");
for (Student student :
students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
然后我们在获取动态代理对象处打一个断点,以调试方式执行: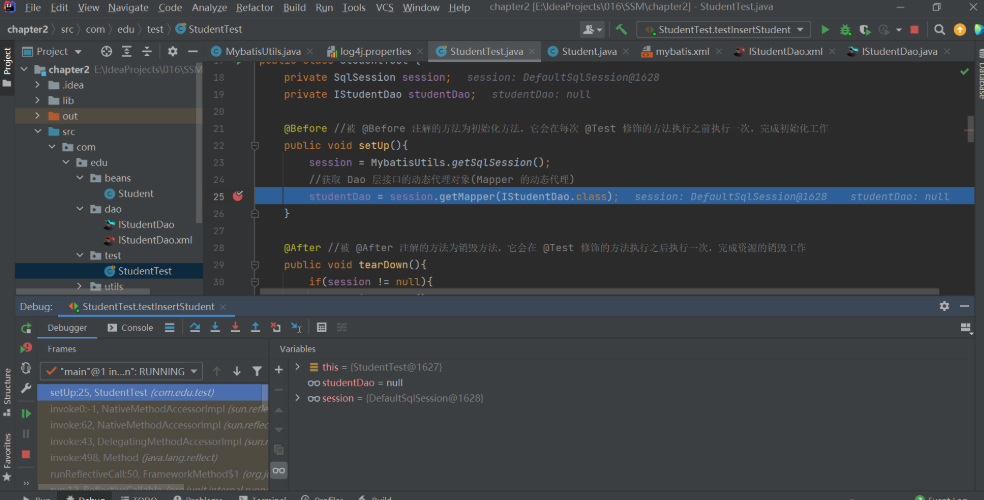
然后我们往下走一步,查看:
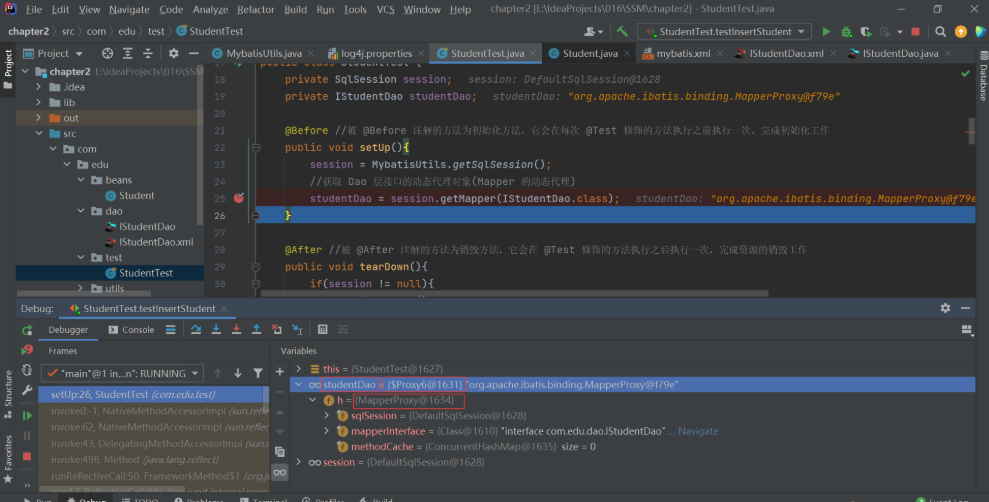
可以看到生成的 studentDao 是一个代理对象。
然后我们重新来调试执行一次,我们跟进到 getMapper() 方法中,不断跟进去:
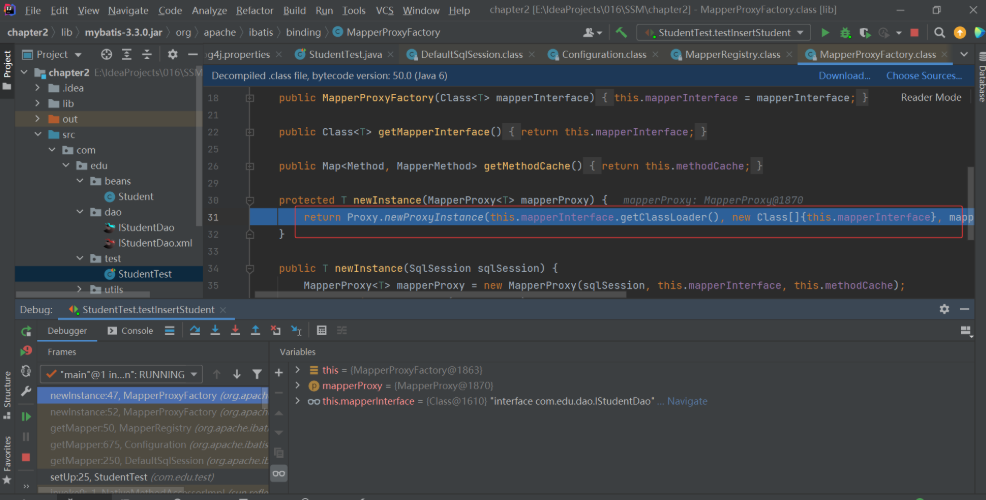
可以看到,Mybatis 的 Mapper 动态代理使用的就是 JDK 的动态代理来创建代理对象的。
五、动态 SQL
1. 动态 SQL
主要用于解决查询条件不确定的情况,在程序运行期间,根据用户提交的查询条件进行查询,提交的条件不同,执行的 SQL 也不同,若将每个不同条件逐一列出,在进行排列组合,将会出现大量的 SQL 语句,我们可以使用动态 SQL 来解决这样的问题。
2. 动态 SQL 的示例
3. 动态 SQL 概述
动态 SQL,即通过 Mybatis 提供的各种标签对条件做出判断以实现动态拼接 SQL 语句, 常用的动态 SQL 标签有<if>、<where>、<choose>、<foreach>等等,有意思的是,这些动态 SQL 标签和 JSTL 语法非常相似。
4. 开发步骤
(1) 准备数据库表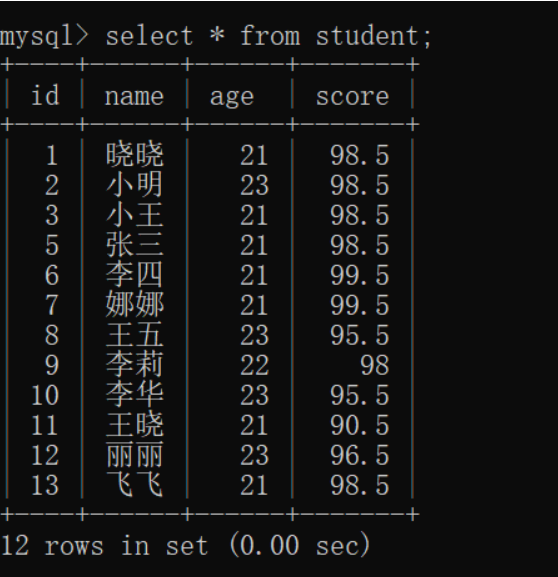
(2) 定义实体类
package com.edu.beans;
public class Student {
private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public Student(long id, String name, int age, double score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
(3) 测试类:
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.dao.IStudentDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class DynamicSQLTest {
private SqlSession session;
private IStudentDao studentDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
