引言:Kubernetes的战略地位与核心价值
在云原生技术生态中,Kubernetes已成为容器编排的事实标准。根据2023年全球云原生调查报告:
- 全球96% 的组织正在使用或评估Kubernetes
- 企业生产环境Kubernetes采用率增长400%(2019-2023)
- Kubernetes集群平均管理容器数量达15,000+
- 使用Kubernetes的企业资源利用率提升65%,部署速度提升90%
Kubernetes核心价值矩阵:
┌───────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┬──────────────────────┐
│ 业务需求 │ 技术挑战 │ Kubernetes解决方案 │
├───────────────────┼──────────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤
│ 快速交付 │ 环境不一致 │ 声明式配置 │
│ 弹性扩展 │ 资源利用率低 │ 自动扩缩容 │
│ 高可用保障 │ 单点故障风险 │ 自愈与滚动更新 │
│ 多云部署 │ 供应商锁定 │ 基础设施抽象 │
│ 微服务治理 │ 服务间通信复杂 │ Service Mesh集成 │
└───────────────────┴──────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────┘本文将全面剖析Kubernetes的:
- 架构设计与核心组件
- 关键概念与资源对象
- 集群部署最佳实践
- 应用部署与管理策略
- 网络与存储解决方案
- 安全加固方案
- 监控与运维体系
- 企业级扩展方案
无论您是初识Kubernetes还是寻求深度优化,本文都将提供专业级的技术洞见。
一、Kubernetes架构深度解析
1.1 核心架构全景
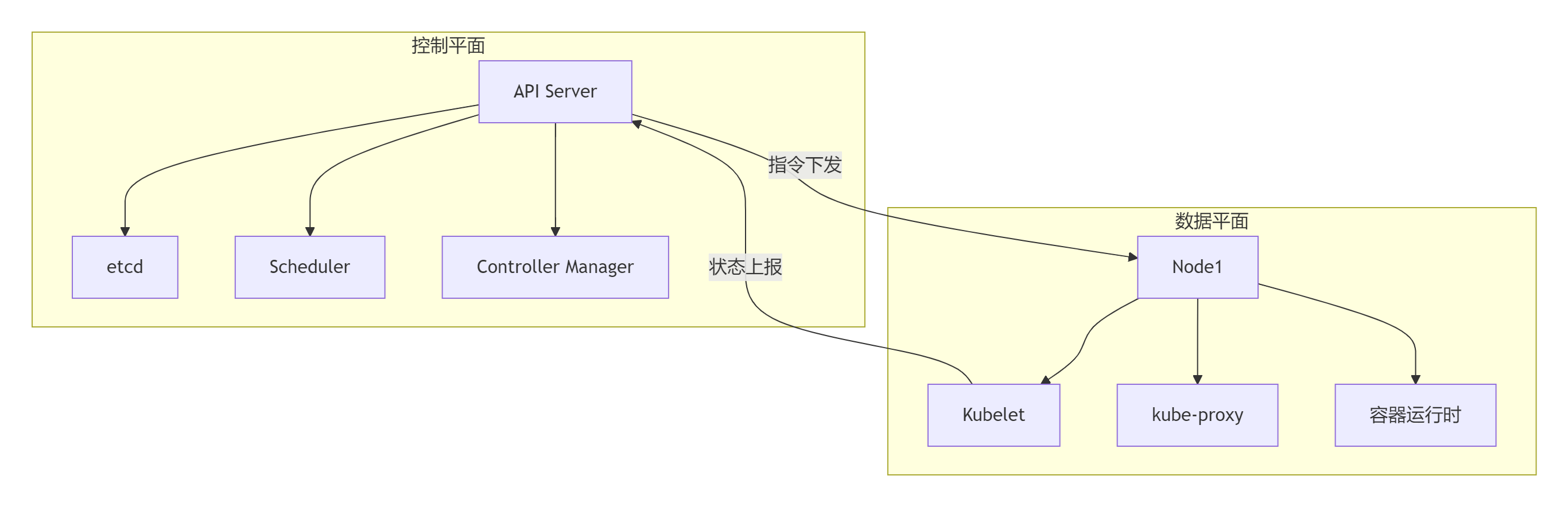
1.2 控制平面组件详解
| 组件 | 核心职责 | 高可用方案 |
|---|---|---|
| API Server | 集群操作入口 | 多实例负载均衡 |
| etcd | 分布式键值存储 | RAFT共识集群 |
| Scheduler | 资源调度决策 | 多副本选举 |
| Controller | 状态协调管理 | 分布式工作队列 |
1.3 节点组件功能矩阵
| 组件 | 核心功能 | 性能影响 |
|---|---|---|
| kubelet | 节点代理,容器生命周期管理 | CPU 5-10% |
| kube-proxy | 网络代理,服务发现 | 网络吞吐关键 |
| 容器运行时 | 容器执行引擎(containerd/docker) | 容器启动性能 |
