文章目录
- 一. 背景
- 二. 你的经历
- 三. 代码实现(龟速版——单线程)
- 3.1 梯度幅值
- 3.1.1 生成 8 个方向模板
- 3.1.2 计算梯度
- 3.1.3 显示梯度图像
- 3.1.4 程序运行演示
- 3.2 梯度方向 (梯度最大幅度值和方向)
- 3.3 单像素边缘
- 3.4 梯度单像素边缘提取 运行测试
- 四 、亚像素坐标
- 五、提取坐标
- 六、 加速版
- 6.1.龟速分析
- 6.2 加速版 亚像素边缘提取 (多线程 + 少模板)
- 6.2 测试结果及分析
- 6.3 结论:梯度最大幅度值和方向 程序是有问题
基于多项式插值的亚像素边缘定位算法
一. 背景
在测量或者定位的应用中会涉及到边缘检测, 但是像 OpenCV 这样的开源库中边缘检测算法的精度在像素级别, 比如 Canny, Sobel blablabla. 要想提高精度就需要用到 亚像素 的技术, 在不改变硬件成本的前提下提高检测精度
二. 你的经历
图像的边缘就是图像灰度值发生突变的位置, "突变"是理想的情况, 因为一些我也讲不清楚你也不愿意看的原因造成了图像边缘变得模糊和平滑. 如下图, 像不像近视眼看到的图像?

对于理想的边缘, 就连一个简单的二值化处理都可以得到准确的边缘, 模糊的边缘二值化就不这么听话了. 二值化作为很多人入门图像处理遇到的第一批函数, 所以肯定有同学就是用二值化来做边缘检测的. 要求不高还好, 光源和被检测物体有变化的时候你就天天都在调阈值, 不要问我怎么知道的
当你进阶一点, 学到了 Canny, Sobel 等待检测方法时, 你就开始用这样的方法做边缘检测, 很明显, 效果比二值化好了很多, 此时的你小小的虚荣心得到了满足, 得到了老板的肯定
又过了一阵, 老板接到一个活, 说要测量一个物体, 客户要求精度(这个精度不是测量系统分析的精度, 你可以理解为分辨能力)是 ±0.01mm, 你嘴算了一下觉得相机分辨率还可行, 就拍胸脯给老板讲可以做, 老板看你信心满满就把活接了下来. 但是当你做出来自己拿料检测的时候, 问题来了, 精度不够. 然后你就在网上开始找解决方法, 当看到"亚像素"时喜出望外, 感觉找到了救命稻草. 这可能是你的救命稻草, 也是你喜极而泣的原因, 因为你不知道这个亚像素的东东怎么用 C++ 写出来. 然后就疯狂地搜索关键字 “C++” “亚像素”, 看到一些所谓的源码, 结果花了好多积分 Download. 发现不能用. 心里还不甘心. 然后一目十行地看各种论文, 其实也看不明白, 就陷入了恶性循环
不过当你看到这篇文章的时候, 真正的希望来了, 因为我会给你提供可用的源代码

三. 代码实现(龟速版——单线程)
本文源代码是根据《一种基于多项式插值改进亚像素细分算法》(作者:李庆利)写的. 要看论文的话, 可以网上搜索. 希望对你有所帮助. 不好用也没有关系, 买卖不成仁义在
龟速版旨在说明算法的原理, 后面会有加速版
3.1 梯度幅值
3.1.1 生成 8 个方向模板
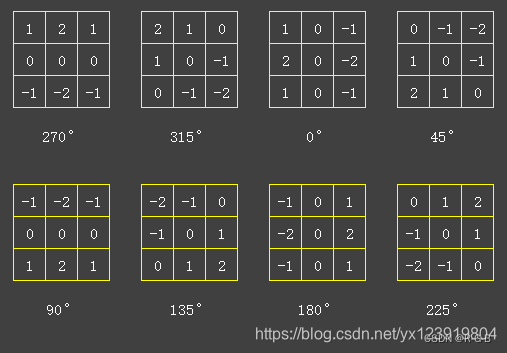
梯度检测包含 幅值和方向, 用 8 个方向模板在检测图像上进行卷积运算(模板滑过的地方的像素值和模板中对应的值相乘, 最后全部加总), 得到 8 张梯度图像, 方向模板如下. 模板的方向就是和 X 轴的夹角
矩阵的镜像运算可以用函数flip()完成,函数flip()的原型如下:
void cv::flip(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flipCode)
- 水平翻转:
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage2, 1); - 垂直翻转:
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage3, 0); - 垂直和水平翻转 :
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage4, -1);
以下代码生成 8 个方向模板
/*
矩阵的镜像运算可以用函数flip()完成,函数flip()的原型如下:
void cv::flip(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flipCode)// 水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage2, 1);
// 垂直翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage3, 0);
// 垂直和水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage4, -1);*/
//生成 8 个方向模板
void gradient_kernels(static Mat kernels[])
{//生成 8 个方向模板if (kernels[0].empty()){int k = 0;kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, -1, -2, -1); // 270°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, -1, -2); // 315°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, -1, 2, 0, -2, 1, 0, -1); // 0°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, -1, -2, 1, 0, -1, 2, 1, 0); // 45°flip(kernels[0], kernels[k++], 0); // 90°(270°垂直翻转得到90°)kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -2, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2); // 135°flip(kernels[2], kernels[k++], 1); // 180°(0°水平翻转得到90°)kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 0); // 225°}
}
3.1.2 计算梯度
接下来利用模板卷积生成梯度图像, 假设要检测的图像长下面这个样, 边缘是模糊的

利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
OpenCV提供了函数filter2D()作图像(矩阵)的相关运算,注意是相关运算,而不是卷积运算。
卷积运算的定义,将核旋转180度再做相关运算就是卷积运算了。
所以我们在使用filter2D卷积运算时,如果模板数据不是中心对称的,需先将卷积核旋转180°(若对称,无需旋转)
将矩阵旋转180度等效于先作一个水平镜像,再作一个垂直镜像,
矩阵的镜像运算可以用函数flip()完成,函数flip()的原型如下:
void cv::flip(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flipCode)
- 水平翻转:
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage2, 1); - 垂直翻转:
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage3, 0); - 垂直和水平翻转 :
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage4, -1);
利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
//利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
void gradient_generate(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat kernels[])
