书接上文
java一个脚手架搭建_redission java脚手架-CSDN博客
以微服务为基础搭建一套脚手架开始前的介绍-CSDN博客
脚手架开发-准备配置-进行数据初始化-配置文件的准备-CSDN博客
脚手架开发-准备配置-配置文件的准备项目的一些中间件-CSDN博客
脚手架开发-Nacos集成-CSDN博客
脚手架开发-网关集成-CSDN博客
Common包
在项⽬开发过程中,常常会进⾏诸如操作JSON、操作字符串、操作时间等⼯具类。在不同的项⽬ ⾥,这些操作往往是相同的。因此,在这个项⽬中,我们可以将这部分操作封装为基础通⽤的部 分。
- 了解封装基础⼯具类;
- 公共模块及基础通⽤包创建;
- 基础通⽤⼯具类封装完成;
- 基础通⽤⼯具类功能验证测试通过。
公共模块及基础通用包创建
相信有的朋友已经注意到了,在这个脚手架开发中是有一个公共模块的,它独立出来就是未来存放所有其他模块公共使用的类,而common包下有一个具体的层次common-core就是专门用来存放我们的基础通用工具类。
common和common-core都是用module创建出来的,到了后面的包则是package
废话不多说,如图
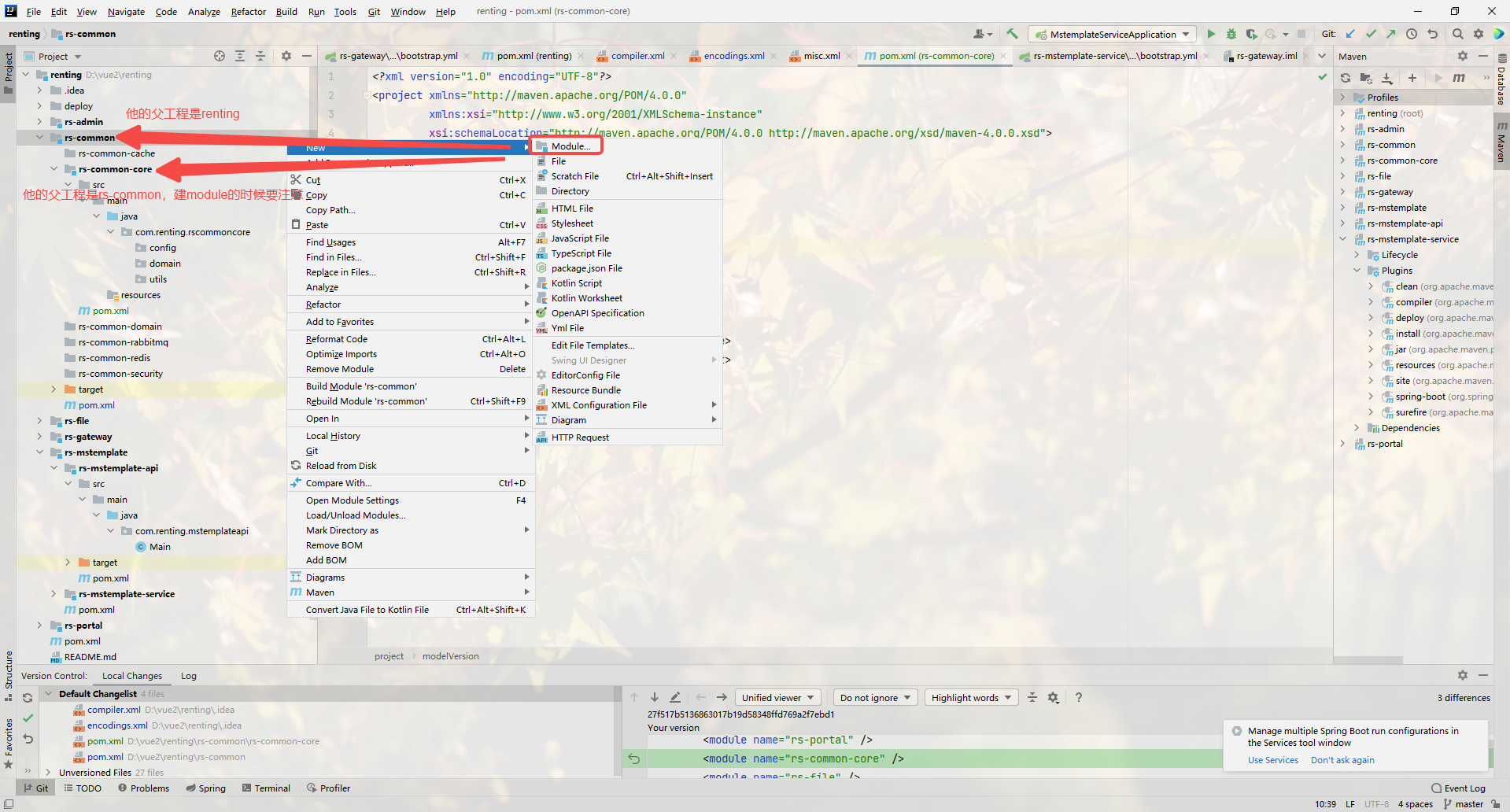
- 1. 创建公共模块 rs-common
- 2.创建公共模块的⼦⼯程基础通⽤包( rs-common-core)
- 3. 在 rs-common-core ⼯程中创建 com.renting.rscommoncore 包。
- 4. 在 com.renting.rscommoncore 包下创建 utils 包⽤于存放基础通⽤⼯具类。
封装JSON基础⼯具类
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是⼀种轻量级的数据交换格式。数据交换指的是客⼾端和服务 器之间业务数据的传输格式。 JSON 是⼀种完全独⽴于语⾔的⽂本格式,开发者很容易阅读和编写, 机器很容易解析和⽣成,能有效地提升⽹络传输效率。这些优点也使 JSON 成为⼀种理想的独⽴语⾔⽂本格式。
需要所有⼯具类的理由都是⼀样的,就是项⽬开发中使⽤的频率⾼。
在⽹络传输场景中,JSON 格式的数据量相对较⼩。与其他格式(如 XML)相⽐,JSON 没有过多的标签和冗余信息,这使得它在带宽有限的⽹络环境下能够更⾼效地传输数据。所以在⽹络传输中我们⼀ 般选择JSON作为数据传输格式。
在项⽬开发中我们经常会涉及到要将对象数据进⾏存储。⽐如说要将对象存储到Redis等存储机制中。 描述同样的消息,json相⽐xml占⽤更少的空间。
我们可以看一个直观的例子。
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<user><id>1</id><name>张三</name><age>30</age>
</user>
Json
{"id": 1,"name": "张三","age": 30}那么我们应该做的,是什么?
