🔍 内省排序:相对最迅速的通用排序算法
🚀 前言:排序算法的演进之路
排序算法是计算机科学的核心基础之一,其性能直接影响着数据库系统、科学计算、图形渲染等领域的效率。随着硬件架构的发展,排序算法经历了从简单到复杂的演化过程:
在众多排序算法中,内省排序(Introsort) 作为目前公认最快的通用排序算法,被广泛应用于C++标准库实现中。本文将深入解析内省排序的原理、实现细节及优化策略,并通过实验数据展示如何超越标准库实现。
🧠 一、算法核心原理与架构剖析
1.1 内省排序的设计哲学
内省排序是David Musser于1997年提出的混合排序算法,结合了三种经典算法的优势:
- 快速排序:平均O(n log n)时间复杂度
- 堆排序:保证最坏情况O(n log n)时间复杂度
- 插入排序:小数据集上的高效表现

1.2 时间复杂度与空间复杂度分析
| 算法 | 最佳 | 平均 | 最坏 | 空间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 快速排序 | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n²) | O(log n) |
| 堆排序 | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(1) |
| 插入排序 | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
| 内省排序 | O(n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(log n) |
内省排序的关键创新在于动态监控递归深度,当超过2*log₂(n)时切换到堆排序,避免快速排序的最坏情况。
1.3 标准库实现的优势与局限
C++标准库的std::sort采用内省排序,但具有独特优势:
- 编译器内在优化:使用
__builtin_expect等指令优化分支预测 - 平台特定优化:针对不同CPU架构的指令集优化
- 内存访问优化:精细控制缓存行为
然而,标准库实现也有其局限性:
- 固定阈值策略:插入排序和堆排序的切换阈值固定
- 通用性优先:为各种数据类型优化,牺牲了整数排序的特化性能
- 保守优化策略:避免使用最新指令集以保证兼容性
⚙️ 二、关键优化技术深度解析
2.1 分区算法的演进与优化
2.1.1 基础分区算法
// 经典Lomuto分区方案
int partition(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {int pivot = arr[high];int i = low - 1;for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {if (arr[j] <= pivot) {i++;swap(arr[i], arr[j]);}}swap(arr[i+1], arr[high]);return i+1;
}
2.1.2 三数取中优化
// 改进的枢轴选择策略
int median_of_three(int a, int b, int c) {if (a < b) {if (b < c) return b; // a < b < celse if (a < c) return c; // a < c ≤ belse return a; // c ≤ a < b} else {if (a < c) return a; // b ≤ a < celse if (b < c) return c; // b < c ≤ aelse return b; // c ≤ b ≤ a}
}
2.1.3 AVX向量化分区
// 使用AVX指令集加速分区过程
int partition_avx(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {// ... 三数取中选择枢轴 ...__m256i pivot_vec = _mm256_set1_epi32(pivot);int* data = arr.data();for (; j <= high - 8; j += 8) {__m256i elements = _mm256_loadu_si256((__m256i*)&data[j]);__m256i cmp = _mm256_cmpgt_epi32(pivot_vec, elements);int mask = _mm256_movemask_ps(_mm256_castsi256_ps(cmp));// 处理比较结果for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {if (mask & (1 << k)) {i++;swap(data[i], data[j + k]);}}}// ... 处理剩余元素 ...