studentDao = session.getMapper(IStudentDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
}
5. <if> 标签
该标签中的 test 属性为 true 时,他会将它包含的 SQL 片段拼接在其所在 SQL 语句中
示例:查询满足动态条件的学生信息:
(1) 修改 Dao 层接口
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
}
(2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml 映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IStudentDao">
<select id="selectStudentIf" resultType="Student">
<!--这里的 where 1=1 是为了保证如果后面的 if 语句不满足,前面的 SQL 语句也是一条有效的语句,if 条件满足,也是一条有效的语句-->
select id,name,age,score from student where 1=1
<!--如果传过来的 name 属性不为 null,且不是空字符串,那么就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</if>
<!--如果传过来的 age > 0,就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="age > 0">
and age > #{age}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
(3) 测试类 DynamicSQLTest
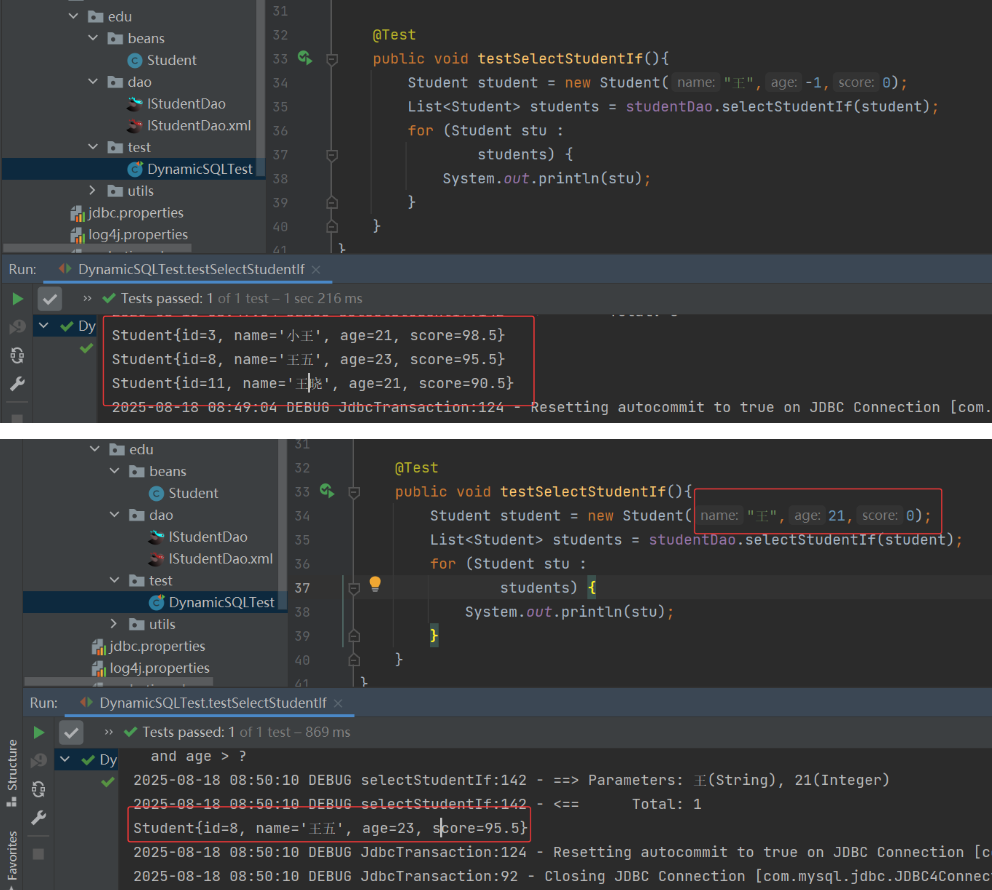
6. <where>标签
<if> 标签有个比较麻烦的地方,就是必须使用 where 1=1 子句,因为若 where 条件后<if> 都不满足,需要 where 1=1 来保证前面的 SQL 语句是一个有效的语句,当然,<if>满足时, where 1=1 也能保证拼接后的 SQL 语句是有效语句。使用<where>标签,在有条件的时候,会自动添加 where 子句,没有条件的时候,不会添加 where 子句
(1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
}
(2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml 映射文件
<select id="selectStudentWhere" resultType="Student">
<!--这里的 where 1=1 是为了保证如果后面的 if 语句不满足,前面的 SQL 语句也是一条有效的语句,if 条件满足,也是一条有效的语句-->