- 提供对象转json(对象序列化)
- 提供对象转json格式化
- 提供json转对象(对象反序列化)
怎么封装?
1.创建JsonUtil类
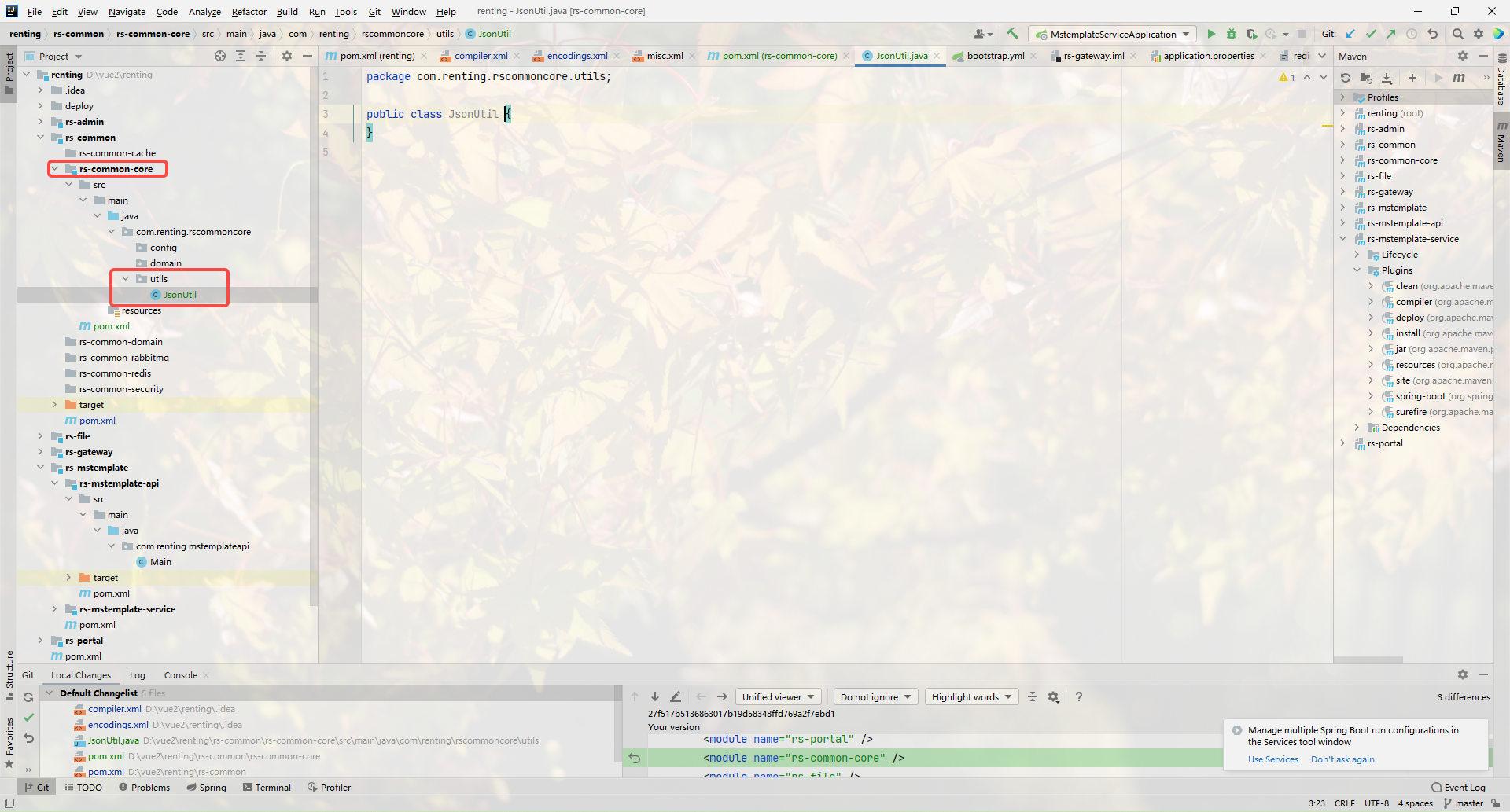
2.引入依赖
rs-common中的pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><parent><artifactId>renting</artifactId><groupId>org.example</groupId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version></parent><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><artifactId>rs-common</artifactId><packaging>pom</packaging><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin></plugins></build><modules><module>rs-common-core</module></modules><properties><maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies>
</project>
3.JsonUtil中的代码
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.json.JsonMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;/*** JSON⼯具类*/@Slf4jpublic class JsonUtil {/*** 对象转换器*/private static ObjectMapper OBJECT_MAPPER;static {OBJECT_MAPPER =JsonMapper.builder().configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false).configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false).configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false).configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false).configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false).configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false).addModule(new JavaTimeModule()).defaultDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat(CommonConstants.S)).serializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL).build();}/*** 禁⽤构造*/private JsonUtil() {}/*** 对象转Json格式字符串* @param obj 对象* @return Json格式字符串* @param <T> 对象类型*/public static <T> String obj2String(T obj) {if (obj == null) {return null;}try {return obj instanceof String ? (String) obj :OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsString(obj);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse Object to String error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 对象转Json格式字符串(格式化的Json字符串)* @param obj 对象* @return 美化的Json格式字符串* @param <T> 对象类型*/public static <T> String obj2StringPretty(T obj) {if (obj == null) {return null;}try {return obj instanceof String ? (String) obj :OBJECT_MAPPER.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(obj);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse Object to String error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串转换为⾃定义对象* @param str 要转换的字符串* @param clazz ⾃定义对象的class对象* @return ⾃定义对象* @param <T> 对象类型*/public static <T> T string2Obj(String str, Class<T> clazz) {if (str == null || str.isEmpty()|| clazz == null) {return null;}try {return clazz.equals(String.class) ? (T) str :OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, clazz);} catch (Exception e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串转换为⾃定义对象,⽀持复杂的泛型嵌套* @param str json字符串* @param valueTypeRef 对象模板信息* @return 对象类对应的对象* @param <T> 对象类*/public static <T> T string2Obj(String str, TypeReference<T> valueTypeRef){if (str == null || str.isEmpty() || valueTypeRef == null) {return null;}try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str,valueTypeRef);} catch (Exception e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串转换为⾃定义字段转为list,⽀持List嵌套简单对象* @param str json字符串* @param clazz 对象类* @return 对象列表* @param <T> 对象类型*/public static <T> List<T> string2List(String str, Class<T> clazz) {if (str == null || str.isEmpty()|| clazz == null) {return null;}JavaType javaType =OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, clazz);try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, javaType);} catch (IOException e) {log.error("Parse String to Object error : {}" + e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串转换为⾃定义字段转为map,⽀持Map嵌套简单对象* @param str str 字符串信息* @param valueClass valueClass value的类别* @return map对象* @param <T> value 的类型*/public static <T> Map<String, T> string2Map(String str, Class<T>valueClass){if (str == null || str.isEmpty() || valueClass == null) {return null;}JavaType javaType =OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructMapType(LinkedHashMap.class,String.class, valueClass);try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, javaType);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}
}
解释:
1.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false)
在反序列化时,当遇到JSON数据中存在Java对象对应类中没有定义的属性时,默认情况下 Jackson会抛出异常。通过将这个配置项设置为false,表⽰允许在反序列化时忽略那些未知的属性,不会因为出现额外的属性⽽导致反序列化失败,增强了对不同来源JSON数据的兼容性。
2. .configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)在序列化时,如果Java对象中包含⽇期类型默认情况下Jackson可能会将⽇期转换为时间戳(⼀个表⽰从某个特定时间点开始到当前时间的毫秒数等形式的数值来表⽰。将此配置设置为false,意味着不采⽤时间戳的⽅式来表⽰⽇期,⽽是会按照后续配置的其他⽇期相关格式进⾏序列 化,以便⽣成更具可读性的⽇期格式表⽰在JSON数据中。
3. .configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS,false)在序列化时,Java对象中没有任何属性值(为空),默认情况下Jackson可能会抛出异常。设置 此项为false后,允许对这样的空对象进⾏序列化,即便对象没有实质内容也能⽣成对应的JSON 表⽰(通常可能是⼀个空的JSON对象{}),避免了因对象为空导致序列化失败的情况。
4. .configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false)在反序列化时,如果JSON数据中指定的类型信息与期望的Java类型层次结构不匹配(例如类型 标识错误等情况),默认会抛出异常。将这个配置设为false,可以放宽这种限制,使得在遇到类 型不太准确但仍有可能处理的情况下,尝试继续进⾏反序列化⽽不是直接失败,提⾼对可能存在错误类型标识的JSON数据的容错性。
5. .configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)在序列化时,如果Java对象中有以⽇期类型作为键(⽐如在Map中,键是Date类型等情况的结构,如果设置为true会将⽇期键转换为时间戳形式。设置为false则按照其他⽇期相关配置来处 理,保证⽇期键也以期望的格式进⾏序列化,使得整个JSON结构中⽇期相关内容都能保持统⼀的 格式呈现。(默认值为false)
6. .configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false) Jackson⽀持通过在Java类的属性或⽅法上添加各种注解来定制序列化和反序列化⾏为。将此配 置设为false,表⽰不依赖这些注解来进⾏相关操作,⽽是更多地依据全局配置(如上述其他配置 项)来控制序列化和反序列化过程,适⽤于希望统⼀管理JSON处理规则,减少因注解使⽤不当或 过多导致的复杂性的场景。
7. addModule(newJavaTimeModule()) 这是序列化LocalDateTIme和LocalDate的必要配置,由Jackson-data-JSR310实现。
8. .defaultDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat(CommonConstants.STANDARD_FORMAT)) 所有的⽇期格式都统⼀为以下的样式,即yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
4.泛型擦除<理解>
我们给出这样一段代码
@Test2
public void string2ListObjTest(){
// TestRegion testRegion = new TestRegion();
// testRegion.setId(1L);
// testRegion.setName("北京");
// testRegion.setFullName("北京市");
// testRegion.setCode("110000");
// List<TestRegion> regionList = new ArrayList<>();
// regionList.add(testRegion);
// System.out.println(JsonUtil.obj2String(regionList));
// [{"id":1,"name":"北京","fullName":"北京市","code":"110000"}]
List list = JsonUtil.string2Obj("[{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"北京\",\"fullName\":\"北京市\",\"code\":\"110000\"}]", List.class);System.out.println(list);我们单步调试可以看到list和我们定义的类型不⼀致
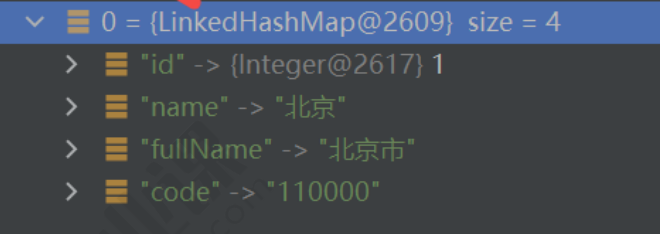
这是因为java的泛型擦除导致的,如果后⾯代码我们基于List继续定义,那么会报类型不匹配。
什么是泛型擦除?