{// 梯度图像for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){filter2D(imgsrc, gradients[k], CV_16S, kernels[k]);}}
3.1.3 显示梯度图像
在cpp开头 定义全局变量 角度列表
// 角度列表
static const short angle_list[] = { 270, 315, 0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225 };
显示梯度图像
//显示梯度图像
void show_gradient(Mat gradients[])
{//显示梯度图Mat imgshow;char gradientImg[50];char strName[50] = "gradient-%d";for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){// 因为梯度有可能是负值, 所以要做归一化和类型转换才可以正常显示normalize(gradients[k], imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);//OpenCV老版本 用 CV_MINMAX,新版用NORM_MINMAX imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);putText(imgshow, to_string(angle_list[k]), Point(70, 110), FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), 3, 8, 0);sprintf_s(gradientImg, strName, angle_list[k]);namedWindow(gradientImg, WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow(gradientImg, imgshow);}waitKey(0);
}3.1.4 程序运行演示
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <windows.h>using namespace cv;
using namespace std;#define KERNEL_SUM 8 //8 个方向卷积模板(卷积核)
#define KERNEL_HALF 4 //4 个卷积模板(270°和90°, 315°和135°是相反的, 其他类推)//卷积核模板
static Mat kernels[KERNEL_SUM];
// 梯度图像
Mat gradients[KERNEL_SUM];
// 检测图像, 路径自己更改, 注意要是单通道图像
Mat imgsrc = imread("1.jpg", IMREAD_UNCHANGED);
// 角度列表
static const short angle_list[] = { 270, 315, 0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225 };//生成 8 个方向模板
void gradient_kernels(static Mat kernels[]);
//利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
void gradient_generate(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat kernels[]);
//显示梯度图像
void show_gradient(Mat gradients[]);void main()
{gradient_kernels(kernels);gradient_generate(imgsrc,gradients,kernels);//显示梯度图像show_gradient(gradients);
}显示 8个方向的梯度图像
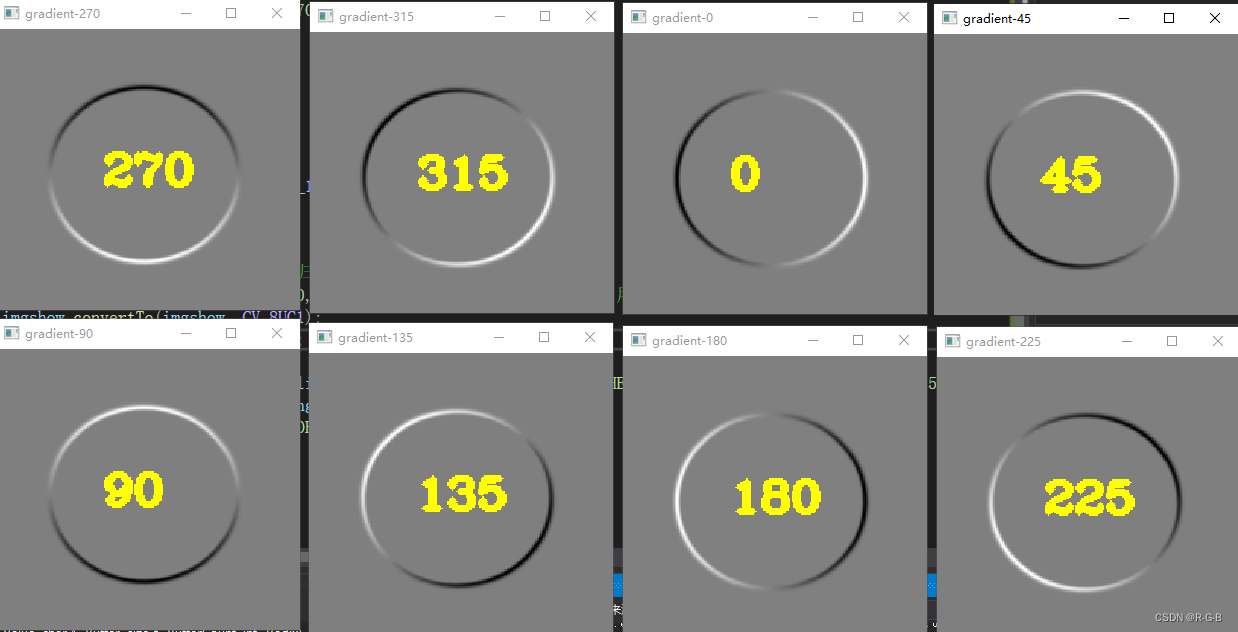
从图中可以看出各模板可以检测出指定方向的边缘, 其中白色表示该方向最大梯度值, 黑色表示反向最大梯度值
梯度幅值最大值处的点就是边缘的整数坐标
3.2 梯度方向 (梯度最大幅度值和方向)
梯度方向指向梯度幅值最大的方向, 现在已经有 8 张幅值图像, 只要比较其中最大的幅值即可得到其方向, 例如第 0 张梯度图像在 (i, j) 处的幅值比其他图像都大, 则 (i, j) 点的梯度方向是 270°. 下面我们用代码求出最大幅度值和方向
在cpp开头 定义全局变量
// 总幅值矩阵
Mat amplitude(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC1, Scalar::all(0));
// 角度矩阵, 后面初始化成 -64 只是为了归一化之后能显示角度 0
Mat angle(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC1, Scalar::all(-64));
梯度最大幅度值和方向
//梯度最大幅度值和方向
void gradient_amplitude_angle(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat amplitude, Mat angle)
{for (int r = 0; r < imgsrc.rows; r++){short* pAmp = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);short* pGrad[KERNEL_SUM] = { nullptr };for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_SUM; i++){pGrad[i] = gradients[i].ptr<short>(r);}for (int c = 0; c < imgsrc.cols; c++){// 找出最大值for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_SUM; i++){if (pAmp[c] < pGrad[i][c]){pAmp[c] = pGrad[i][c];pAng[c] = angle_list[i];}}}}
}
显示 最大幅度值和方向
//显示 最大幅度值和方向
void show_amplitude_angle(Mat amplitude,Mat angle)
{//显示梯度图Mat imgshow;// 显示幅值图像和角度图像normalize(amplitude, imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);namedWindow("amplitude", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("amplitude", imgshow);cout << "amplitude.size : " << amplitude.size()<< " imgshow.size :"<< imgshow.size()<<endl;normalize(angle, imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);namedWindow("angle", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("angle", imgshow);cout << "angle.size : " << angle.size() << " imgshow.size :" << imgshow.size() << endl;waitKey(0);
}原教程 最大幅度值和方向
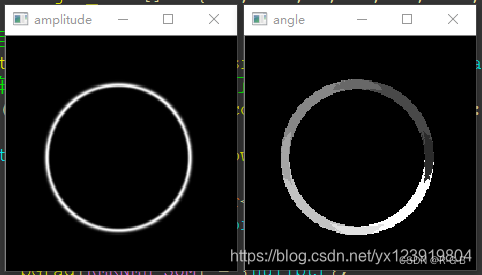
本文运行结果: 最大幅度值和方向
3.3 单像素边缘
到这里有同学可能有疑问, 既然幅值最大处是边缘, 我们也把幅值最大的地方找出来了, 但是这个边缘怎么这么粗?