select id,name,age,score from student
<!--如果下面的 <if> 语句都不满足条件,则不会条件 where 子句,如果有一个 <if> 条件满足,就会添加 where 子句-->
<where>
<!--如果传过来的 name 属性不为 null,且不是空字符串,那么就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
<!--第一个 <if> 语句可以省略 and,但是其他的 <if> 语句必须加上 and-->
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</if>
<!--如果传过来的 age > 0,就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="age > 0">
<!--其他 <if> 语句的 and 不能省略-->
and age > #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(3) 测试类 DynamicSQLTest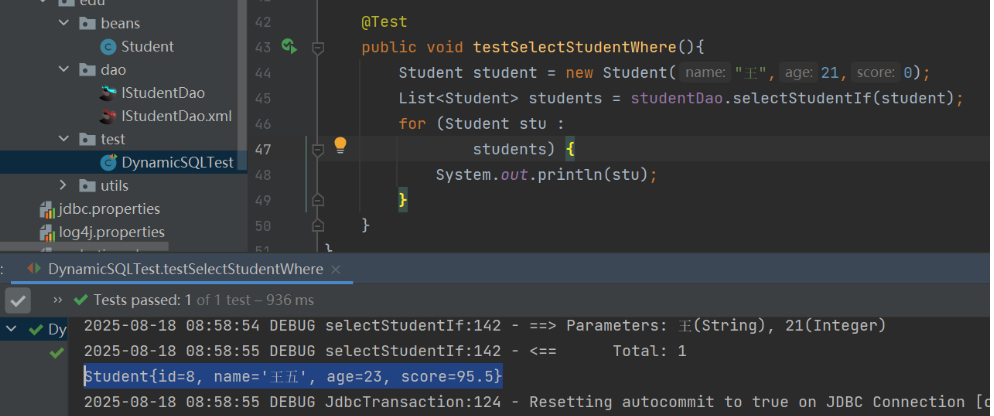
7. <choose>...<when>...<otherwise>:类似于switch...case
对于 <choose> 标签,会从第一个 <when> 开始逐个向后进行条件判断,若某个 <when> 的 test 属性值为 true 的情况,则拼接其 SQL 片段,然后直接结束 <choose> 标签,其他的不执行 <when>,直到所有的 <when> 都不满足时,执行 <otherwise>。
(1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
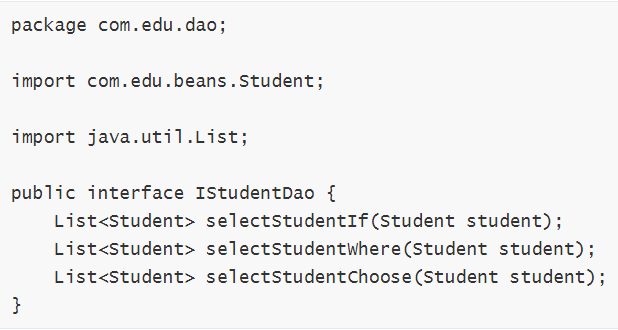
(2) 修改StudentDao.xml:

(3) 测试类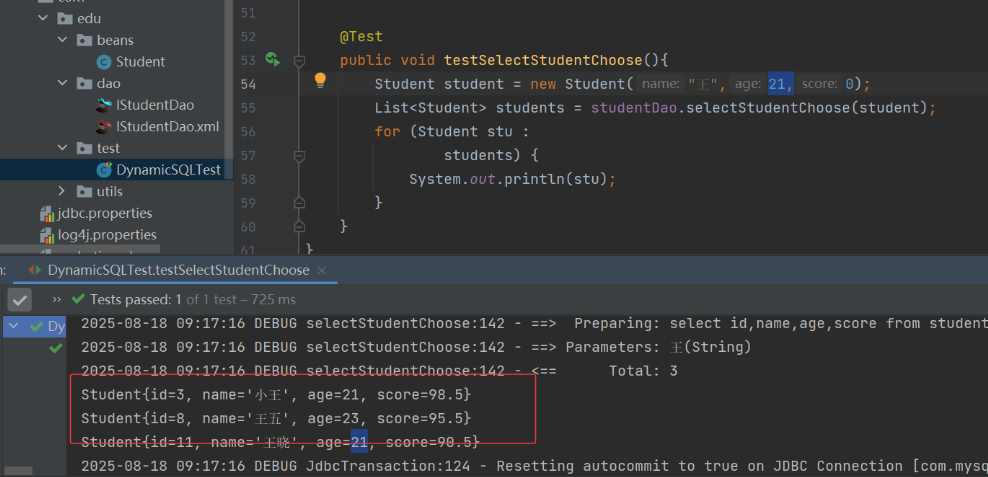
从上可知,“王”的姓名满足第一个 <when> 之后,就不会去判断第一个 age 的 <when>。
8. <foreach> 标签:遍历集合
(1) 遍历数组
1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentChoose(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachArray(Object[] studentIds);
}
2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml
<select id="selectStudentForEachArray" resultType="Student">
select id,name,age,score from student
<!--
这里的 array 是指接口方法传过来的参数是一个数组,而且这里只是使用 array 这个名字,不能是其他名称,
array.length 表示数组的长度
-->
<if test="array != null and array.length > 0">
where id in
<!--
collection:待遍历的集合,这里是数组,统一写成 array
open:遍历项放入的地方,这里以"("开始
item:每一个遍历项
separator:每个遍历项之间以","分割
close:遍历项放入的地方,这里以")"结束
最终遍历出来得到的 SQL 语句形式如下:select id,name,age,score from student where id in (2,3,4)
-->
<foreach collection="array" open="(" item="myid" separator="," close=")">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
3) 测试类
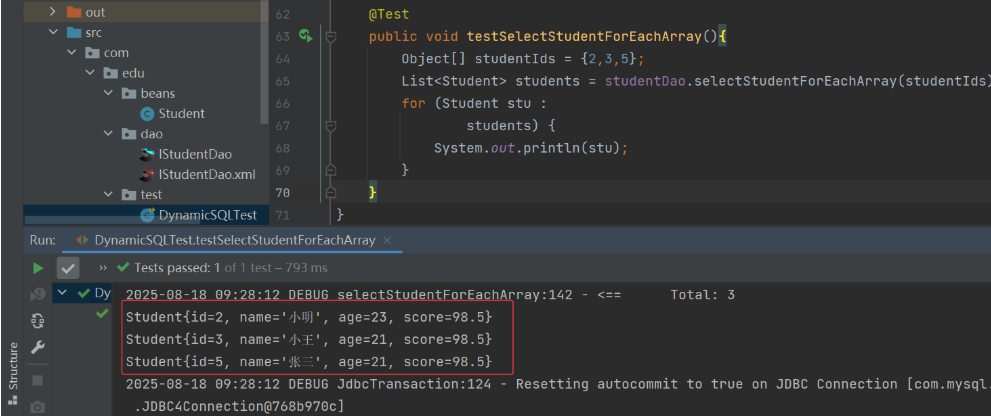
(2) 遍历泛型为基本类型的 List
1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentChoose(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachArray(Object[] studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList(List<Integer> studentIds);
}
2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml
<select id="selectStudentForEachList" resultType="Student">
select id,name,age,score from student
<!--
这里的 list 是指接口方法传过来的参数是一个 List,而且这里只是使用 list 这个名字,不能是其他名称,
list.size 表示集合的大小
-->
<if test="list != null and list.size > 0">
where id in
<!--
collection:待遍历的集合,这里是List,统一写成 list
open:遍历项放入的地方,这里以"("开始
item:每一个遍历项
separator:每个遍历项之间以","分割
close:遍历项放入的地方,这里以")"结束