| CNI插件 | 容器网络实现 | 网络延迟决定性因素 |
二、核心概念与资源对象
2.1 核心资源关系图
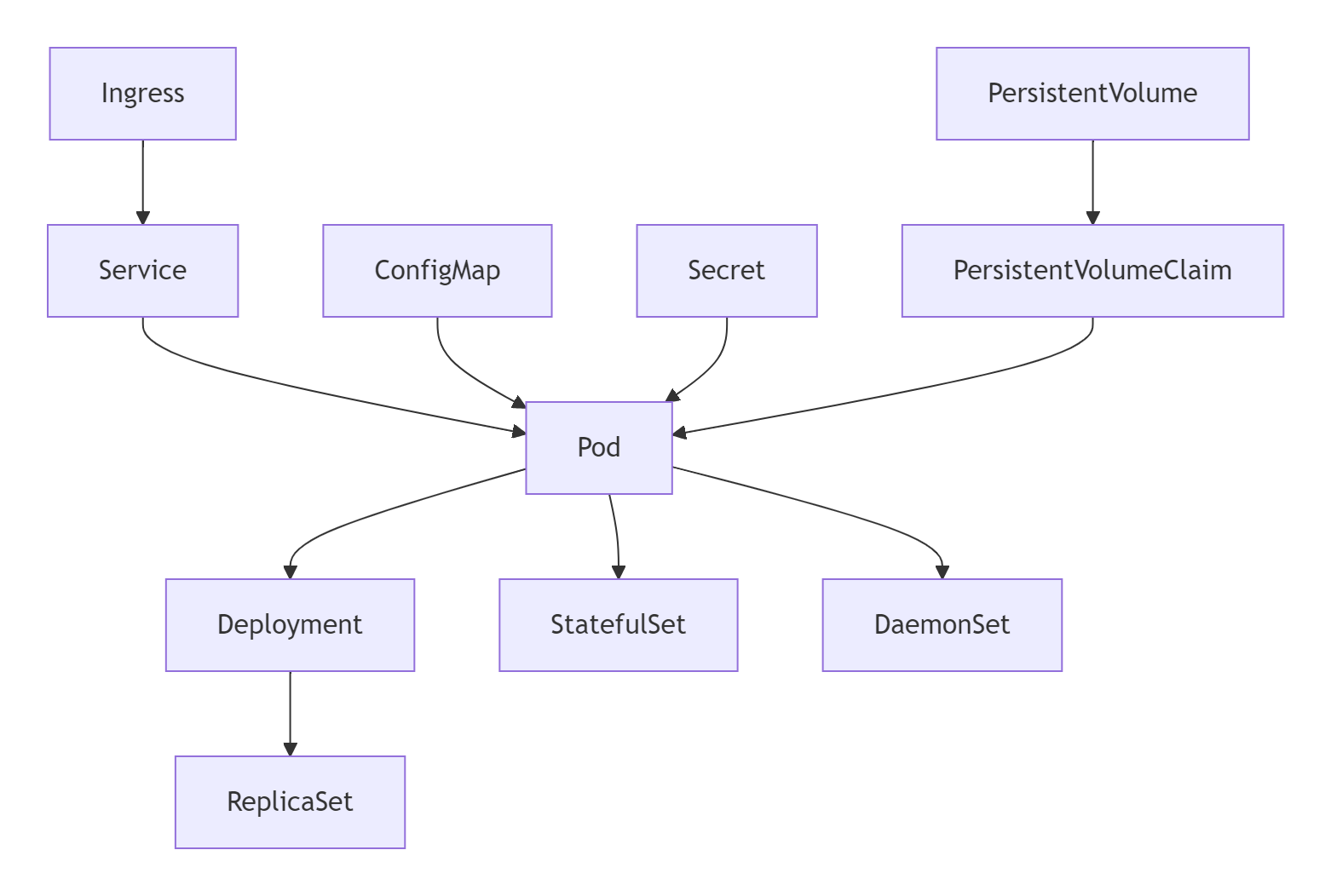
2.2 关键资源详解
Pod设计模式:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: adapter-pattern
spec:containers:- name: appimage: my-app:1.2- name: adapterimage: log-adapter:3.1# 适配器容器处理日志格式转换高级Deployment策略:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:name: canary-deployment
spec:replicas: 10strategy:type: RollingUpdaterollingUpdate:maxSurge: 25%maxUnavailable: 10%selector:matchLabels:app: frontendtemplate:metadata:labels:app: frontendversion: v1.5spec:affinity:podAntiAffinity:requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:- labelSelector:matchExpressions:- key: appoperator: Invalues: [frontend]topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"containers:- name: webimage: nginx:1.25resources:limits:memory: "256Mi"cpu: "500m"readinessProbe:httpGet:path: /healthport: 80initialDelaySeconds: 5periodSeconds: 10三、集群部署最佳实践
3.1 高可用架构设计
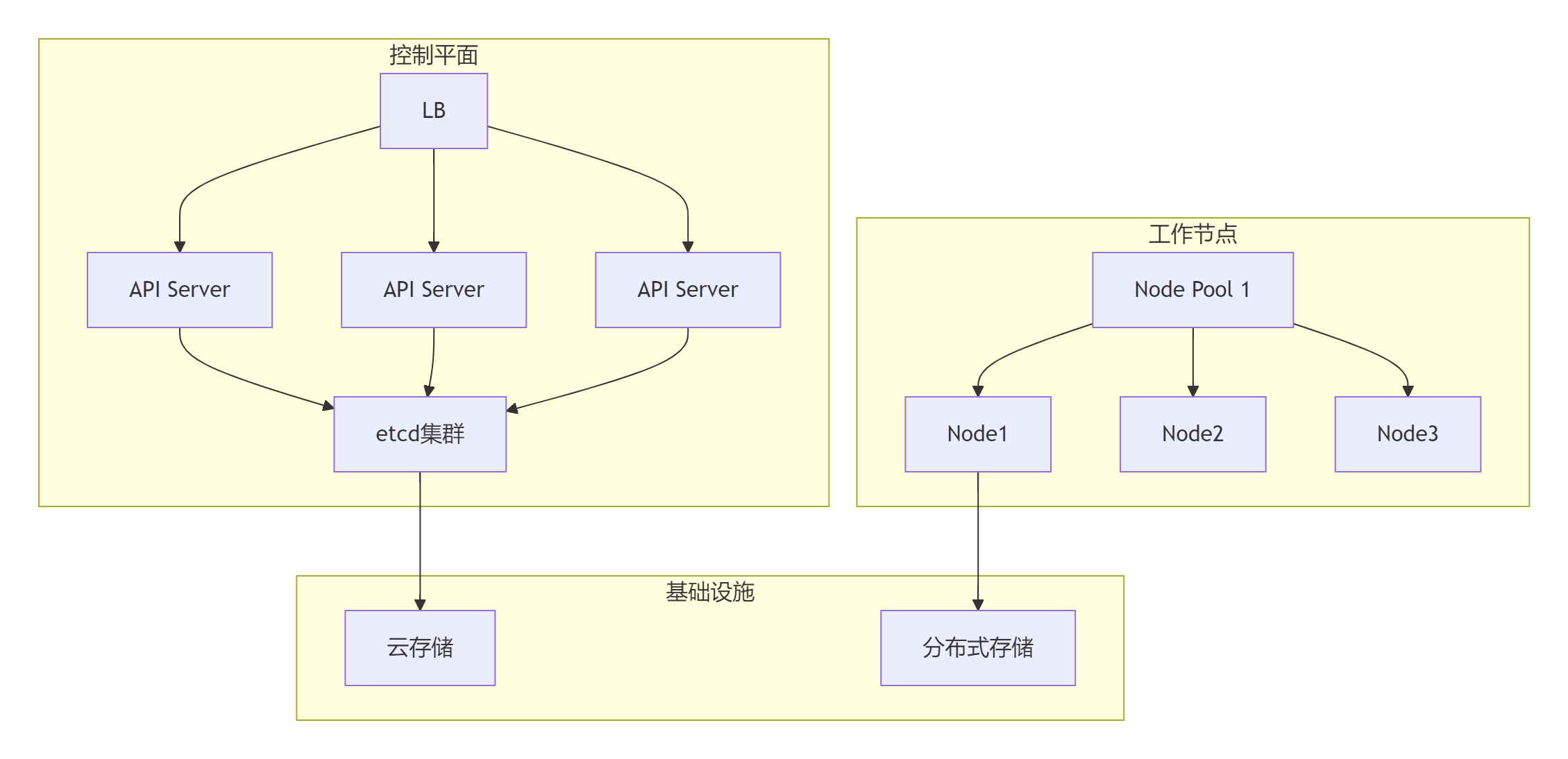
3.2 部署工具对比
| 工具 | 适用场景 | 特点 | 生产就绪 |
|---|---|---|---|
| kubeadm | 自定义集群 | 官方推荐,灵活 | ★★★★☆ |
| kOps | 云环境部署 | AWS/GCP优化 | ★★★★★ |
| Rancher | 多集群管理 | UI驱动,易用 | ★★★★☆ |
| OpenShift | 企业级平台 | 全栈解决方案 | ★★★★★ |