首先要说明的是这不是边缘, 只是 8 个梯度图中幅值比较大的地方, 幅值图中最亮的点才是边缘. 那如何能找出图中最亮的点呢? 这个也比较简单, 只要在 3 × 3 的邻域中根据梯度的方向比较中心点 “左右” 的两个点幅值就可以知道了. 左右我打了引号, 有可能是在对角方向和上下方向. 如果不能理解的话, 把幅值图放大如下, 仿佛看到了马赛克
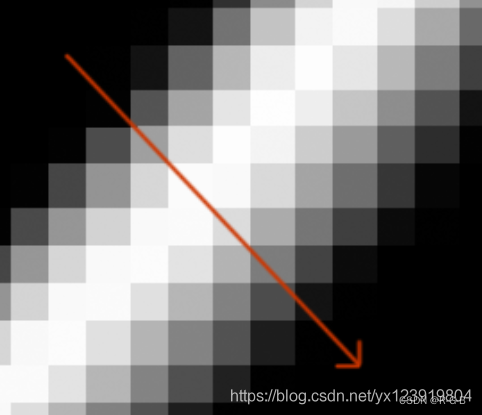
有没有发现在梯度方向幅值从小到大, 再变小, 我们只需要判断中间是否大于两边(“左右”)的幅值, 如果同时大于两边, 则是边缘点, 如果不是同时大于两边, 则不是边缘点, 下面用代码实现此判断
注: BYTE 为 unsigned char 类型, 有的新手同学可能不知道, 特别在这里注明
void get_singlePix_edges(Mat imgsrc,Mat amplitude, Mat angle)
{// 整数坐标边缘图像Mat edge(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));for (int r = 1; r < imgsrc.rows - 1; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用 3 个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmp1 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmp2 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmp3 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r + 1);const short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);//BYTE 为 unsigned char 类型,包含#include <windows.h>BYTE* pEdge = edge.ptr<BYTE>(r);for (int c = 1; c < imgsrc.cols - 1; c++){switch (pAng[c]){case 270:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 90:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 315:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 135:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 0:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 180:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 45:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 225:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;default:break;}}}namedWindow("edge", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("edge", edge);waitKey(0);
}
原教程 最大幅度值和方向
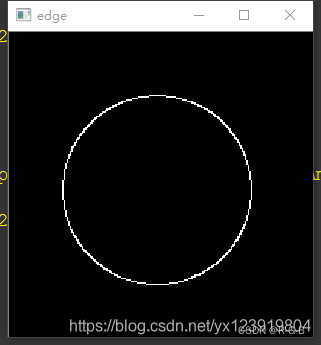
本文运行结果: 最大幅度值和方向
现在的边缘是不是只有一个像素宽了, 到这里可以算是完成了 50% 工作了,
还有两个问题需要解决, 一是如何求出亚像素坐标, 二是怎样表示亚像素坐标
3.4 梯度单像素边缘提取 运行测试
以lena为例,检测轮廓

#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <windows.h>using namespace cv;
using namespace std;#define KERNEL_SUM 8 //8 个方向卷积模板(卷积核)
#define KERNEL_HALF 4 //4 个卷积模板(270°和90°, 315°和135°是相反的, 其他类推)/*OpenCV提供了函数filter2D()作图像(矩阵)的相关运算,注意是相关运算,而不是卷积运算。
卷积运算的定义,将核旋转180度再做相关运算就是卷积运算了。
所以我们在使用filter2D卷积运算时,如果模板数据不是中心对称的,需先将卷积核旋转180°(若对称,无需旋转)
将矩阵旋转180度等效于先作一个水平镜像,再作一个垂直镜像,矩阵的镜像运算可以用函数flip()完成,函数flip()的原型如下:
void cv::flip(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flipCode)// 水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage2, 1);
// 垂直翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage3, 0);
// 垂直和水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage4, -1);*///卷积核模板
static Mat kernels[KERNEL_SUM];
// 梯度图像
Mat gradients[KERNEL_SUM];
// 检测图像, 路径自己更改, 注意要是单通道图像
Mat imgsrc = imread("2.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
// 总幅值矩阵
Mat amplitude(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC1, Scalar::all(0));
// 角度矩阵, 后面初始化成 -64 只是为了归一化之后能显示角度 0
Mat angle(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC1, Scalar::all(-64));
// 角度列表
static const short angle_list[] = { 270, 315, 0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225 };// 整数坐标边缘图像
Mat edge(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));//生成 8 个方向模板
void gradient_kernels(static Mat kernels[]);
//利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
void gradient_generate(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat kernels[]);
//显示梯度图像
void show_gradient(Mat gradients[]);
//梯度最大幅度值和方向
void gradient_amplitude_angle(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[],Mat amplitude,Mat angle);
//显示 最大幅度值和方向
void show_amplitude_angle(Mat amplitude, Mat angle);
void get_singlePix_edges(Mat imgsrc, Mat amplitude, Mat angle);void main()
{gradient_kernels(kernels);gradient_generate(imgsrc,gradients,kernels);//显示梯度图像//show_gradient(gradients);gradient_amplitude_angle(imgsrc,gradients, amplitude, angle);//显示 最大幅度值和方向show_amplitude_angle(amplitude, angle);get_singlePix_edges(imgsrc,amplitude,angle);}//生成 8 个方向模板
void gradient_kernels(static Mat kernels[])
{//生成 8 个方向模板if (kernels[0].empty()){int k = 0;kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, -1, -2, -1); // 270°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, -1, -2); // 315°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, -1, 2, 0, -2, 1, 0, -1); // 0°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, -1, -2, 1, 0, -1, 2, 1, 0); // 45°flip(kernels[0], kernels[k++], 0); // 90°(270°垂直翻转得到90°)kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -2, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2); // 135°flip(kernels[2], kernels[k++], 1); // 180°(0°水平翻转得到90°)kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 0); // 225°}
}//利用 filter2D 函数计算梯度
void gradient_generate(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat kernels[])
{// 梯度图像for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){filter2D(imgsrc, gradients[k], CV_16S, kernels[k]);}}//显示梯度图像
void show_gradient(Mat gradients[])
{//显示梯度图Mat imgshow;char gradientImg[50];char strName[50] = "gradient-%d";for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){// 因为梯度有可能是负值, 所以要做归一化和类型转换才可以正常显示normalize(gradients[k], imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);//OpenCV老版本 用 CV_MINMAX,新版用NORM_MINMAX imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);putText(imgshow, to_string(angle_list[k]), Point(70, 110), FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), 3, 8, 0);sprintf_s(gradientImg, strName, angle_list[k]);namedWindow(gradientImg, WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow(gradientImg, imgshow);}waitKey(0);