最终遍历出来得到的 SQL 语句形式如下:select id,name,age,score from student where id in (2,3,5)
-->
<foreach collection="list" open="(" item="myid" separator="," close=")">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
3) 测试类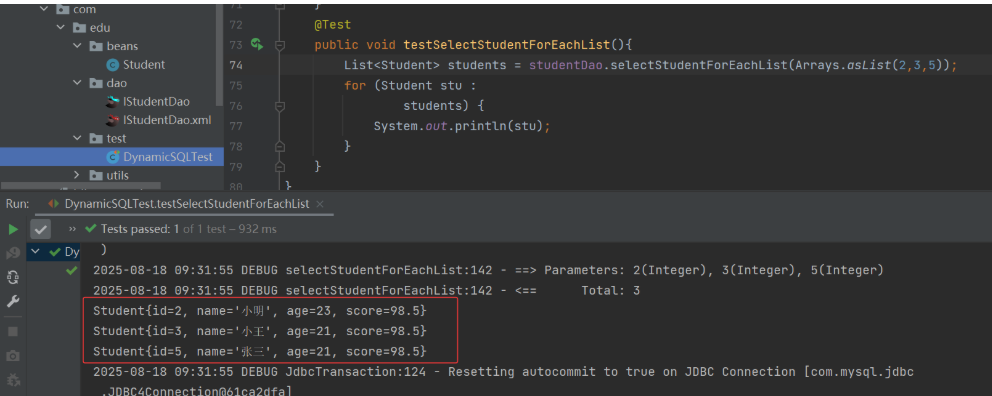
(3) 遍历泛型为自定义类型的 List
1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentChoose(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachArray(Object[] studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList(List<Integer> studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList2(List<Student> students);
}
2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml
<select id="selectStudentForEachList2" resultType="Student">
select id,name,age,score from student
<!--
这里的 list 是指接口方法传过来的参数是一个 List,而且这里只是使用 list 这个名字,不能是其他名称,
list.size 表示集合的大小
-->
<if test="list != null and list.size > 0">
where id in
<!--
collection:待遍历的集合,这里是List,统一写成 list
open:遍历项放入的地方,这里以"("开始
item:每一个遍历项
separator:每个遍历项之间以","分割
close:遍历项放入的地方,这里以")"结束
最终遍历出来得到的 SQL 语句形式如下:select id,name,age,score from student where id in (2,3,5)
-->
<foreach collection="list" open="(" item="student" separator="," close=")">
#{student.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
3) 测试类
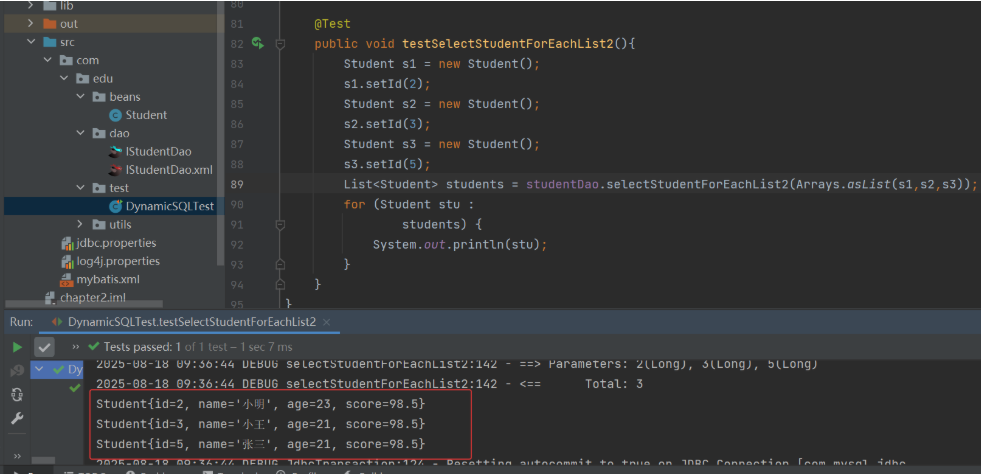