| EKS/GKE/AKS | 托管服务 | 云厂商集成 | ★★★★★ |
3.3 生产环境配置示例
# kubeadm 高可用配置
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: ClusterConfiguration
controlPlaneEndpoint: "k8s-api.example.com:6443"
etcd:external:endpoints:- "https://etcd1:2379"- "https://etcd2:2379"- "https://etcd3:2379"caFile: /etc/etcd/ca.pemcertFile: /etc/etcd/etcd.pemkeyFile: /etc/etcd/etcd-key.pem
networking:podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
apiServer:certSANs:- "k8s-api.example.com"- "192.168.1.100"extraArgs:feature-gates: "RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true"
controllerManager:extraArgs:node-monitor-grace-period: "20s"
scheduler:extraArgs:bind-address: "0.0.0.0"四、应用部署与管理策略
4.1 GitOps工作流实现
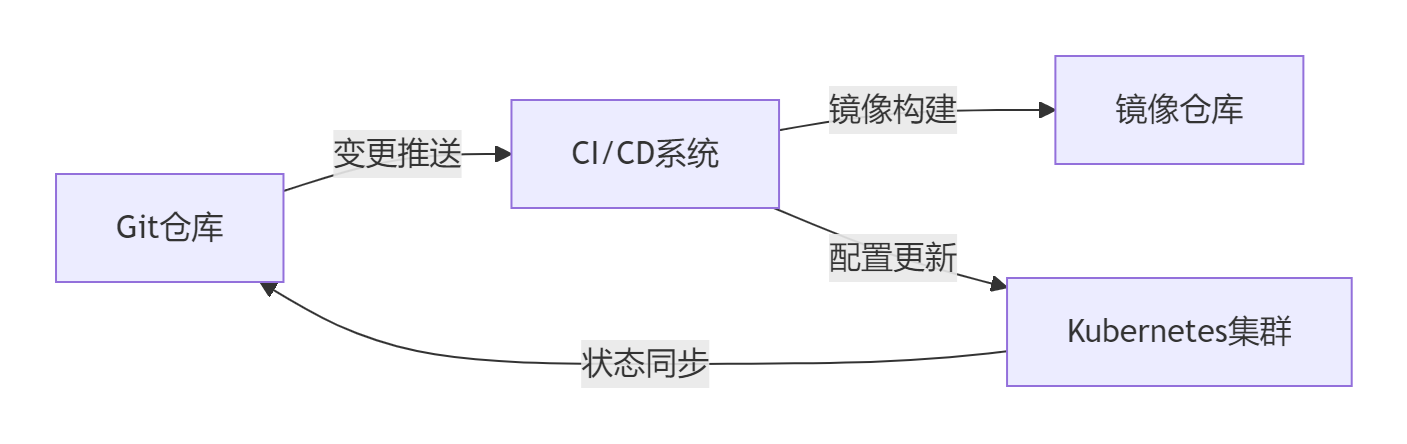
Argo CD配置示例:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:name: production-app
spec:project: defaultsource:repoURL: 'https://git.example.com/app-config.git'path: productiontargetRevision: HEADdestination:server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'namespace: productionsyncPolicy:automated:prune: trueselfHeal: truesyncOptions:- CreateNamespace=true4.2 金丝雀发布策略
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: Canary