}//梯度最大幅度值和方向
void gradient_amplitude_angle(Mat imgsrc, Mat gradients[], Mat amplitude, Mat angle)
{for (int r = 0; r < imgsrc.rows; r++){short* pAmp = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);short* pGrad[KERNEL_SUM] = { nullptr };for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_SUM; i++){pGrad[i] = gradients[i].ptr<short>(r);}for (int c = 0; c < imgsrc.cols; c++){// 找出最大值for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_SUM; i++){if (pAmp[c] < pGrad[i][c]){pAmp[c] = pGrad[i][c];pAng[c] = angle_list[i];}}}}
}//显示 最大幅度值和方向
void show_amplitude_angle(Mat amplitude,Mat angle)
{//显示梯度图Mat imgshow;// 显示幅值图像和角度图像normalize(amplitude, imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);namedWindow("amplitude", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("amplitude", imgshow);cout << "amplitude.size : " << amplitude.size()<< " imgshow.size :"<< imgshow.size()<<endl;normalize(angle, imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC1);namedWindow("angle", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("angle", imgshow);cout << "angle.size : " << angle.size() << " imgshow.size :" << imgshow.size() << endl;waitKey(0);
}void get_singlePix_edges(Mat imgsrc, Mat amplitude, Mat angle)
{// 整数坐标边缘图像Mat edge(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));for (int r = 1; r < imgsrc.rows - 1; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用 3 个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmp1 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmp2 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmp3 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r + 1);const short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);//BYTE 为 unsigned char 类型,包含#include <windows.h>BYTE* pEdge = edge.ptr<BYTE>(r);for (int c = 1; c < imgsrc.cols - 1; c++){switch (pAng[c]){case 270:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 90:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 315:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 135:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 0:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 180:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 45:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 225:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;default:break;}}}namedWindow("edge", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("edge", edge);waitKey(0);
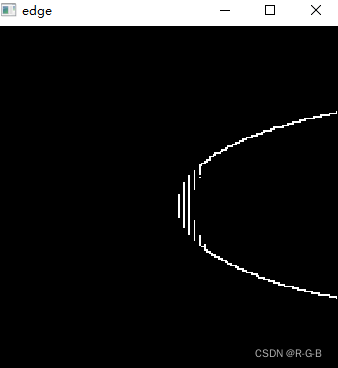
}本文运行结果
原教程结果
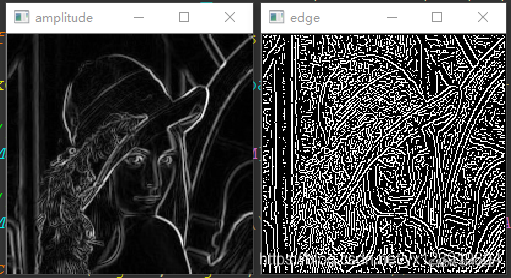
看到边缘图像有的同学可能要伤心了, 女神怎么变成这样了, 那么多边缘被检测出来了, 我们不需要那么多边缘啊. 同学别急, 检测出来那么多边缘是因为我们没有对梯度幅度进行筛选, 你想一下, 我们在计算单像素边缘的时候只要满足中间大于两边就算边缘, 女神图像中有一些中间只比两边大了一点点, 所以这种边缘可以去除, 我们想要的是比较强烈的边缘. 解决办法就是设定一个阈值, 当梯度值大于阈值是才算真正的边缘
将单像素边缘检测修改如下
void get_singlePix_edges2(Mat imgsrc, Mat edge, Mat amplitude, Mat angle, int threshVal)
{// 增加threshVal, 设定一个阈值, 当梯度值大于阈值是才算真正的边缘for (int r = 1; r < imgsrc.rows - 1; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用 3 个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmp1 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmp2 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmp3 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r + 1);const short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);BYTE* pEdge = edge.ptr<BYTE>(r);for (int c = 1; c < imgsrc.cols - 1; c++){// 以下判断为增加部分if (pAmp2[c] < threshVal){continue;}//switch (pAng[c]){case 270:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 90:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 315:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 135:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 0:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 180:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp2[c - 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp2[c + 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 45:if (pAmp2[c] >= pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] > pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;case 225:if (pAmp2[c] > pAmp1[c + 1] && pAmp2[c] >= pAmp3[c - 1]){pEdge[c] = 255;}break;default:break;}}}cout << "edge.size :" << edge.size() << endl;namedWindow("edge", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("edge", edge);waitKey(0);
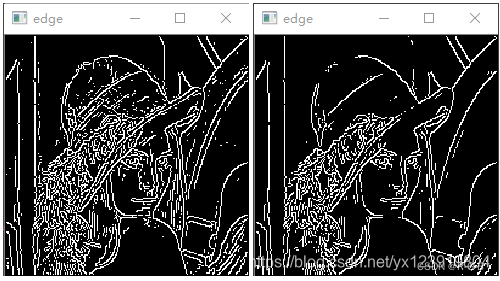
本文运行效果:
以下是阈值分别为 64, 128 的效果
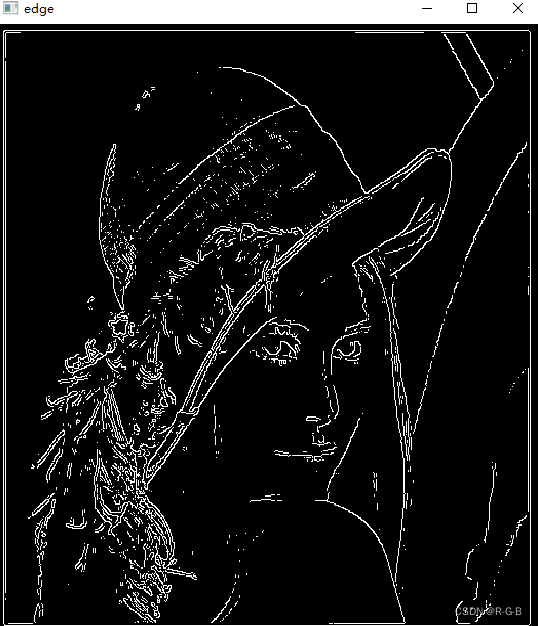


以下是原教程结果:
以下是阈值分别为 64, 128 的效果
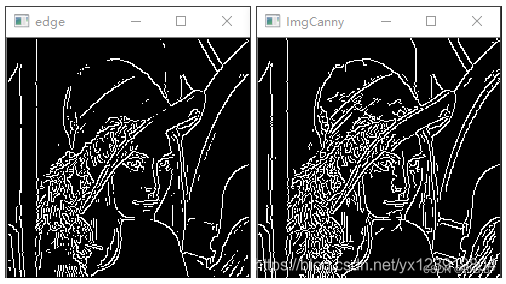
下面是阈值为 128 和 Canny 参数为 64, 128, 3, false 的对比图
原教程数据:
时间测试:
CPU: I9 9900K
OpenCV: 2413
图像分辩率: 2592 * 1944,边缘阈值 128
Debug模式: 406mS
Release模式: 125mS
四 、亚像素坐标
根据以下公式可计算亚像素坐标, 其实这个公式是二次多项式拟合
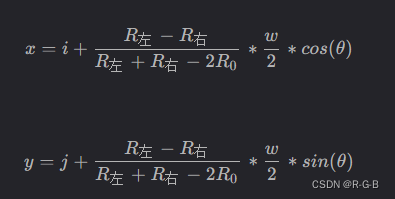
i: 当前整数坐标边缘点横坐标
j: 当前整数坐标边缘点纵坐标
R左: 边缘点左边梯度值
R0: 边缘点梯度值
R右: 边缘点右边梯度值
w: 相邻像素到边缘点的距离(梯度方向为 0°, 90°, 180°, 270° 时等于 1, 其他角度为sqrt(2)(根号2)
计算式是有了, 但是怎么在图像上表示小数坐标? 有两种方法
- 使用 vector 或其他容器把计算好的小数坐标保存起来, 这种方式可以直接操作数据
- 创建两个通道的图像, 第一个通道表示 x, 第二个通道表示 y, 这样装有值的像素点就表示在整数坐标的这个点的实际小数坐标, 要用的时候, 直接在这个坐标点取值就可以了, 这种方式还保持和图像相关联的状态
两种方式你选喜欢的就好
下面代码中, sin 前面的负号非常关键, 因为图像的 y 方向和直角坐标系的 y 方向相反
vector<Point2f> subPixPoint2f(Mat edge)