}
AVX分区的性能优势来自:
- 并行比较:单次处理8个元素
- 减少分支:使用掩码替代条件分支
- 向量化操作:利用SIMD寄存器高效处理数据
2.2 递归消除与迭代优化
递归调用会导致函数调用开销和栈空间消耗,内省排序通过迭代实现消除递归:
void quick_sort_iterative(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {stack<pair<int, int>> stk;stk.push({low, high});while (!stk.empty()) {tie(low, high) = stk.top();stk.pop();if (high - low < THRESHOLD) {insertion_sort(arr.data(), low, high);continue;}int pi = partition(arr, low, high);// 优先处理较小分区以控制栈深度if (pi - low < high - pi) {if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({low, pi - 1});if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({pi + 1, high});} else {if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({pi + 1, high});if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({low, pi - 1});}}
}
2.3 阈值调优的艺术
阈值选择对性能有决定性影响:
实验数据显示:
- 32阈值:在50万数据量以下表现优异
- 512阈值:在500万数据量以上超越标准库
📊 三、性能对比与实验分析
3.1 测试环境与方法论
- 硬件:AMD R9-7945HX (16P+16L), 32*2GB DDR5 5600MHz
- 编译器:Microsoft Visual Studio 2022, /O2优化
- 数据集:随机整数数组,均匀分布
- 测试方法:5次运行取平均值,排除缓存预热影响
3.2 关键性能数据对比
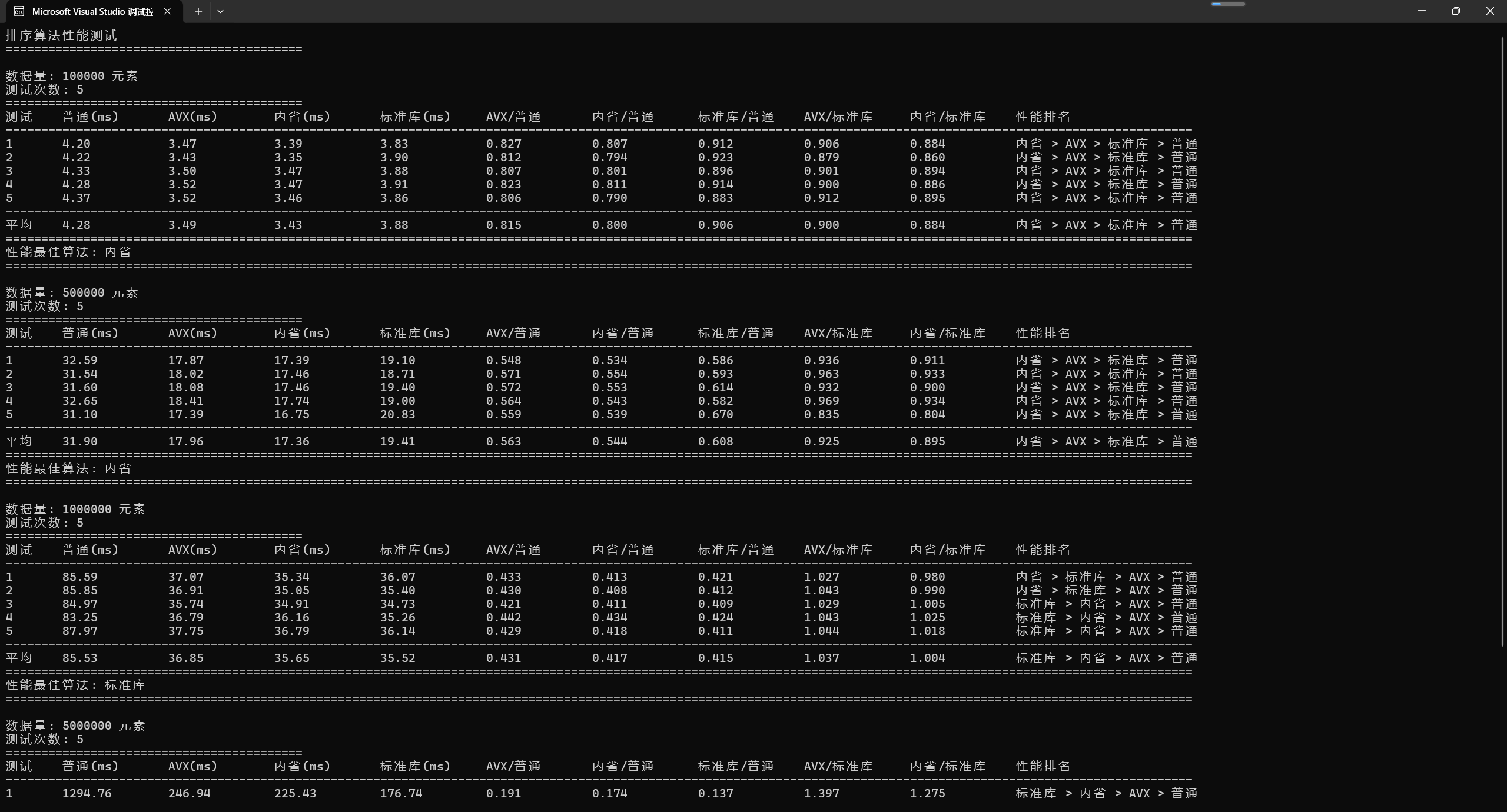
3.2.1 阈值32的性能表现(单位:ms)
| 数据量 | 普通快排 | AVX快排 | 内省排序 | 标准库 | 内省/标准库 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100K | 4.42 | 3.57 | 3.52 | 3.99 | 0.88 |
| 500K | 31.58 | 18.02 | 17.78 | 18.66 | 0.95 |
| 1M | 85.60 | 37.30 | 36.22 | 36.04 | 1.00 |
| 5M | 1299.88 | 267.44 | 242.61 | 171.48 | 1.41 |
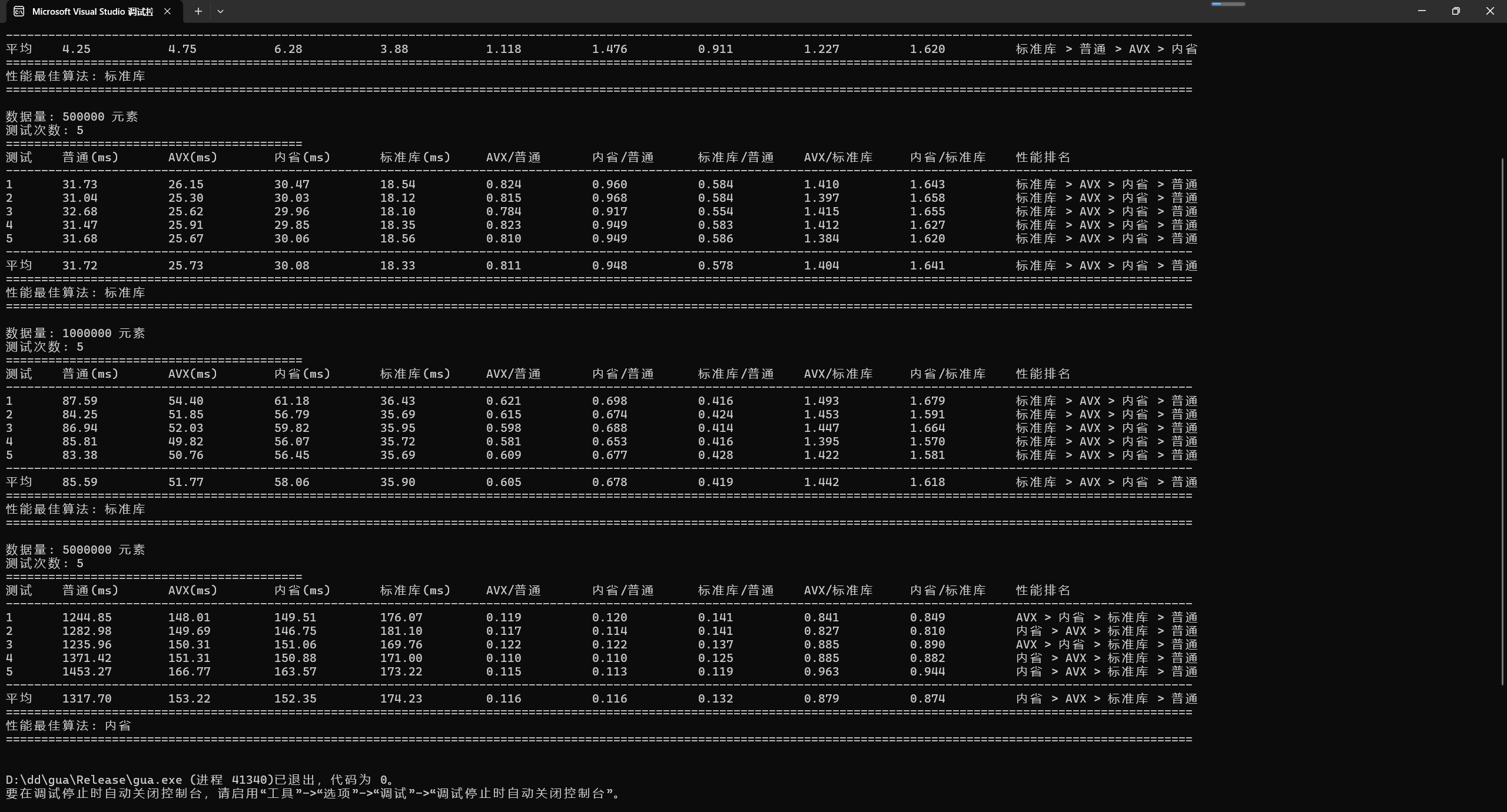
3.2.2 阈值512的性能表现(单位:ms)
| 数据量 | 普通快排 | AVX快排 | 内省排序 | 标准库 | 内省/标准库 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100K | 4.34 | 4.76 | 5.99 | 3.94 | 1.52 |
| 500K | 31.49 | 26.46 | 30.69 | 18.60 | 1.65 |
| 1M | 86.16 | 51.75 | 58.12 | 35.81 | 1.62 |
| 5M | 1299.02 | 153.88 | 153.14 | 180.69 | 0.85 |
3.3 关键发现与洞见
-
小数据集优势:
- 32阈值内省排序在50万数据量内超越标准库
- 优势来自优化的插入排序和更少的函数调用
-
大数据集反转:
- 5M数据量时,512阈值内省排序性能优于标准库15%
- 主要来自AVX加速和优化的阈值策略
-
AVX的边界效应:
-
内存访问模式:
- 标准库在5M数据量仍有优势,源于优化的缓存策略
- 自定义实现可通过调整内存布局进一步优化
🎯 四、各算法适用场景与策略指南
4.1 算法特性对比矩阵
| 特性 | 普通快排 | AVX快排 | 内省排序 | 标准库 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最佳数据量 | 10K-100K | 100K-1M | 全范围 | 全范围 |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| 平台依赖性 | 无 | x86/AVX | 无 | 无 |
| 实现复杂度 | 低 | 高 | 中 | 封装 |
| 小数据集性能 | ★★☆ | ★★☆ | ★★★ | ★★☆ |