Java中的泛型擦除(Type Erasure)是指Java编译器在编译泛型代码时,会移除泛型类型参数的相关信息,使得⽣成的字节码中不包含泛型类型信息。这使得Java泛型在运⾏时(Runtime)表现为原始类型(Raw Type)。
为什么出现泛型擦除:
向后兼容:新旧代码兼容,在编译时泛型信息就擦除了,所以旧版本jvm可以运载新代码
类型安全:尽管泛型信息在编译时被擦除,但在编译时会进⾏类型检查,确保泛型的使用是安全的。这意味着你可以在编译时发现类型错误,而不是在运行时
避免性能开销:所有的类型信息在编译时就已经确定,泛型擦除避免了如果JVM需要在运⾏时维护泛型类型信息引入的额外开销。
解决方法:
常见的Collection如 List、Map 中包含泛型,需要先反序列化Collection类型为泛型的CollectionType。
如果是ArrayList那么使⽤ObjectMapper的 getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(collectionClass,YourBean.class)。
HashMap那么 ObjectMapper 的 getTypeFactory().constructMapType(HashMap.class,String.class, YourBean.class)。
封装Bean拷贝基础工具类
Bean拷⻉(BeanCopy)是指在⾯向对象编程中,将⼀个Java对象(通常称为源Bean)的属性值复制到另⼀个Java对象(目标Bean)中的操作。
示例:
@Testpublic void beanCopyTest() {//源bean : TestUser {"name" : "张三","sex" : "男","age" : 29}//⽬标bean: TestUserVO TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();userVO.setName(testUser.getName());userVO.setAge(testUser.getAge());
}
Web项目中有控制器(Controller)层、业务逻辑(service)层、数据访问 (DAO)层。不同层之间通常会使用不同的数据模型,这就意味着项目中往往不止一种数据模型,经常需要将数据从一种数据模型转换成另外一种 数据模型,正因如此,才需要Bean拷贝。
具体来说分为这
几种常见的数据模型:
DO(Data Object)是⼀个与数据库表结构对应的对象,也叫持久化对象。DO通常⽤来在DAO层 (数据访问层)和数据库进⾏交互。
BO(Business Object)是⼀个封装业务逻辑的对象,主要存在于业务逻辑层。它封装了业务逻辑 相关的数据和操作。BO不仅仅是简单的数据容器,还包含了业务规则和业务流程相关的⽅法。
DTO(Data Transfer Object)是⼀个⽤来传输数据的对象。DTO⽤来在不同层或不同系统之间传 递数据,⽐如从Service层传递到Controller层或者Controller层传递到service层等。DTO可以避免 在层与层之间传递过多的不必要的数据,同时也可以隐藏内部的数据结构和实现细节。
VO(View Object)是⼀个⽤来展⽰数据的对象(返回给前端的数据)。它是根据具体的视图(如 Web⻚⾯、桌⾯应⽤的界⾯等)的要求,将数据以⼀种合适的形式进⾏组织和封装,以便于在视图中进进行展示。
POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object)是⼀个普通的Java对象,它没有任何特殊的要求或约束,可 以⽤来表⽰任何类型的数据。
拷贝
手动拷贝
private String QQ;...............public TestUserVO convertToVO() {TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();userVO.setName(this.name);userVO.setAge(this.age);............return userVO ;
拷贝工具
BeanUtils.copyProperties() 是 Spring 框架提供的⼀个⼯具⽅法,它可以简化对象属性的拷贝操作
TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(user, userVO);但如果源bean和⽬标bean之间的属性名称不⼀致,或者源bean向⽬标bean拷⻉时需要对源bean 中的属性值进⾏处理后再进⾏拷⻉。此时使⽤⼯具类就⽆法准确的完成拷⻉⼯作了
拷贝工具类+手动拷贝
使⽤spring提供的⼯具类,针对具体的对象提供专⽤的bean拷⻉⽅法,就是拷贝工具类+手动拷贝
例如
@Getter
@Setter
@ToStringpublic class TestUserVO {private String nickName;private int age;private String school;private String contactInfo;