{// 根号2const double root2 = sqrt(2.0);// 三角函数表double tri_list[2][KERNEL_SUM] = { 0 };for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_SUM; i++){tri_list[0][i] = cos(angle_list[i] * CV_PI / 180.0);// sin前面的负号非常关键, 因为图像的y方向和直角坐标系的y方向相反tri_list[1][i] = -sin(angle_list[i] * CV_PI / 180.0);}// vector 方式记录小数坐标vector<Point2f> vPts;// Mat 方式记录小数坐标, 注意这里是双通道Mat coordinate(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_32FC2, Scalar::all(0));for (int r = 1; r < imgsrc.rows - 1; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用3个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmp1 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmp2 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmp3 = amplitude.ptr<short>(r + 1);const short* pAng = angle.ptr<short>(r);const BYTE* pEdge = edge.ptr<BYTE>(r);float* pCoordinate = coordinate.ptr<float>(r);for (int c = 1; c < imgsrc.cols - 1; c++){if (pEdge[c]){int nAngTmp = 0;double dTmp = 0;switch (pAng[c]){case 270:nAngTmp = 0;dTmp = ((double)pAmp1[c] - pAmp3[c]) / (pAmp1[c] + pAmp3[c] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * 0.5;break;case 90:nAngTmp = 4;dTmp = -((double)pAmp1[c] - pAmp3[c]) / (pAmp1[c] + pAmp3[c] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * 0.5;break;case 315:nAngTmp = 1;dTmp = ((double)pAmp1[c - 1] - pAmp3[c + 1]) / (pAmp1[c - 1] + pAmp3[c + 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * root2 * 0.5;break;case 135:nAngTmp = 5;dTmp = -((double)pAmp1[c - 1] - pAmp3[c + 1]) / (pAmp1[c - 1] + pAmp3[c + 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * root2 * 0.5;break;case 0:nAngTmp = 2;dTmp = ((double)pAmp2[c - 1] - pAmp2[c + 1]) / (pAmp2[c - 1] + pAmp2[c + 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * 0.5;break;case 180:nAngTmp = 6;dTmp = -((double)pAmp2[c - 1] - pAmp2[c + 1]) / (pAmp2[c - 1] + pAmp2[c + 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * 0.5;break;case 45:nAngTmp = 3;dTmp = ((double)pAmp3[c - 1] - pAmp1[c + 1]) / (pAmp1[c + 1] + pAmp3[c - 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * root2 * 0.5;break;case 225:nAngTmp = 7;dTmp = -((double)pAmp3[c - 1] - pAmp1[c + 1]) / (pAmp1[c + 1] + pAmp3[c - 1] - 2 * pAmp2[c]) * root2 * 0.5;break;default:break;}const double x = c + dTmp * tri_list[0][nAngTmp];const double y = r + dTmp * tri_list[1][nAngTmp];// vector方式vPts.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));// Mat 方式pCoordinate[c << 1] = (float)x;pCoordinate[(c << 1) + 1] = (float)y;}}}return vPts;
}
打印坐标函数
template<typename T>
void display(vector<T> pts)
{int num = 0;for (auto iter = pts.begin(); iter != pts.end(); iter++){num++;if(num%10 == 0)cout << "\n";cout << *iter << " ";}cout << "\n";
}
下面是原始图像的底部放大图, 绿色部分是整数坐标, 由 270° 模板检测出来的边缘, 黄色是最低点, 可以看出圆的底部变成了一条直线, 这是我们不能接受的, 根据检测出来的小数坐标用红色标记出来, 可以看到底部的小数坐标为边弧形边缘, 精度提升了不少.
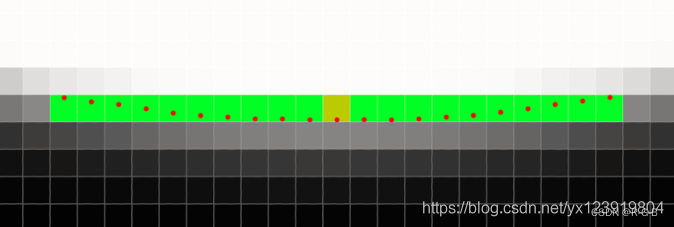
五、提取坐标
假定在 edge 图像的 (10, 20) (10 为行, 20 为列) 处不为 0, 则这点是边缘, coordinate 图像 (10, 20) 处通道 1 的值为 10.1234, 通道 2 的值为 20.2345, 则小数坐标 x = 20.2345, y = 10.1234
六、 加速版
6.1.龟速分析
卷积模板耗时, 在做图像卷积时有 8 个模板, 卷积这个操作相对比较耗时, 可以改进为多线程 + 少模板方式
-
多线程: 这不用讲吧, 一个模板一个线程
-
少模板: 其实模板没有少, 只是 270° 和 90° 是相反的, 315° 和 135° 是相反的, 其他类推, 只需要卷积 4 个模板就好了, 剩下的4个模板把前面卷积好的梯度图像乘以 -1
逐个像素点访问耗时, 每个像素点的操作都是一样的, 所以可以把图像分块, 然后用多线程对各块单独操作
角度和三角函数计算重复, 用 0~7 替换各个角度表示方便查表操作
6.2 加速版 亚像素边缘提取 (多线程 + 少模板)
注意: 函数只能输入单通道图像, 三通道的 RGB 图像计算会有问题
时间测试:
CPU: I9 9900K
OpenCV: 2413
图像分辩率: 2592 * 1944,边缘阈值 128图像分块数: 1
Debug模式: 203mS
Release模式: 103mS图像分块数: 8
Debug模式: 125mS
Release模式: 63mS
其实大多数实际应用中处理的不会是整张图像, 所以可以只处理目标区域来减少计算时间
修改后的代码最耗时的部分在梯度方向的判断, 大约占了整个处理过程的 80% 时间, 所以这个地方有待优化,
void SubPixelEdge(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, vector<Point2f>& vPts, int thres, int parts);
void SubPixelEdge2(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, Mat& coordinate, int thres, int parts);
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2\\opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2\\features2d.hpp>
#include <windows.h>using namespace cv;
using namespace std;#define KERNEL_SUM 8 //8 个方向卷积模板(卷积核)
#define KERNEL_HALF 4 //4 个卷积模板(270°和90°, 315°和135°是相反的, 其他类推)/*OpenCV提供了函数filter2D()作图像(矩阵)的相关运算,注意是相关运算,而不是卷积运算。
卷积运算的定义,将核旋转180度再做相关运算就是卷积运算了。
所以我们在使用filter2D卷积运算时,如果模板数据不是中心对称的,需先将卷积核旋转180°(若对称,无需旋转)
将矩阵旋转180度等效于先作一个水平镜像,再作一个垂直镜像,矩阵的镜像运算可以用函数flip()完成,函数flip()的原型如下:
void cv::flip(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flipCode)// 水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage2, 1);
// 垂直翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage3, 0);
// 垂直和水平翻转
cv::flip(srcImage, resultImage4, -1);*/typedef struct _tagEdgeParam
{int filter_count;int thres;//梯度阈值int parts;//图像分块数, 当图像比较小时, 就没有分块的必要了std::mutex mtx;
} EDGE_PARAM;// imgsrc: 检测图像, CV_8UC1
// edge: 整数坐标边缘图像
// vPts: 坐标记录 vector
// thres: 梯度阈值
// parts: 图像分块数, 当图像比较小时, 就没有分块的必要了
void SubPixelEdge(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, vector<Point2f>& vPts, int thres, int parts);// imgsrc: 检测图像, CV_8UC1
// edge: 整数坐标边缘图像
// coordinate: 小数坐标记录矩阵
// thres: 梯度阈值
// parts: 图像分块数, 当图像比较小时, 就没有分块的必要了
void SubPixelEdge2(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, Mat& coordinate, int thres, int parts);void main()
{// 检测图像, 路径自己更改, 注意要是单通道图像Mat imgsrc = imread("1.jpg", IMREAD_UNCHANGED);// 整数坐标边缘图像Mat edge(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));vector<Point2f> vPts;Mat coordinate;int thres = 100;int parts = 10;SubPixelEdge2(imgsrc, edge, coordinate, thres,parts);
}// imgsrc: 检测图像, CV_8UC1
// edge: 整数坐标边缘图像
// vPts: 坐标记录 vector
// thres: 梯度阈值
// parts: 图像分块数, 当图像比较小时, 就没有分块的必要了