9. <sql> 标签
<sql> 标签可以用来定义一个 SQL 片段,以便复用,其他地方要用到的时候,通过 <include> 标签引入即可:
(1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentChoose(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachArray(Object[] studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList(List<Integer> studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList2(List<Student> students);
List<Student> selectStudentBySQL(Student student);
}
(2) 修改 IStudentDao.xml
<sql id="selectHead">
select id,name,age,score from student
</sql>
<select id="selectStudentBySQL" resultType="Student">
<include refid="selectHead"/>
<!--如果下面的 <if> 语句都不满足条件,则不会条件 where 子句,如果有一个 <if> 条件满足,就会添加 where 子句-->
<where>
<!--如果传过来的 name 属性不为 null,且不是空字符串,那么就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
<!--第一个 <if> 语句可以省略 and,但是其他的 <if> 语句必须加上 and-->
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</if>
<!--如果传过来的 age > 0,就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<if test="age > 0">
<!--其他 <if> 语句的 and 不能省略-->
and age > #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(3) 测试类:
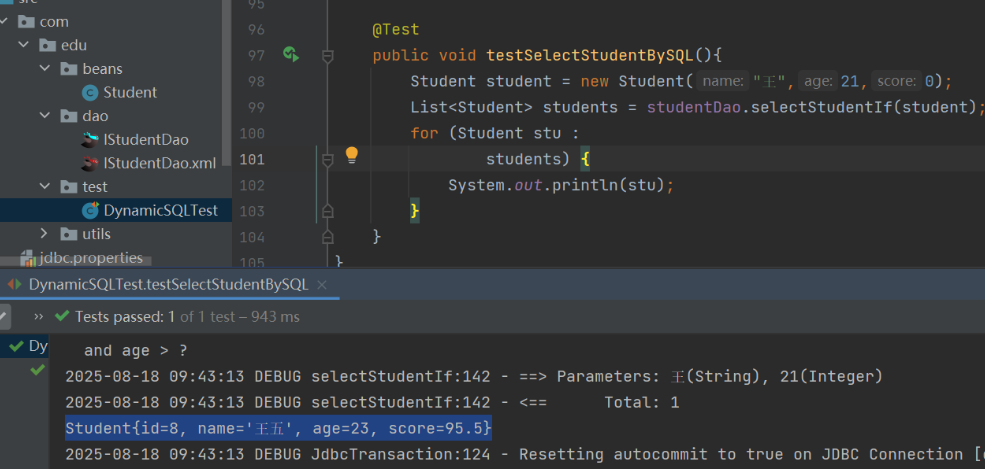
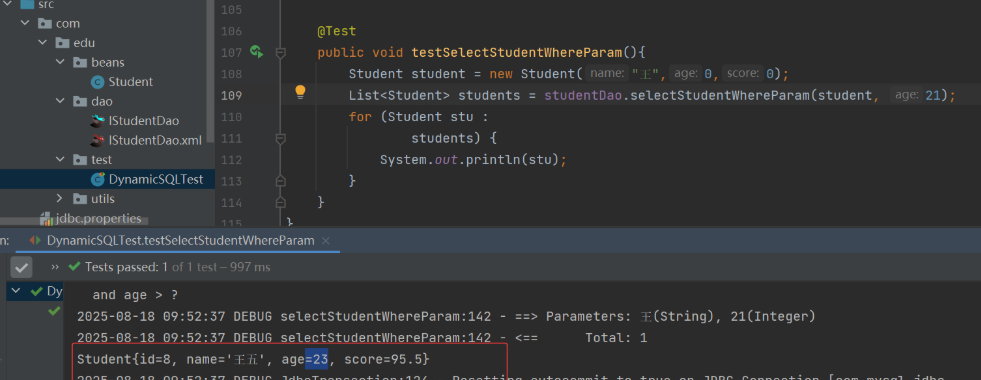
10. @Param 注解
Mybatis 中的 @Param 注解:该注解指定的名称要作为 SQL 语句中动态参数的前缀,例如:
