CUB 是 NVIDIA 提供的 高性能 CUDA 基础库,包含常用的并行原语(Reduction、Scan、Histogram 等),可以极大简化代码,并且比手写版本更优化。
CUB无需链接,只用包含<cub/cub.cuh>头文件即可
需要先临时获取空间
CUB 内部需要额外的缓冲区来做并行归约、扫描等操作,而这个缓冲区的大小依赖于 输入数据量、算法、GPU 结构,编译期无法确定。
通用函数接口-Device-level(设备级)
运行在整个设备(grid)范围,需要全局内存临时空间。
cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce
template <typename InputIteratorT,typename OutputIteratorT,typename ReductionOp,typename T>
static cudaError_t Reduce(void *d_temp_storage, // 临时存储区指针size_t &temp_storage_bytes, // 存储区大小InputIteratorT d_in, // 输入迭代器(GPU 内存)OutputIteratorT d_out, // 输出迭代器(GPU 内存)int num_items, // 输入元素个数ReductionOp reduction_op, // 归约操作符(如加法、最大值)T init, // 归约初始值cudaStream_t stream = 0); // CUDA 流
d_temp_storage和temp_storage_bytes:两阶段调用机制(先获取大小再分配)d_in/d_out:输入和输出数组指针(在 GPU 上)num_items:元素数量reduction_op:归约操作(例如cub::Sum(),cub::Max(),或自定义 Lambda)init:归约起始值stream:运行在哪个 CUDA stream 上
求和
#ifndef __CUDACC__
#define __CUDACC__
#endif
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <cufft.h>
#include<cub/cub.cuh>
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include <vector>void error_handling(cudaError_t res) {if (res !=cudaSuccess) {std::cout << "error!" << std::endl;}
}
int main() {const int N = 8;float h_in[N] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };float* d_in, * d_out;cudaMalloc(&d_in, N * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc(&d_out, sizeof(float));cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, N * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);void* d_temp_storage = nullptr;size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0;cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(d_temp_storage,temp_storage_bytes,d_in,d_out,N,cub::Sum(),0.0f);// 分配临时空间cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes);// 第二次调用:执行归约cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes,d_in, d_out, N,cub::Sum(), 0.0f);float h_out;cudaMemcpy(&h_out, d_out, sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);std::cout << "Sum = " << h_out << std::endl;cudaFree(d_in);cudaFree(d_out);cudaFree(d_temp_storage);return 0;
}
当然,Reduce是通用版本,也有Sum的特化版本
template <typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT>cudaError_tstatic Sum(void* d_temp_storage,size_t& temp_storage_bytes,InputIteratorT d_in,OutputIteratorT d_out,NumItemsT num_items,cudaStream_t stream = 0);
#ifndef __CUDACC__
#define __CUDACC__
#endif
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <cufft.h>
#include<cub/cub.cuh>
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include <vector>void error_handling(cudaError_t res) {if (res !=cudaSuccess) {std::cout << "error!" << std::endl;}
}
int main() {const int N = 8;float h_in[N] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };float* d_in, * d_out;cudaMalloc(&d_in, N * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc(&d_out, sizeof(float));cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, N * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);void* d_temp_storage = nullptr;size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0;// 先获取临时空间大小cub::DeviceReduce::Sum(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N);cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes);// 执行 Reducecub::DeviceReduce::Sum(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N);float h_out;cudaMemcpy(&h_out, d_out, sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);std::cout << "Sum = " << h_out << std::endl;cudaFree(d_in);cudaFree(d_out);cudaFree(d_temp_storage);return 0;
}
自定义乘积
可以求数组所有元素的乘积;乘积Reduce没有提供接口,可以自己写一个可执行对象(仿函数类,lambda表达式等都可以)
这里使用lambda表达式