void SubPixelEdge(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, vector<Point2f>& vPts, int thres, int parts)
{static Mat kernels[KERNEL_SUM];if (kernels[0].empty()){int k = 0;kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, -1, -2, -1); // 270°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, -1, -2); // 315°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, -1, 2, 0, -2, 1, 0, -1); // 0°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, -1, -2, 1, 0, -1, 2, 1, 0); // 45°flip(kernels[0], kernels[k++], 0); // 90°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -2, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2); // 135°flip(kernels[2], kernels[k++], 1); // 180°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 0); // 225°}// 梯度图像Mat gradients[KERNEL_SUM];EDGE_PARAM edge_param;edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.thres = thres;for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_HALF; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* src, Mat* grad, Mat* ker, EDGE_PARAM* param){filter2D(*src, *grad, CV_16S, *ker);*(grad + KERNEL_HALF) = -(*grad);param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &imgsrc, &gradients[i], &kernels[i], &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < KERNEL_HALF){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}// 幅值和角度矩阵合并成一个矩阵// 新创建的图像总是连续的, 所以可以按行来操作提高效率Mat amp_ang(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC2, Scalar::all(0));edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.parts = parts;//assert用来检测程序运行时的一些错误情况,比如数组越界、指针为空等。当程序发现错误时,assert会使程序崩溃,并输出错误信息。assert的使用可以提高代码的鲁棒性及可靠性。assert(parts >= 1 && parts < (amp_ang.rows >> 1));for (int i = 0; i < parts; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* amp_ang, Mat* grad, int cur_part, EDGE_PARAM* param){const int length = amp_ang->rows * amp_ang->cols;const int step = length / param->parts;const int start = cur_part * step;int end = start + step;if (cur_part >= param->parts - 1){end = length;}short* amp_ang_ptr = (short*)amp_ang->data + (start << 1);short* grad_ptr[KERNEL_SUM] = { nullptr };for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){grad_ptr[k] = (short*)grad[k].data + start;}for (int j = start; j < end; j++){// 找出最大值来判断方向for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){if (*amp_ang_ptr < *grad_ptr[k]){*amp_ang_ptr = *grad_ptr[k];*(amp_ang_ptr + 1) = k;}grad_ptr[k]++;}amp_ang_ptr += 2;}param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &_ang, gradients, i, &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < parts){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.thres = thres;edge = Mat::zeros(amp_ang.rows, amp_ang.cols, CV_8UC1);vector<vector<Point2f>> vvtmp(parts);for (int i = 0; i < parts; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* amp_ang, Mat* edge, vector<Point2f>* v, int cur_part, EDGE_PARAM* param){static const float root2 = (float)sqrt(2.0);static const float a2r = (float)(CV_PI / 180.0);static const short angle_list[] = { 270, 315, 0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225 };// 三角函数表float tri_list[2][KERNEL_SUM] = { 0 };float tri_list_root2[2][KERNEL_SUM] = { 0 };for (int j = 0; j < KERNEL_SUM; j++){tri_list[0][j] = (float)(0.5f * cos(angle_list[j] * a2r));// 0.5 前面的负号非常关键, 因为图像的 y 方向和直角坐标系的 y 方向相反tri_list[1][j] = (float)(-0.5f * sin(angle_list[j] * a2r));tri_list_root2[0][j] = tri_list[0][j] * root2;tri_list_root2[1][j] = tri_list[1][j] * root2;}const int thres = param->thres;const int end_x = amp_ang->cols - 1;const int rows = amp_ang->rows / param->parts;int start_y = rows * cur_part;int end_y = start_y + rows;if (cur_part){start_y -= 2;}if (cur_part >= param->parts - 1){end_y = amp_ang->rows;}v->reserve((end_y - start_y) * amp_ang->cols);start_y++;end_y--;for (int r = start_y; r < end_y; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用 3 个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmpang1 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmpang2 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmpang3 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r + 1);BYTE* pEdge = edge->ptr<BYTE>(r);for (int c = 1; c < end_x; c++){const int j = c << 1;if (pAmpang2[j] >= thres){switch (pAmpang2[j + 1]){case 0:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j]){pEdge[c] = 255;v->push_back(Point2f((float)c, r + tri_list[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang1[j] - pAmpang3[j]) /(pAmpang1[j] + pAmpang3[j] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1))));}break;case 4:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j]){pEdge[c] = 255;v->push_back(Point2f((float)c, r - tri_list[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang1[j] - pAmpang3[j]) /(pAmpang1[j] + pAmpang3[j] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1))));}break;case 1:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang1[j - 2] - pAmpang3[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j - 2] + pAmpang3[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));v->push_back(Point2f(c + tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]],r + tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]]));}break;case 5:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang1[j - 2] - pAmpang3[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j - 