(1) 修改 IStudentDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface IStudentDao {
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentChoose(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachArray(Object[] studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList(List<Integer> studentIds);
List<Student> selectStudentForEachList2(List<Student> students);
List<Student> selectStudentBySQL(Student student);
List<Student> selectStudentWhereParam(@Param("stu") Student student, @Param("myage") int age);
}
(2) 修改 IStudenDao.xml
<select id="selectStudentWhereParam" resultType="Student">
select id,name,age,score from student
<!--如果下面的 <if> 语句都不满足条件,则不会条件 where 子句,如果有一个 <if> 条件满足,就会添加 where 子句-->
<where>
<!--如果传过来的 name 属性不为 null,且不是空字符串,那么就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<!--如果接口方法参数是一个对象,并且使用的 @Param 注解,那么再使用方法参数时,要加上@Param指定的前缀 "stu."-->
<if test="stu.name != null and stu.name != ''">
<!--第一个 <if> 语句可以省略 and,但是其他的 <if> 语句必须加上 and-->
and name like '%' #{stu.name} '%'
</if>
<!--如果传过来的 age > 0,就拼接如下的 SQL 片段-->
<!--如果接口方法参数是基本类型,且被 @Param 注解,那么这里的动态参数名就是 @Param 指定的名称-->
<if test="myage > 0">
<!--其他 <if> 语句的 and 不能省略-->
and age > #{myage}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(3) 测试类
)








总结)




排序优化之搜索大数据酒店,进销存AI—仙盟创梦IDE)
)



)