#ifndef __CUDACC__
#define __CUDACC__
#endif
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <cufft.h>
#include<cub/cub.cuh>
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include <vector>void error_handling(cudaError_t res) {if (res !=cudaSuccess) {std::cout << "error!" << std::endl;}
}
int main() {const int N = 8;float h_in[N] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };float* d_in, * d_out;cudaMalloc(&d_in, N * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc(&d_out, sizeof(float));cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, N * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);void* d_temp_storage = nullptr;size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0;cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N, []__device__(float a, float b) ->float{ return a * b; }, 1.0f);// 分配临时空间cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes);// 第二次调用:执行乘积cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N, []__device__(float a, float b) ->float{ return a * b; }, 1.0f);float h_out;cudaMemcpy(&h_out, d_out, sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);std::cout << "mul = " << h_out << std::endl;cudaFree(d_in);cudaFree(d_out);cudaFree(d_temp_storage);return 0;
}
如果想要使用在设备使用lambda表达式,需要编译时加上:
nvcc main.cu -o main --extended-lambda
如果用VS,打开项目属性,在这里加:
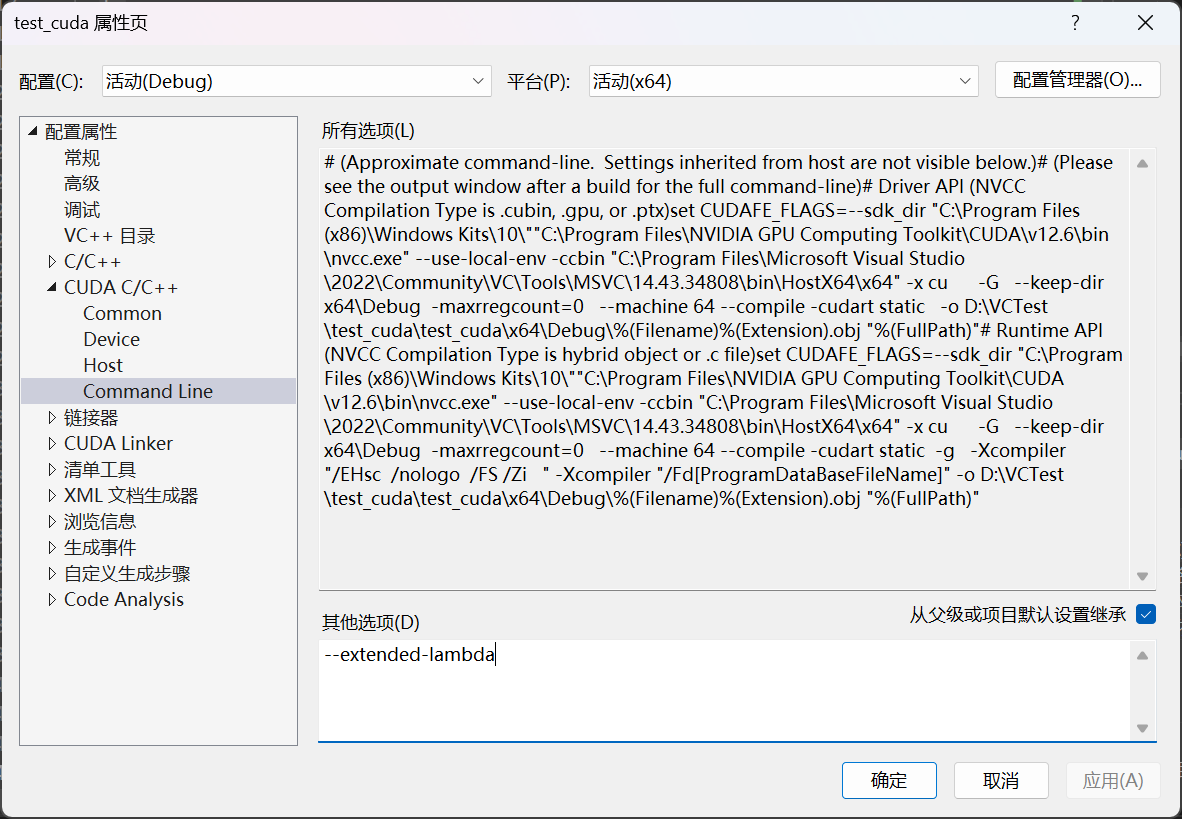
(用仿函数类就不用开启这个,如此即可)
struct MultiplyOp {__device__ float operator()(float a, float b) const {return a * b;}
};// 调用
cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes,d_in, d_out, N,MultiplyOp(), 1.0f);前缀和
前缀和有专门的函数
template <typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT>static cudaError_t ExclusiveSum(void* d_temp_storage,// 临时存储指针size_t& temp_storage_bytes,// 临时存储大小InputIteratorT d_in,// 输入迭代器(指针)OutputIteratorT d_out,// 输出迭代器(指针)int num_items,// 元素数量cudaStream_t stream = 0)// CUDA 流(可选)
;使用起来没有任何差别
#ifndef __CUDACC__
#define __CUDACC__
#endif
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <cufft.h>
#include<cub/cub.cuh>
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include <vector>void error_handling(cudaError_t res) {if (res !=cudaSuccess) {std::cout << "error!" << std::endl;}
}
int main() {const int N = 8;float h_in[N] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };float* d_in, * d_out;cudaMalloc(&d_in, N * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc(&d_out, N*sizeof(float));cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, N * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);void* d_temp_storage = nullptr;size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0;// 获取临时空间大小cub::DeviceScan::ExclusiveSum(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N);cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes);// 执行 Exclusive Scancub::DeviceScan::ExclusiveSum(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, N);float h_out[N];cudaMemcpy(h_out, d_out, N * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);std::cout << "Exclusive Scan: ";for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) std::cout << h_out[i] << " ";std::cout << std::endl;cudaFree(d_in);cudaFree(d_out);cudaFree(d_temp_storage);return 0;
}
ExclusiveScan 是前缀和,不包括当前元素:
输入: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
输出: [0, 1, 3, 6,10,15,21,28]
Block-level (线程块级)
作用
用于一个 Block 内的线程协作,通常替代手写的
__shared__+ 手写 reduce/scan。比 Warp-level 更大范围(整个 block),但不涉及 grid 级同步。
用途:块内归约、块内前缀和、块内排序。
线程块级类的调用套路是一样的
定义类型(
typedef)申请共享内存(
TempStorage)调用对象的方法
BlockReduce模板类