2] + pAmpang3[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));v->push_back(Point2f(c - tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]],r - tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]]));}break;case 2:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang2[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang2[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;v->push_back(Point2f(c + tri_list[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang2[j - 2] - pAmpang2[j + 2]) /(pAmpang2[j - 2] + pAmpang2[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1)), (float)r));}break;case 6:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang2[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang2[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;v->push_back(Point2f(c - tri_list[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang2[j - 2] - pAmpang2[j + 2]) /(pAmpang2[j - 2] + pAmpang2[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1)), (float)r));}break;case 3:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j + 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j - 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang3[j - 2] - pAmpang1[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j + 2] + pAmpang3[j - 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));v->push_back(Point2f(c + tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]],r + tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]]));}break;case 7:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j + 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j - 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang3[j - 2] - pAmpang1[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j + 2] + pAmpang3[j - 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));v->push_back(Point2f(c - tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]],r - tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]]));}break;default:break;}}}}param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &_ang, &edge, &vvtmp[i], i, &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < parts){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}for (int i = 0; i < parts; i++){vPts.insert(vPts.end(), vvtmp[i].begin(), vvtmp[i].end());cout << vPts[i] << endl;}}// imgsrc: 检测图像, CV_8UC1
// edge: 整数坐标边缘图像
// coordinate: 小数坐标记录矩阵
// thres: 梯度阈值
// parts: 图像分块数, 当图像比较小时, 就没有分块的必要了
void SubPixelEdge2(Mat& imgsrc, Mat& edge, Mat& coordinate, int thres, int parts)
{static Mat kernels[KERNEL_SUM];if (kernels[0].empty()){int k = 0;kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, -1, -2, -1); // 270°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, -1, -2); // 315°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, -1, 2, 0, -2, 1, 0, -1); // 0°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, -1, -2, 1, 0, -1, 2, 1, 0); // 45°flip(kernels[0], kernels[k++], 0); // 90°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -2, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2); // 135°flip(kernels[2], kernels[k++], 1); // 180°kernels[k++] = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 0); // 225°}// 梯度图像Mat gradients[KERNEL_SUM];EDGE_PARAM edge_param;edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.thres = thres;for (int i = 0; i < KERNEL_HALF; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* src, Mat* grad, Mat* ker, EDGE_PARAM* param){filter2D(*src, *grad, CV_16S, *ker);*(grad + KERNEL_HALF) = -(*grad);param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &imgsrc, &gradients[i], &kernels[i], &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < KERNEL_HALF){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}// 幅值和角度矩阵合并成一个矩阵// 新创建的图像总是连续的, 所以可以按行来操作提高效率Mat amp_ang(imgsrc.rows, imgsrc.cols, CV_16SC2, Scalar::all(0));edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.parts = parts;assert(parts >= 1 && parts < (amp_ang.rows >> 1));for (int i = 0; i < parts; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* amp_ang, Mat* grad, int cur_part, EDGE_PARAM* param){const int length = amp_ang->rows * amp_ang->cols;const int step = length / param->parts;const int start = cur_part * step;int end = start + step;if (cur_part >= param->parts - 1){end = length;}short* amp_ang_ptr = (short*)amp_ang->data + (start << 1);short* grad_ptr[KERNEL_SUM] = { nullptr };for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){grad_ptr[k] = (short*)grad[k].data + start;}for (int j = start; j < end; j++){// 找出最大值来判断方向for (int k = 0; k < KERNEL_SUM; k++){if (*amp_ang_ptr < *grad_ptr[k]){*amp_ang_ptr = *grad_ptr[k];*(amp_ang_ptr + 1) = k;}grad_ptr[k]++;}amp_ang_ptr += 2;}param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &_ang, gradients, i, &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < parts){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}edge_param.filter_count = 0;edge_param.thres = thres;edge = Mat::zeros(amp_ang.rows, amp_ang.cols, CV_8UC1);coordinate = Mat::zeros(amp_ang.rows, amp_ang.cols, CV_32FC2);for (int i = 0; i < parts; i++){std::thread f([](Mat* amp_ang, Mat* edge, Mat* coordinate, int cur_part, EDGE_PARAM* param){static const float root2 = (float)sqrt(2.0);static const float a2r = (float)(CV_PI / 180.0);static const short angle_list[] = { 270, 315, 0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225 };// 三角函数表float