}
public class TestUser {private String name;private int age;private String sex;private String school;private String weChat;private String QQ;...............public TestUserVO convertToVO() {TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();BeanUtils.copyProperties(user, userVO);userVO.setNickName(this.name);userVO.setContactInfo(this.weChat + "--" + this.QQ);return userVO ;}
}
内置拷⻉⼯具类+拷⻉⼯具类+⼿动拷⻉
单个对象普通拷⻉:直接使⽤spring提供的⼯具类。
列表对象普通拷⻉:由于拷⻉spring框架提供的bean拷⻉⼯具类⽆法⽀持对列表对象的拷⻉⼯作,所 以我们需要⾃⼰封装内置Bean拷⻉⼯具类提供对列表对象的拷⻉⽅法。
特殊拷⻉(包括列表对象和单个对象):需要⼿动拷⻉。针对具体的对象提供专⽤的bean拷⻉⽅法。
Bean拷贝工具类
1.创建BeanCopyUtil工具类
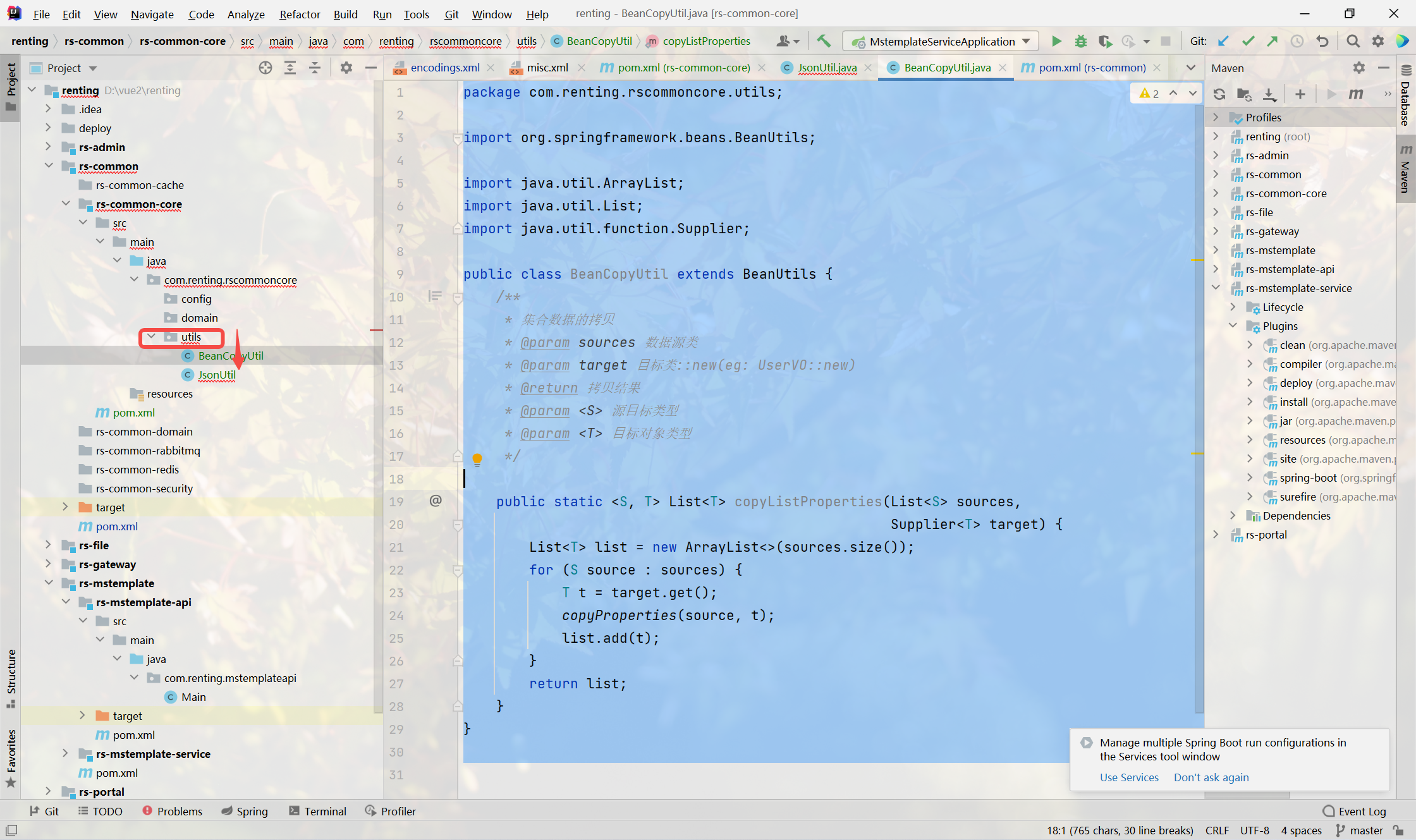
BeanUtils.copyProperties 不⽀持列表拷⻉,默认只⽀持java bean,我们扩展下该⽅法⽀持 列表拷⻉
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Supplier;public class BeanCopyUtil extends BeanUtils {/*** 集合数据的拷⻉* @param sources 数据源类* @param target ⽬标类::new(eg: UserVO::new)* @return 拷⻉结果* @param <S> 源⽬标类型* @param <T> ⽬标对象类型*/public static <S, T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<S> sources,Supplier<T> target) {List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(sources.size());for (S source : sources) {T t = target.get();copyProperties(source, t);list.add(t);}return list;}
}2.Spring框架提供的Bean拷⻉⼯具类问题
属性类型不⼀致导致拷⻉失败
实际开发中,很可能会出现同⼀字段在不同的类中定义的类型不⼀致,例如ID,可能在A类中 定义的类型为Long,在B类中定义的类型为String,此时如果使⽤BeanUtils.copyProperties进⾏拷⻉,就会出现拷⻉失败的现象,导致对应的字段为null
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructorclass SourcePoJo{private String username;private Long id;
}@Data class TargetPoJo{private String username;private String id;
}@Testvoid copyfail1() {SourcePoJo sourcePoJo = new SourcePoJo("bite", (long) 1000000);TargetPoJo targetPoJo = new TargetPoJo();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePoJo,targetPoJo);System.out.println(targetPoJo);
}输出结果会变成
BeanUtilsTests.TargetPoJo(username=bite, id=null)在实际开发中,很可能会出现同⼀字段在不同的类中定义的类型不⼀致,例如ID,可能在A类中 定义的类型为Long,在B类中定义的类型为long,此时如果使BeanUtils.copyProperties进⾏拷⻉,就会出现拷⻉失败的现象,会抛出FatalBeanException。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructorclass SourcePoJo{private String username;private Long id;
}@Dataclass TargetPoJo2{private String username;private long id;