metadata:name: frontend
spec:targetRef:apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentname: frontendservice:port: 8080analysis:interval: 1mthreshold: 5metrics:- name: request-success-ratethresholdRange:min: 99interval: 1m- name: latencythresholdRange:max: 500interval: 30ssteps:- setWeight: 5- pause: {duration: 2m}- setWeight: 25- pause: {duration: 5m}- setWeight: 50- pause: {duration: 10m}- setWeight: 100五、网络与存储解决方案
5.1 CNI插件性能对比
| CNI插件 | 网络模型 | 性能 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calico | BGP/IPIP | ★★★★☆ | 大规模集群 |
| Flannel | VxLAN | ★★★☆☆ | 中小规模 |
| Cilium | eBPF | ★★★★★ | 高性能需求 |
| Weave Net | Mesh | ★★★☆☆ | 简单部署 |
| AWS VPC CNI | 原生集成 | ★★★★☆ | AWS环境 |
5.2 高级存储方案
CSI驱动架构:
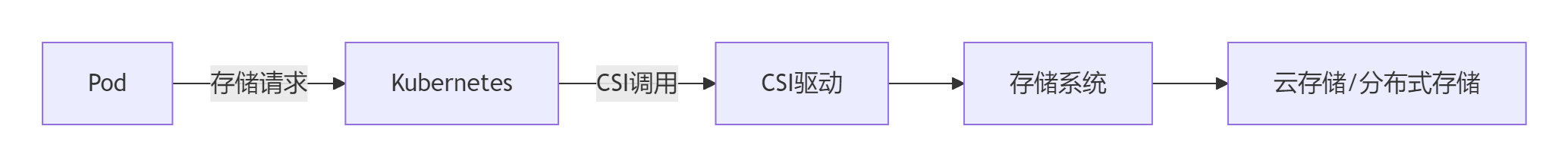
多存储类配置:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:name: fast-ssd
provisioner: ebs.csi.aws.com
parameters:type: gp3iops: "10000"throughput: "500"
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
allowVolumeExpansion: true
reclaimPolicy: Delete---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:name: db-pvc
spec:accessModes:- ReadWriteOncestorageClassName: fast-ssdresources:requests:storage: 200Gi六、安全加固方案
6.1 安全防护层级