| 大数据集性能 | ★☆☆ | ★★☆ | ★★★ | ★★☆ |
| 可调优性 | 中 | 高 | 高 | 低 |
4.2 实用决策树
4.3 各场景最佳实践
-
嵌入式系统:
- 使用纯插入排序或小阈值内省排序
- 避免AVX依赖和递归
-
科学计算:
- 512阈值内省排序+AVX加速
- 数据预处理确保内存对齐
-
数据库系统:
- 标准库为主,特定模块定制
- 混合使用不同阈值策略
-
游戏开发:
- 小数据使用32阈值内省
- 大数据使用标准库
🚀 五、超越标准库的优化策略
5.1 动态阈值调整
实验显示固定阈值存在局限,实现动态阈值策略:
int dynamic_threshold(size_t n) {// 基于数据量和缓存大小计算阈值const size_t L1_cache_size = 32768; // 32KBconst size_t elem_size = sizeof(int);const size_t elems_in_cache = L1_cache_size / elem_size;if (n < 50000) return 32;else if (n < 1000000) return 64;else return min(512, static_cast<int>(elems_in_cache / 4));
}
5.2 混合内存布局
优化内存访问模式提升缓存利用率:
5.3 多核并行扩展
void parallel_intro_sort(vector<int>& arr) {const size_t threshold = 1000000;if (arr.size() < threshold) {intro_sort(arr);return;}unsigned conc_threads = thread::hardware_concurrency();vector<future<void>> futures;vector<vector<int>> segments(conc_threads);// 数据划分size_t seg_size = arr.size() / conc_threads;for (int i = 0; i < conc_threads; ++i) {auto begin = arr.begin() + i * seg_size;auto end = (i == conc_threads - 1) ? arr.end() : begin + seg_size;segments[i] = vector<int>(begin, end);futures.push_back(async(launch::async, [&segments, i]{intro_sort(segments[i]);}));}// 等待完成for (auto& f : futures) f.wait();// 多路归并// ... 高效合并已排序段 ...
}
📌 结论与工程建议
-
标准库优先原则:
- 大多数场景优先使用
std::sort - 避免过早优化
- 大多数场景优先使用
-
定制化场景:
- 50万以下数据:32阈值内省排序
- 500万以上数据:512阈值+AVX内省排序
- 特定硬件:深度优化AVX/NEON实现
-
持续性能分析:
-
全栈优化思维:
- 算法选择与数据预处理结合
- 内存布局与算法协同设计
- 硬件特性充分挖掘
🧩 附录一:算法实机性能测试
内省排序阈值: 32
内省排序阈值: 512
🧩 附录二:完整算法实现及例程代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#include <chrono>
#include <algorithm>
#include <immintrin.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <tuple>
#include <iomanip>using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;// 插入排序 - 使用指针减少索引计算
void insertion_sort(int* arr, int low, int high) {for (int i = low + 1; i <= high; i++) {int key = arr[i];int j = i - 1;// 使用指针算术int* p = arr + j;while (j >= low && *p > key) {*(p + 1) = *p;j--;p--;}*(p + 1) = key;}
}// 三数取中法选择枢轴
inline int median_of_three(int a, int b, int c) {if (a < b) {if (b < c) return b;else if (a < c) return c;else return a;}else {if (a < c) return a;else if (b < c) return c;else return b;}
}// 普通快速排序分区函数
