kmp算法

最大相同真前后缀:
如 ababa的最大真前后缀为aba, 而不是ababa(真前后缀与真子集类似,不可是本身,不然没意义)
所以next[1] = 0;//string的下标从1开始
kmp模拟

next初始化:
注意:下标从1开始

KMP用法示例code

例题1:斤斤计较的小z
link:1.斤斤计较的小Z - 蓝桥云课
code
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const ll MAXN = 1e6 + 7;
char p[MAXN], s[MAXN];
ll n, m;
ll nex[MAXN];int main()
{ll ans = 0;cin>>p+1>>s+1;// 保证字符串下标从1开始m = strlen(p + 1);n = strlen(s + 1);// init nexnex[0] = nex[1] = 0;for(int i = 2, j = 0; i <= m; i++){while(j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = nex[j];if(p[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;nex[i] = j;}// KMPfor(int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i++){while(j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = nex[j];if(s[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;if(j == m) ans++;}cout<<ans<<endl;return 0;
}字符串hash

字符串hash初始化
使用ull类型,不用担心溢出(溢出时自动取模,不会影响结果)

tips:
- s[i] - 'A' + 1是为了保证其不为0,如字符串为AAA时,不加1的话,其哈希值为0,与A,AA哈希值相同,这是我们不希望的
- 更方便地,我们直接令h[i] = h[i-1] * base + s[i]即可
- 注意base值要比字符值的范围更大,以降低hash冲突的概率(一般设置为131)
获取字串s[l] ~ s[r]的hash
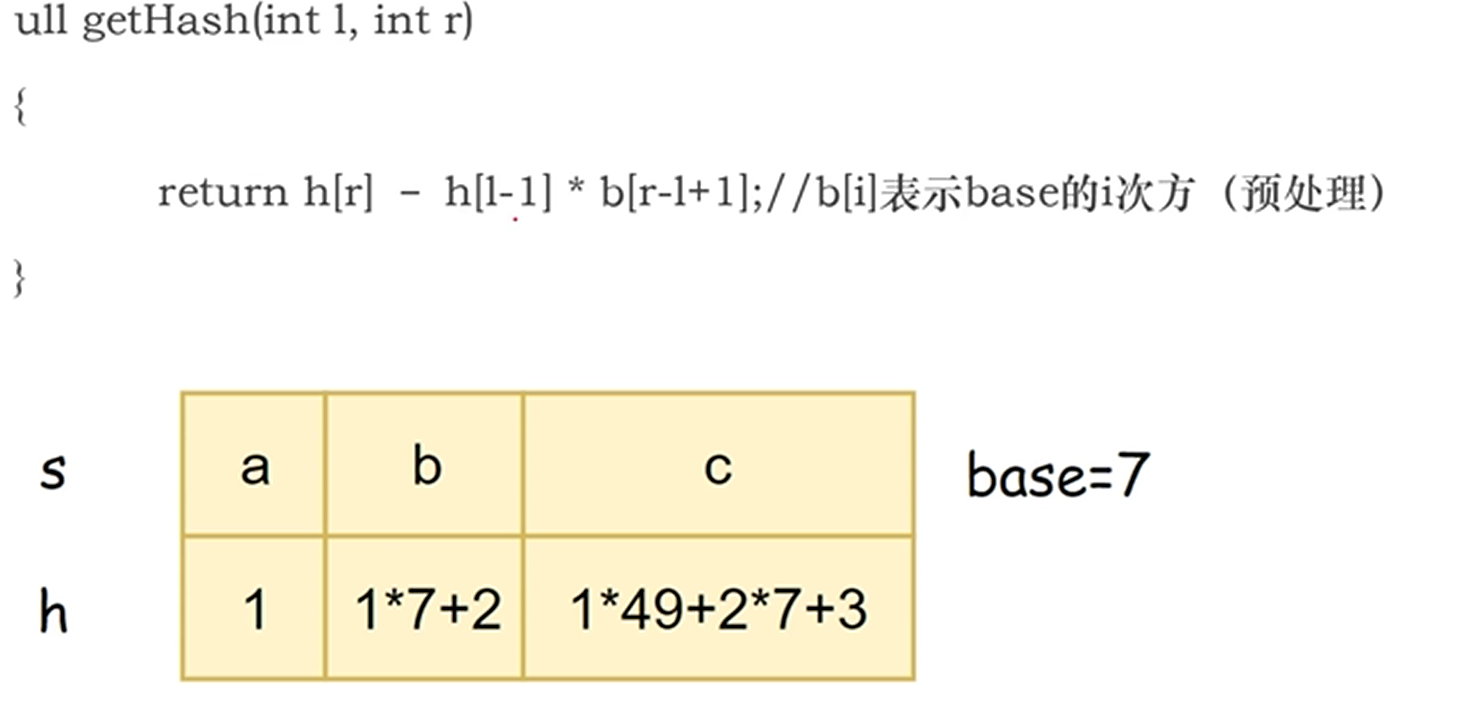
例题1的字符串hash解法
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
const ll MAXN = 1e6 + 7;
ull hp[MAXN], hs[MAXN], b[MAXN];// hs[i]:s[1]~s[i]对应的hash值; b[i]:base的i次方
ull base = 131;
char p[MAXN], s[MAXN];
ll n, m;ull getHash(ull* h, ull bg, ull ed)
{return h[ed] - h[bg] * b[ed - bg];// ull溢出相当于自动取模, 所以不用担心溢出
}int main()
{ll ans = 0;cin>>p+1>>s+1;// 保证字符串下标从1开始m = strlen(p + 1);n = strlen(s + 1);// init hp, hs, bb[0] = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){b[i] = base * b[i-1];hp[i] = hp[i-1] * base + p[i];hs[i] = hs[i-1] * base + s[i];}// 匹配相同字符串(利用hash值)for(int i = 1; i + m - 1 <= n; i++){if(getHash(hp, 1, m) == getHash(hs, i, i + m - 1)) ans++;}cout<<ans<<endl;return 0;
}总结
KMP与字符串hash都是用于字符串匹配的算法,字符串hash非常简单(虽然有极小概率的hash冲突导致判断失误,匹配失败),KMP算法更加严谨;


 本节目标 1. 掌握树的基本概念 2. 掌握二叉树概念及特性 3. 掌握二叉树的基本操作 4. 完成二叉树相关的面试题练习)





![【系列文章】Linux中的并发与竞争[05]-互斥量](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【系列文章】Linux中的并发与竞争[05]-互斥量)




预测)

)