1. 集群层:- RBAC权限控制- API Server认证- etcd加密2. 节点层:- 容器运行时加固- 内核安全模块(AppArmor/SELinux)- 节点隔离3. 容器层:- 非root用户- 只读文件系统- 能力限制4. 网络层:- 网络策略- 服务网格mTLS- 入口防护6.2 Pod安全策略
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:name: restricted
spec:privileged: falseallowPrivilegeEscalation: falserequiredDropCapabilities:- ALLvolumes:- 'configMap'- 'emptyDir'- 'secret'- 'persistentVolumeClaim'hostNetwork: falsehostIPC: falsehostPID: falserunAsUser:rule: 'MustRunAsNonRoot'seLinux:rule: 'RunAsAny'supplementalGroups:rule: 'MustRunAs'ranges:- min: 1max: 65535fsGroup:rule: 'MustRunAs'ranges:- min: 1max: 65535七、监控与运维体系
7.1 监控架构设计
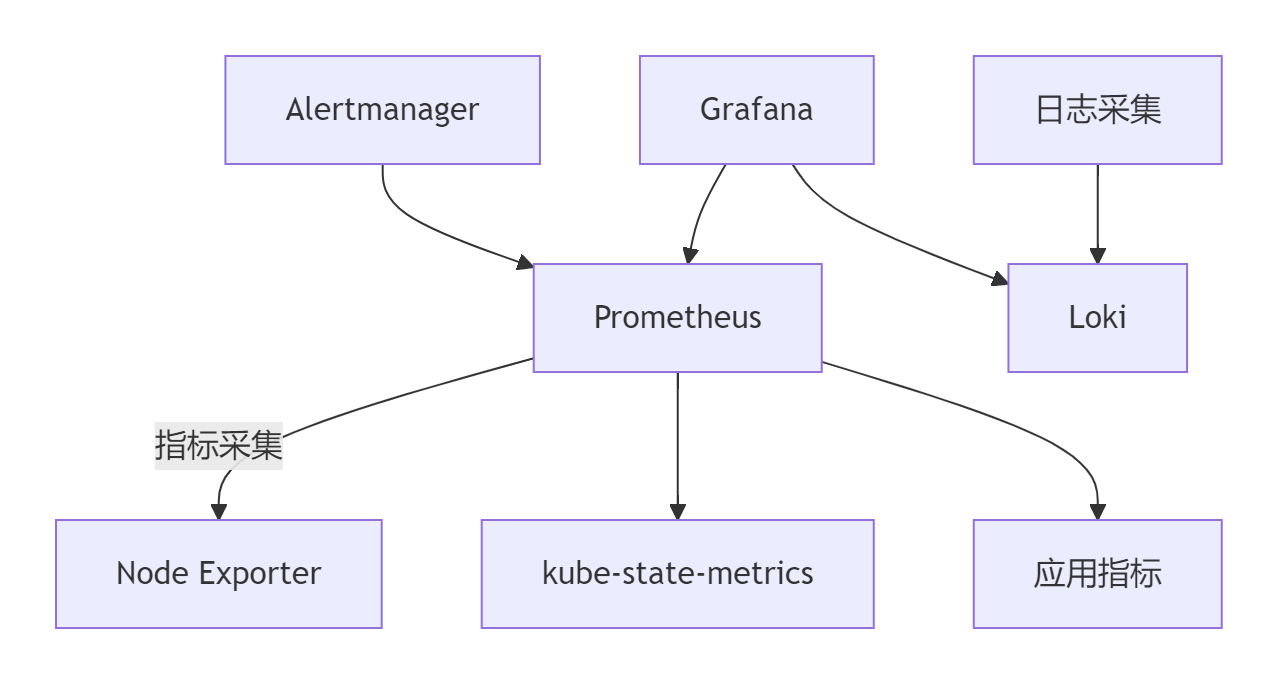
7.2 关键监控指标
| 类别 | 核心指标 | 告警阈值 |
|---|---|---|
| 集群健康 | API Server延迟 | >500ms |
| 节点资源 | 节点CPU使用率 | >80%持续5min |
| Pod状态 | Pod重启次数 | >5次/小时 |
| 网络性能 | 网络丢包率 | >1% |
| 存储性能 | IO延迟 | >50ms |
7.3 自动化运维方案
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:name: cluster-maintenance
spec:schedule: "0 3 * * 6" # 每周六凌晨3点jobTemplate:spec:template:spec:containers:- name: maintenanceimage: kubectl:1.27command:- /bin/sh- -c- |kubectl get nodes --no-headers | awk '{print $1}' | while read node; dokubectl drain $node --ignore-daemonsets --delete-emptydir-datassh $node "sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y"kubectl uncordon $nodedonerestartPolicy: OnFailure八、企业级扩展方案