}@Testvoid copyfail2() {SourcePoJo sourcePoJo = new SourcePoJo();sourcePoJo.setUsername("bite");TargetPoJo2 targetPoJo2 = new TargetPoJo2();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePoJo,targetPoJo2);System.out.println(targetPoJo2);
}输出结果:
org.springframework.beans.FatalBeanException: Could not copy property 'id'
from source to targetat
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties(BeanUtils.java...(报错信息)
底层实现为反射拷⻉效率低
BeanUtils.copyProperties底层是通过反射获取到对象的set和get⽅法,然后通过get、set完成数据的 拷⻉,整体拷⻉效率较低。
使⽤BeanUtils.copyProperties拷⻉数据和直接set的⽅式赋值效率对⽐,为了便于直观的看出 效果,这⾥以拷⻉1万次为例:
@Testvoid copyslow(){long copyStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();SourcePoJo source = new SourcePoJo("bite",1000000L);TargetPoJo2 target = new TargetPoJo2();for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);}System.out.println("copy⽅式:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-
copyStartTime));long setStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {target.setUsername(source.getUsername());target.setId(source.getId());}System.out.println("set⽅式:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-setStartTime));
}结果:
copy⽅式:127
set⽅式:0BeanUtils.copyProperties是浅拷⻉
浅拷贝是说在创建⼀个新对象(⽬标对象),⽬标对象的属性值与原始对象相同,但对于引⽤类型的属性,仍然共享相同的引⽤。也就是说在浅拷⻉下,当源对象的引⽤属性的值发⽣变化时,⽬标对象的引⽤属性值也会随之发⽣变化。
我们可以举一个简单的例子
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructorclass Card {private String num;
}@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Dataclass Person {private String name;private Card card;
}@Testvoid copylight(){Person sourcePerson = new Person("bite",new Card("123456"));Person targetPerson = new Person();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson, targetPerson);System.out.println(targetPerson);sourcePerson.getCard().setNum("654321");System.out.println(targetPerson);//修改后代码:
Person sourcePerson = new Person("bite",new Card("123456"));Person targetPerson = new Person();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson, targetPerson);Card targetCard = new Card();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson.getCard(), targetCard);targetPerson.setCard(targetCard);System.out.println(targetPerson);sourcePerson.getCard().setNum("654321");System.out.println(targetPerson);
}结果如下:
BeanCopyUtilTests.Person(name=bite, card=BeanCopyUtilTests.Card(num=123456))
BeanCopyUtilTests.Person(name=bite, card=BeanCopyUtilTests.Card(num=654321))内部类数据无法成功拷贝
Spring 的 BeanUtils.copyProperties 在处理内部类属性时会遇到拷贝失败的问题,这是由其设计机制决定的。
-
访问权限限制:
-
内部类的字段默认是
private访问级别 -
BeanUtils使用反射访问字段时,无法突破 Java 的访问控制规则 -
示例:内部类
Inner的字段innerValue无法被外部访问
-
-
Getter/Setter 缺失:
-
内部类的字段通常没有公共的 getter/setter 方法
-
BeanUtils依赖标准的 JavaBean 规范(通过 getter/setter 访问属性) -
当缺少这些方法时,属性拷贝会静默失败
-
其它的一些公共工具类
时间戳工具类
- 获取当前时间戳
- 获取未来x秒的时间戳
- 获取未来x天的时间戳
- 获取未来x⽉的时间戳
- 获取未来x年的时间戳
- 计算两个时间戳之间的差异
- 所有⽅法均提供返回秒级时间和毫秒级时间两种实现
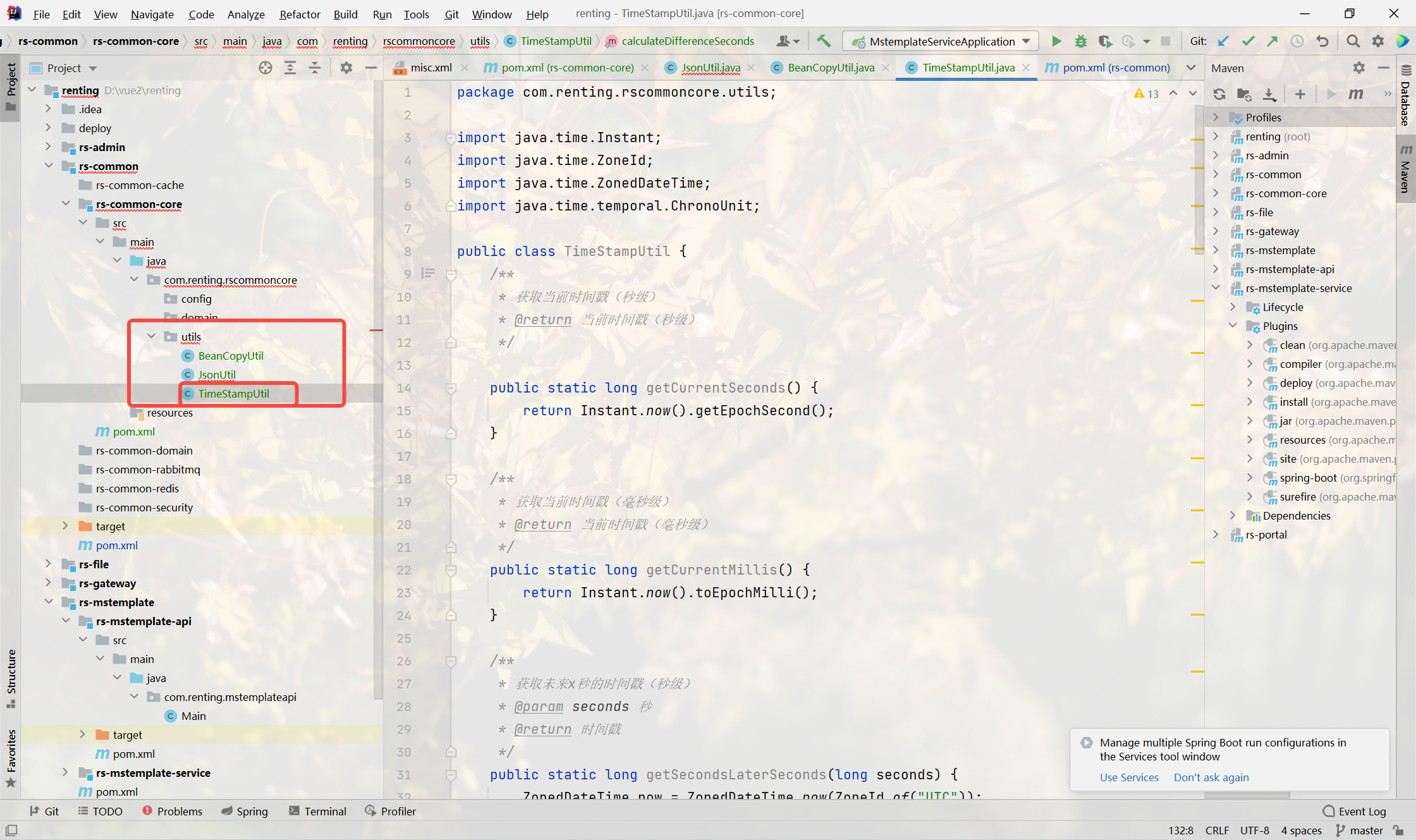
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;public class TimeStampUtil {/*** 获取当前时间戳(秒级)* @return 当前时间戳(秒级)*/public static long getCurrentSeconds() {return Instant.now().getEpochSecond();}/*** 获取当前时间戳(毫秒级)* @return 当前时间戳(毫秒级)*/public static long getCurrentMillis() {return Instant.now().toEpochMilli();}/*** 获取未来x秒的时间戳(秒级)* @param seconds 秒* @return 时间戳*/public static long getSecondsLaterSeconds(long seconds) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 获取未来x秒的时间戳(毫秒级)* @param seconds 秒* @return 时间戳*/public static long getSecondsLaterMillis(long seconds) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);return secondsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 获取未来x天的时间戳(秒级)* @param days 天* @return 时间戳*/public static long getDaysLaterSeconds(long days) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusDays(days);return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 获取未来x天的时间戳(毫秒级)* @param days 天* @return 时间戳*/public static long getDaysLaterMillis(long days) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusDays(days);return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 获取未来x⽉的时间戳(秒级)* @param months ⽉* @return 时间戳*/public static long getMonthsLaterSeconds(long months) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);return monthsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 获取未来x⽉的时间戳(毫秒级)* @param months ⽉* @return 时间戳*/public static long getMonthsLaterMillis(long months) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 获取未来x年的时间戳(秒级)* @param years 年* @return 时间戳*/public static long getYearLaterSeconds(long years) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);return yearLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 获取未来x年的时间戳(毫秒级)* @param years 年* @return 时间戳*/public static long getYearLaterMillis(long years) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);return yearLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 计算两个时间戳之间的差异(毫秒)* @param timestamp1 时间戳1* @param timestamp2 时间戳2* @return 时间戳差异(毫秒)*/public static long calculateDifferenceMillis(long timestamp1, longtimestamp2) {return ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp1),Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp2));}/*** 计算两个时间戳之间的差异(秒)* @param timestamp1 时间戳1* @param timestamp2 时间戳2* @return 时间戳差异(秒)*/public static long calculateDifferenceSeconds(long timestamp1, longtimestamp2) {return ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp1),Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp2));}
}String⼯具类
- 提供字符串常⽤操作
- 判断url是否与规则匹配(url:特殊的字符串)
- 判断指定字符串(url)是否与指定匹配规则链表中的任意⼀个匹配规则匹配
引入依赖
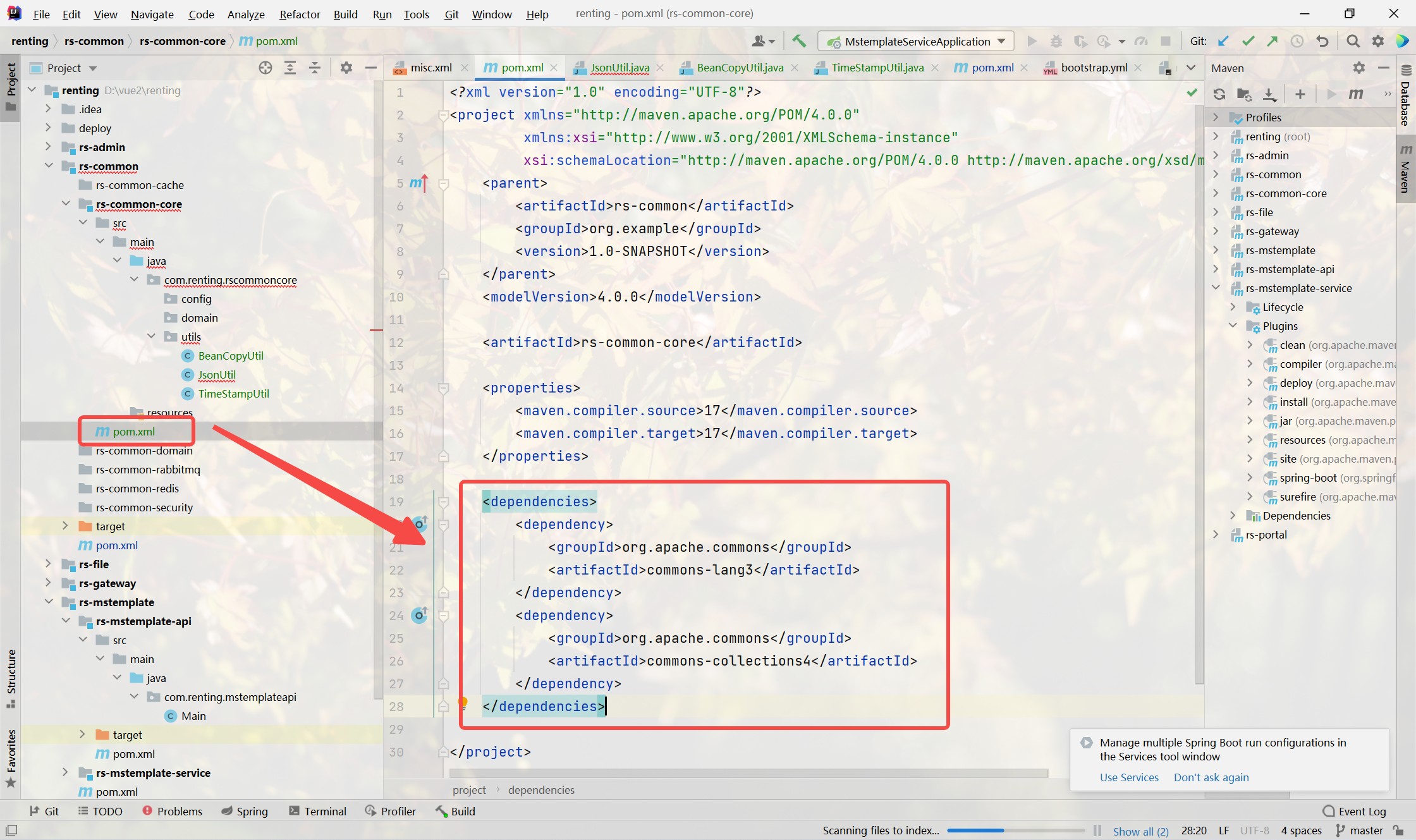
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId></dependency>
</dependencies>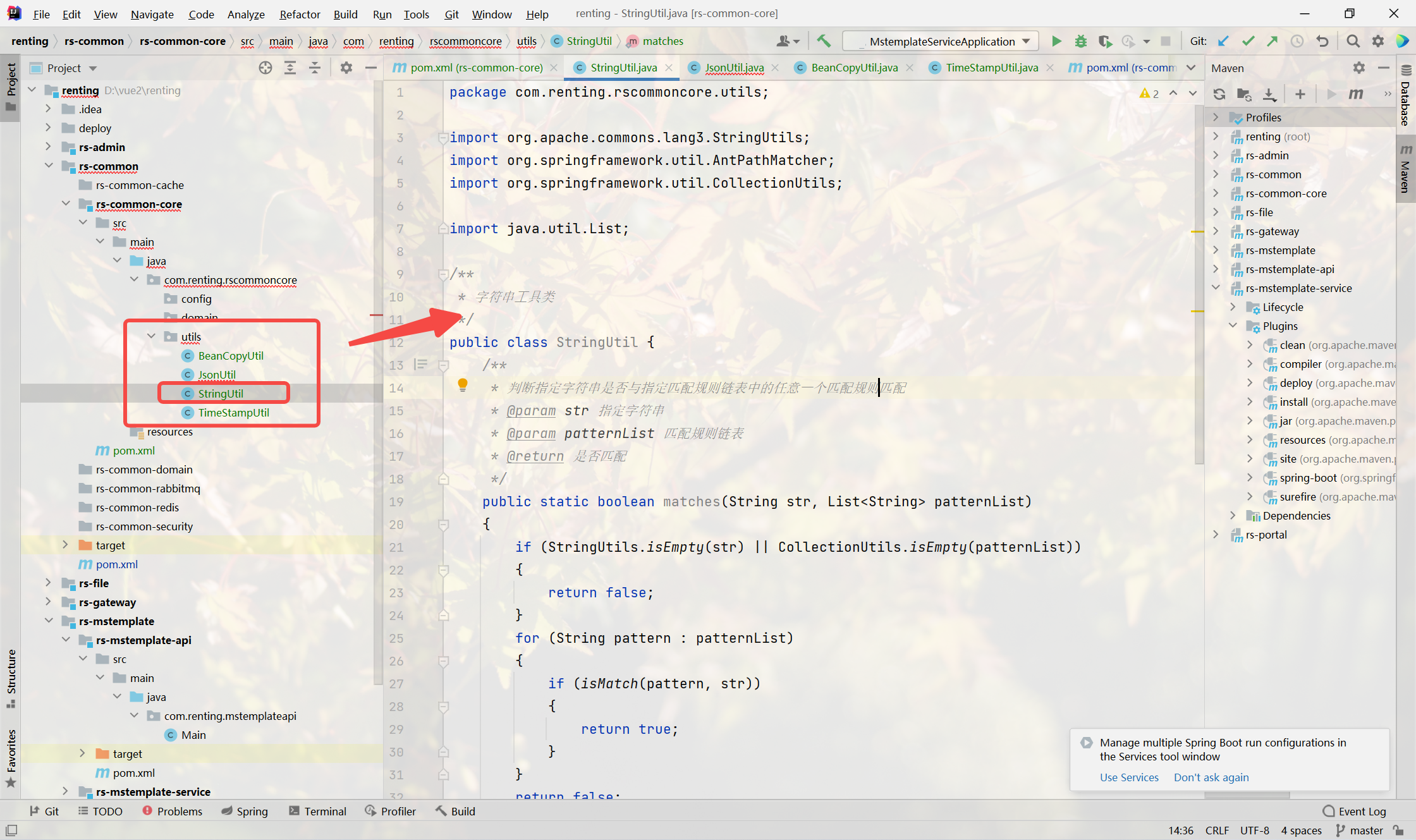
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;import java.util.List;/*** 字符串⼯具类*/
public class StringUtil {/*** 判断指定字符串是否与指定匹配规则链表中的任意⼀个匹配规则匹配* @param str 指定字符串* @param patternList 匹配规则链表* @return 是否匹配*/public static boolean matches(String str, List<String> patternList){if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(patternList)){return false;}for (String pattern : patternList){if (isMatch(pattern, str)){return true;}}return false;}/*** 判断url是否与规则匹配* 匹配规则:* 精确匹配* 匹配规则中包含 ? 表⽰任意单个字符;* 匹配规则中包含 * 表⽰⼀层路径内的任意字符串,不可跨层级;* 匹配规则中包含 ** 表⽰任意层路径的任意字符,可跨层级* @param pattern 匹配规则* @param url 需要匹配的url* @return 是否匹配*/public static boolean isMatch(String pattern, String url){if (StringUtils.isEmpty(url) || StringUtils.isEmpty(pattern)) {return false;}AntPathMatcher matcher = new AntPathMatcher();return matcher.match(pattern, url);}
}
如果说还有需要添加的,不论是说你需要的还是后面加上来的,满足下面三个原则即可
⼯具类封装原则
- 先从成熟的⼚商所提供的⼯具类当中寻找,推荐:spring和apache,具体不做限制,但是要确定安 全可靠,明确⼯具类的特点。
- 如果成熟⼚商所提供的⼯具类当中没有们想要使⽤的⽅法,再封装内置⼯具类提供。
- 公司如果对此有明确要求,以公司要求为准。(常⻅要求:对于⼀种⼯具类的使⽤尽可能统⼀)





)
)



详解和完整示例)




变量的梯度)



摘自Openloong社区)