tri_list[2][KERNEL_SUM] = { 0 };float tri_list_root2[2][KERNEL_SUM] = { 0 };for (int j = 0; j < KERNEL_SUM; j++){tri_list[0][j] = (float)(0.5f * cos(angle_list[j] * a2r));// 0.5 前面的负号非常关键, 因为图像的 y 方向和直角坐标系的 y 方向相反tri_list[1][j] = (float)(-0.5f * sin(angle_list[j] * a2r));tri_list_root2[0][j] = tri_list[0][j] * root2;tri_list_root2[1][j] = tri_list[1][j] * root2;}const int thres = param->thres;const int end_x = amp_ang->cols - 1;const int rows = amp_ang->rows / param->parts;int start_y = rows * cur_part;int end_y = start_y + rows;if (cur_part){start_y -= 2;}if (cur_part >= param->parts - 1){end_y = amp_ang->rows;}start_y++;end_y--;for (int r = start_y; r < end_y; r++){// 3 * 3 邻域, 所以用 3 个指针, 一个指针指一行const short* pAmpang1 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r - 1);const short* pAmpang2 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r);const short* pAmpang3 = amp_ang->ptr<short>(r + 1);BYTE* pEdge = edge->ptr<BYTE>(r);float* pCoord = coordinate->ptr<float>(r);for (int c = 1; c < end_x; c++){const int j = c << 1;if (pAmpang2[j] >= thres){switch (pAmpang2[j + 1]){case 0:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j]){pEdge[c] = 255;pCoord[j] = (float)c;pCoord[j + 1] = r + tri_list[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang1[j] - pAmpang3[j]) /(pAmpang1[j] + pAmpang3[j] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));}break;case 4:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j]){pEdge[c] = 255;pCoord[j] = (float)c;pCoord[j + 1] = r - tri_list[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang1[j] - pAmpang3[j]) /(pAmpang1[j] + pAmpang3[j] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));}break;case 1:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang1[j - 2] - pAmpang3[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j - 2] + pAmpang3[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j] = c + tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]];pCoord[j + 1] = r + tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]];}break;case 5:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang1[j - 2] - pAmpang3[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j - 2] + pAmpang3[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j] = c - tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]];pCoord[j + 1] = r - tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]];}break;case 2:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang2[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang2[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;pCoord[j] = c + tri_list[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang2[j - 2] - pAmpang2[j + 2]) /(pAmpang2[j - 2] + pAmpang2[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j + 1] = (float)r;}break;case 6:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang2[j - 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang2[j + 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;pCoord[j] = c - tri_list[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]] * (pAmpang2[j - 2] - pAmpang2[j + 2]) /(pAmpang2[j - 2] + pAmpang2[j + 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j + 1] = (float)r;}break;case 3:if (pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang1[j + 2] && pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang3[j - 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang3[j - 2] - pAmpang1[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j + 2] + pAmpang3[j - 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j] = c + tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]];pCoord[j + 1] = r + tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]];}break;case 7:if (pAmpang2[j] > pAmpang1[j + 2] && pAmpang2[j] >= pAmpang3[j - 2]){pEdge[c] = 255;const float tmp = (float)(pAmpang3[j - 2] - pAmpang1[j + 2]) /(pAmpang1[j + 2] + pAmpang3[j - 2] - (pAmpang2[j] << 1));pCoord[j] = c - tmp * tri_list_root2[0][pAmpang2[j + 1]];pCoord[j + 1] = r - tmp * tri_list_root2[1][pAmpang2[j + 1]];}break;default:break;}}}}param->mtx.lock();param->filter_count++;param->mtx.unlock();}, &_ang, &edge, &coordinate, i, &edge_param);f.detach();}while (edge_param.filter_count < parts){std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));}waitKey(0);
}加速版原文没有给出显示图像,只保存了最后 亚像素边缘点集;
//显示 最大幅度值和方向
void show_amplitude_angle(Mat amp_ang)
{//显示梯度图Mat imgshow;// 显示幅值图像和角度图像normalize(amp_ang, imgshow, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);imgshow.convertTo(imgshow, CV_8UC2);namedWindow("amp_ang", WINDOW_NORMAL);imshow("amp_ang", imgshow);cout << "amp_ang : " << amp_ang.size() << " imgshow.size :" << imgshow.size() << endl;waitKey(0);
}
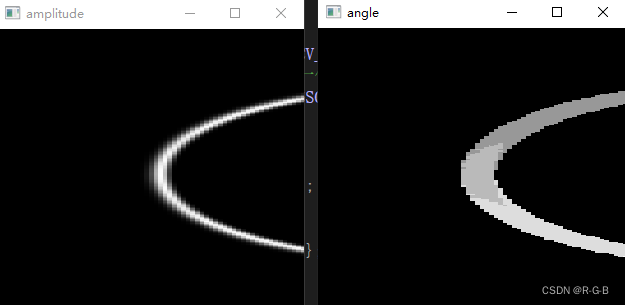
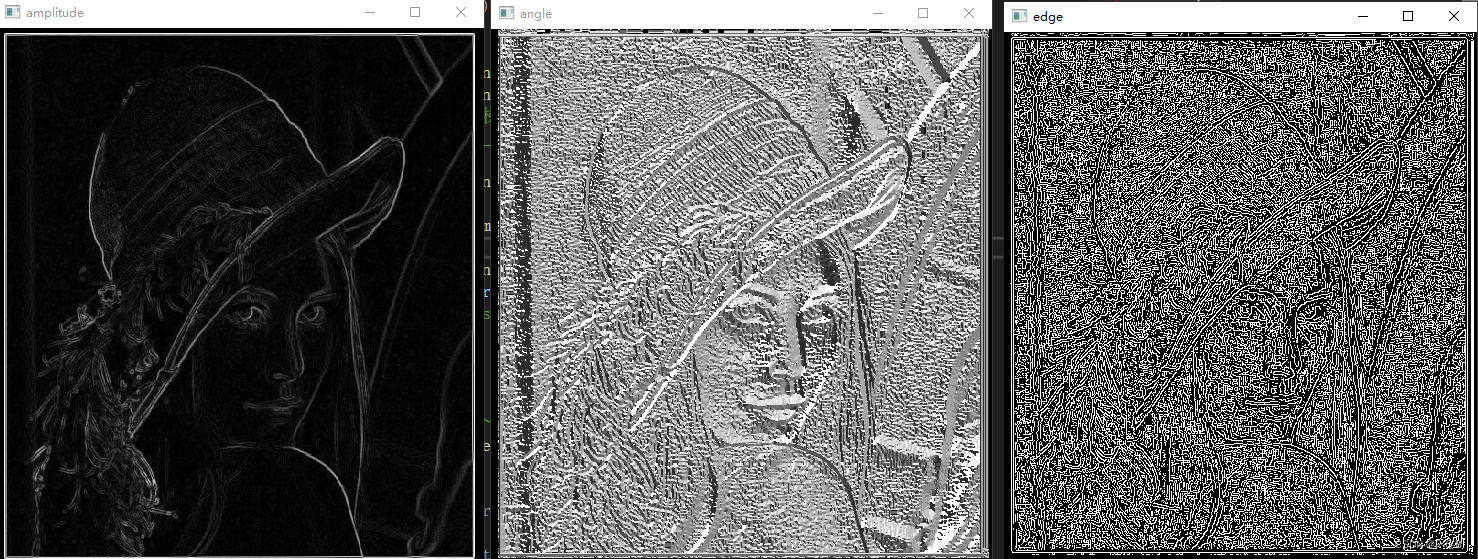
6.2 测试结果及分析
测试图片

parts: 图像分块数,>1 时报错
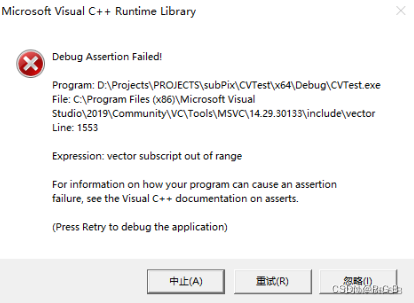
原文没有显示图像,自己增加了 最大幅度值和方向、edge 的显示,都报错
显示最大幅度值和方向,报错
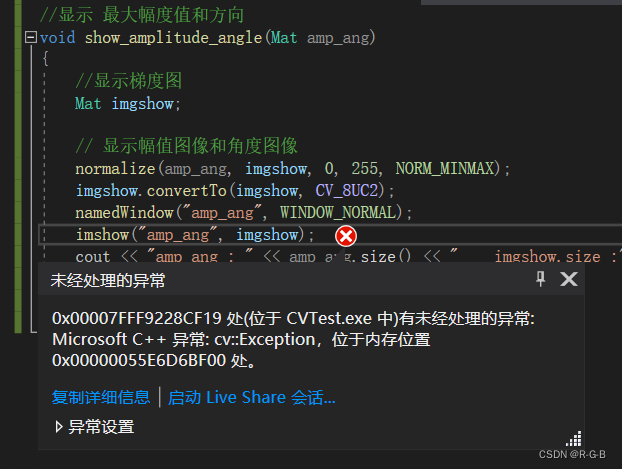
edge 的显示啥也没有
namedWindow("edge", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("edge", edge);
于是,断点调试,image watch 查看
SubPixelEdge(imgsrc, edge, vPts, thres, parts);
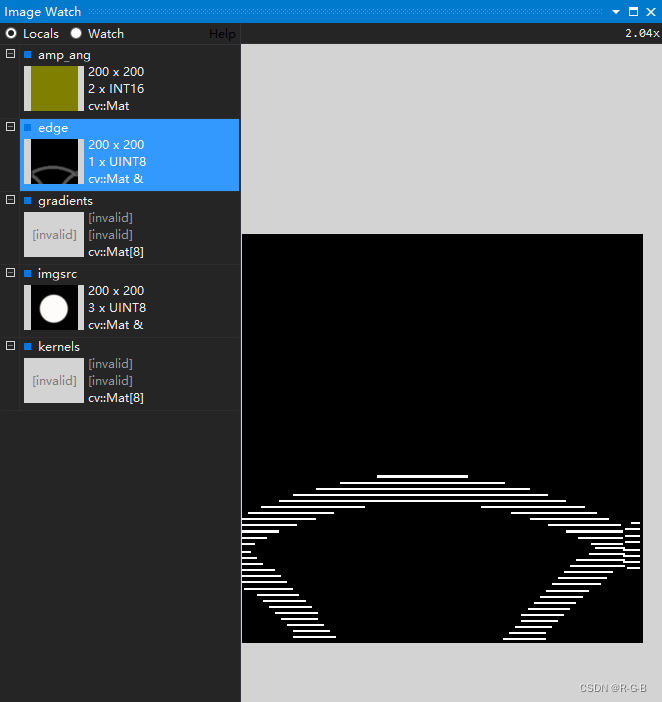
SubPixelEdge2(imgsrc, edge, coordinate, thres,parts);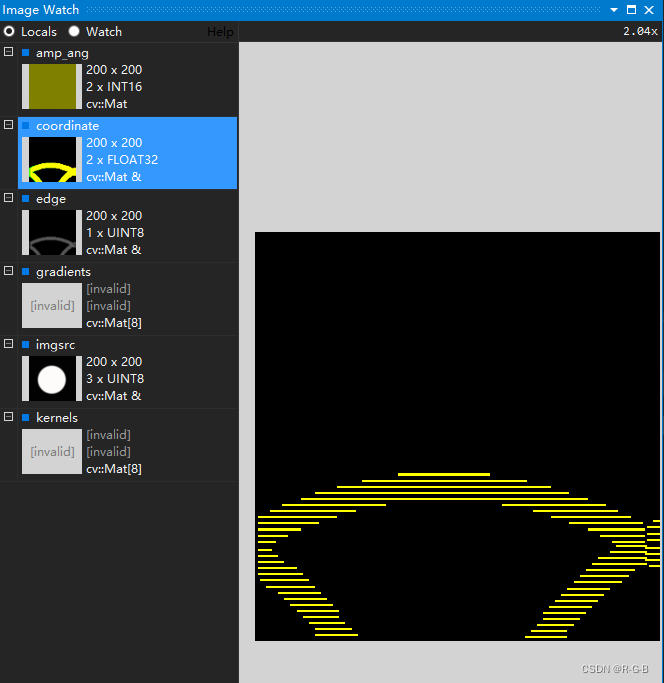
6.3 结论:梯度最大幅度值和方向 程序是有问题
结论:圆边缘检测成了这样,说明3.2 梯度方向 (梯度最大幅度值和方向)程序是有问题的







)




docker 安装 /客户端(win)分离部署)


:回调机制、通用排序与数组指针逻辑)