8.1 服务网格集成
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:meshConfig:accessLogFile: /dev/stdoutcomponents:pilot:k8s:resources:limits:cpu: 500mmemory: 1024MiingressGateways:- name: istio-ingressgatewayenabled: truek8s:service:type: LoadBalancerports:- port: 80targetPort: 8080name: http- port: 443targetPort: 8443name: https8.2 Kubernetes Operator框架
// 自定义Operator示例
func (r *MyAppReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {// 获取自定义资源实例myApp := &appv1alpha1.MyApp{}if err := r.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, myApp); err != nil {return ctrl.Result{}, client.IgnoreNotFound(err)}// 检查Deployment状态dep := &appsv1.Deployment{}if err := r.Get(ctx, types.NamespacedName{Name: myApp.Name, Namespace: myApp.Namespace}, dep); err != nil {// 创建新Deploymentif errors.IsNotFound(err) {newDep := r.createDeployment(myApp)if err := r.Create(ctx, newDep); err != nil {return ctrl.Result{}, err}return ctrl.Result{Requeue: true}, nil}return ctrl.Result{}, err}// 更新Deploymentif *dep.Spec.Replicas != myApp.Spec.Replicas {dep.Spec.Replicas = &myApp.Spec.Replicasif err := r.Update(ctx, dep); err != nil {return ctrl.Result{}, err}}return ctrl.Result{}, nil