namespace cub {template <typename T, // 数据类型,例如 float, intint BLOCK_DIM_X, // 线程块大小cub::BlockReduceAlgorithm ALGORITHM = cub::BLOCK_REDUCE_WARP_REDUCTIONS // 可选//还有一些其他模板参数,一般都可以忽略
>
class BlockReduce {
public:// 内部类型:临时存储struct TempStorage;// 构造函数:传入共享内存__device__ __forceinline__ BlockReduce(TempStorage& temp_storage);// 常用方法:__device__ T Sum(T input); // 块内所有线程求和template <typename ReductionOp>__device__ T Reduce(T input, ReductionOp reduction_op); // 自定义规约操作__device__ T Sum(T input, T identity); // 带初始值的求和// 返回最大值和索引struct ArgMax { T value; int index; };__device__ ArgMax Reduce(T input, ReductionOp reduction_op, ArgMax identity);
};} // namespace cub特点
不需要手写循环/
__syncthreads(),CUB 自动优化 bank conflict。自定义操作用
.Reduce(val, binary_op)。
块内归约
__global__ void block_reduce_sum(float* d_in, float* d_out) {// 定义 BlockReduce 类型:数据类型 float,block 大小 256typedef cub::BlockReduce<float, 256> BlockReduceT;// 共享内存(临时存储)__shared__ typename BlockReduceT::TempStorage temp_storage;int tid = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;float val = d_in[tid];// 每个 block 归约,返回该 block 的总和float block_sum = BlockReduceT(temp_storage).Sum(val);if (threadIdx.x == 0) {d_out[blockIdx.x] = block_sum; // 每个 block 的结果}
}BlockReduce::Sum(T input) 里的 input 参数 是 当前线程贡献的单个值,也就是参与规约的元素。
BlockReduce::Sum() 会在整个 线程块(block)内,把所有线程的 input 值加起来,返回 块内的总和。
自定义规约
__device__ T Reduce(T input, ReductionOp reduction_op); // 自定义规约操作该成员函数可以让我们实现自定义的规约操作
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
input | 每个线程的本地值,类型为 T。 |
binary_op | 一个二元操作函数对象,类型为 BinaryOp,定义了如何将两个 T 类型的值合并。例如:加法、乘法、最大值等。 |
比如可以用cub库提供的可调用对象类
float block_sum = BlockReduceT(temp_storage).Reduce(val, cub::Sum());//规约加法
float block_prod = BlockReduceT(temp_storage).Reduce(val, cub::Multiply());//规约乘法也可以自己实现仿函数类或lambda表达式;具体操作与上文Device级别的自定义乘积类似;
BlockScan
namespace cub {template <typename T, // 数据类型int BLOCK_DIM_X, // 线程块大小cub::BlockScanAlgorithm ALGORITHM = cub::BLOCK_SCAN_WARP_SCANS // 可选
>
class BlockScan {
public:struct TempStorage;__device__ __forceinline__ BlockScan(TempStorage& temp_storage);// 前缀和(不包含自己)template <typename ScanOp>__device__ void ExclusiveScan(T input, T &output, ScanOp scan_op, T identity);// 前缀和(包含自己)template <typename ScanOp>__device__ void InclusiveScan(T input, T &output, ScanOp scan_op);// 常用简化版本__device__ void ExclusiveSum(T input, T &output, T identity = 0);__device__ void InclusiveSum(T input, T &output);
};} // namespace cub
使用
typedef cub::BlockScan<int, 256> BlockScanT;
__shared__ typename BlockScanT::TempStorage temp_storage;
int output;
BlockScanT(temp_storage).ExclusiveSum(input, output);
BlockRadixSort
namespace cub {template <typename KeyT, // 键类型int BLOCK_DIM_X, // 线程块大小typename ValueT = void, // 可选,值类型int ITEMS_PER_THREAD = 1 // 每线程处理的元素个数
>
class BlockRadixSort {
public:struct TempStorage;__device__ __forceinline__ BlockRadixSort(TempStorage& temp_storage);// 对键排序(升序),排序后把属于该线程的key更新__device__ void Sort(KeyT &key);// 降序__device__ void SortDescending(KeyT &key);// 键值对排序__device__ void Sort(KeyT &key, ValueT &value);__device__ void SortDescending(KeyT &key, ValueT &value);
};} // namespace cub
使用模式
#include <cub/cub.cuh>__global__ void block_sort(int *d_keys) {typedef cub::BlockRadixSort<int, 256> BlockRadixSortT;__shared__ typename BlockRadixSortT::TempStorage temp_storage;int thread_id = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;int key = d_keys[thread_id];// 在 block 内排序(升序)BlockRadixSortT(temp_storage).Sort(key);// 写回排序后的值d_keys[thread_id] = key;
}
Warp-level
Warp-level 原语(线程束级)
用于warp 内高效协作,替代手写
__shfl_*。适合 warp 内归约(reduce)、前缀和(scan),比手写更可读。
具体用法与block级一模一样,只是模板类名改为WarpReduce、WarpScan

)
)

ARM体系架构)







)






-Java并发篇)