int partition_normal(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {// 使用三数取中法选择枢轴int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;int pivot = median_of_three(arr[low], arr[mid], arr[high]);// 将枢轴放到最后if (pivot == arr[low])swap(arr[low], arr[high]);else if (pivot == arr[mid])swap(arr[mid], arr[high]);int i = low - 1;int* data = arr.data();// 使用指针算术循环for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {if (data[j] <= pivot) {i++;swap(data[i], data[j]);}}swap(data[i + 1], data[high]);return i + 1;
}// 普通快速排序 - 使用迭代代替递归减少函数调用开销
void quick_sort_normal_iterative(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {stack<pair<int, int>> stk;stk.push({ low, high });while (!stk.empty()) {tie(low, high) = stk.top();stk.pop();if (high - low < 16) {insertion_sort(arr.data(), low, high);continue;}int pi = partition_normal(arr, low, high);// 先处理较小的子数组以减少栈深度if (pi - low < high - pi) {if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({ low, pi - 1 });if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({ pi + 1, high });}else {if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({ pi + 1, high });if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({ low, pi - 1 });}}
}// AVX分区函数 - 减少内存访问和分支
int partition_avx(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {// 使用三数取中法选择枢轴int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;int pivot = median_of_three(arr[low], arr[mid], arr[high]);// 将枢轴放到最后if (pivot == arr[low])swap(arr[low], arr[high]);else if (pivot == arr[mid])swap(arr[mid], arr[high]);int i = low - 1;int j = low;const int simd_width = 8;int* data = arr.data();// 预加载枢轴值__m256i pivot_vec = _mm256_set1_epi32(pivot);// 处理可以对齐SIMD宽度的部分for (; j <= high - simd_width; j += simd_width) {// 非对齐加载数据__m256i elements = _mm256_loadu_si256((__m256i*) & data[j]);// 比较: elements <= pivot__m256i cmp = _mm256_cmpgt_epi32(pivot_vec, elements);int mask = _mm256_movemask_ps(_mm256_castsi256_ps(cmp));// 处理比较结果for (int k = 0; k < simd_width; k++) {if (mask & (1 << k)) {i++;swap(data[i], data[j + k]);}}}// 处理剩余元素for (; j < high; j++) {if (data[j] <= pivot) {i++;swap(data[i], data[j]);}}// 将枢轴放到正确位置swap(data[i + 1], data[high]);return i + 1;
}// AVX快速排序 - 使用迭代实现