}总结:Kubernetes的企业级实践全景
通过本文的深度探讨,我们全面掌握了Kubernetes的:
- 架构原理:控制平面与数据平面协同
- 核心概念:Pod/Service/Deployment等关键抽象
- 集群部署:高可用架构与生产配置
- 应用管理:GitOps与金丝雀发布策略
- 网络存储:CNI与CSI高级方案
- 安全体系:多层次纵深防御
- 监控运维:全栈可观测性方案
- 扩展生态:Operator与服务网格集成
[!TIP] Kubernetes实施黄金法则:
1. 声明式配置:所有资源版本化管理
2. 最小权限原则:RBAC精细控制
3. 资源配额管理:LimitRange与ResourceQuota
4. 滚动更新策略:保证服务连续性
5. 多环境隔离:Namespace逻辑分区企业效能提升数据
Kubernetes实施效果对比:
┌───────────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┐
│ 指标 │ 传统架构 │ Kubernetes │ 提升幅度 │
├───────────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┤
│ 部署频率 │ 周/次 │ 小时/次 │ 1680% │
│ 故障恢复时间 │ 小时级 │ 分钟级 │ 90%↓ │
│ 资源利用率 │ 30%-40% │ 60%-80% │ 100%↑ │
│ 运维人力投入 │ 5人/100节点 │ 1人/200节点 │ 90%↓ │
│ 扩展速度 │ 天/次 │ 分钟级 │ 99%↓ │
└───────────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┘未来演进方向
- 边缘计算:KubeEdge与OpenYurt
- Serverless:Knative集成
- AI赋能:智能调度与资源预测
- 混合云:多集群联邦管理
- 安全增强:机密计算与零信任
掌握Kubernetes技术后,您将成为云原生架构的核心构建者,能够设计并管理企业级容器化平台。立即开始Kubernetes实践,引领企业数字化转型!
最新技术动态请关注作者:Python×CATIA工业智造
版权声明:转载请保留原文链接及作者信息

采用分布式哈希表优化区块链索引结构,提高区块链检索效率)
配置元件详解01)


)
--Cartographer在Gazebo仿真环境下的建图以及建图与定位阶段问题(实车也可参考))



)








)