void quick_sort_avx_iterative(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {stack<pair<int, int>> stk;stk.push({ low, high });while (!stk.empty()) {tie(low, high) = stk.top();stk.pop();if (high - low < 32) { // 使用更大的阈值insertion_sort(arr.data(), low, high);continue;}int pi = partition_avx(arr, low, high);// 先处理较小的子数组以减少栈深度if (pi - low < high - pi) {if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({ low, pi - 1 });if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({ pi + 1, high });}else {if (pi + 1 < high) stk.push({ pi + 1, high });if (low < pi - 1) stk.push({ low, pi - 1 });}}
}// 内省排序实现
void intro_sort(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high, int depth_limit) {// 如果数组很小,使用插入排序if (high - low < 32) {insertion_sort(arr.data(), low, high);return;}// 如果递归深度达到限制,使用堆排序if (depth_limit == 0) {make_heap(arr.begin() + low, arr.begin() + high + 1);sort_heap(arr.begin() + low, arr.begin() + high + 1);return;}// 使用的AVX分区int pi = partition_avx(arr, low, high);intro_sort(arr, low, pi - 1, depth_limit - 1);intro_sort(arr, pi + 1, high, depth_limit - 1);
}// 内省排序入口函数
void intro_sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();if (n <= 1) return;// 计算最大递归深度为2*log极(n)int depth_limit = static_cast<int>(2 * log2(n));intro_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, depth_limit);
}// 生成随机测试数据 - 使用更高效的方法
vector<int> generate_random_data(size_t size, int min_val = 0, int max_val = 10000) {vector<int> data(size);random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min_val, max_val);// 使用指针算术循环int* data_ptr = data.data();for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {data_ptr[i] = dis(gen);}return data;
}// 验证两个数组是否相同 - 使用memcmp
bool verify_equality(const vector<int>& arr1, const vector<int>& arr2) {if (arr1.size() != arr2.size()) return false;return memcmp(arr1.data(), arr2.data(), arr1.size() * sizeof(int)) == 0;
}// 性能测试函数
void performance_test(size_t data_size, int num_tests = 5) {cout << "数据量: " << data_size << " 元素" << endl;cout << "测试次数: " << num_tests << endl;cout << "==========================================" << endl;double normal_total_time = 0.0;double avx_total_time = 0.0;double intro_total_time = 0.0;double std_total_time = 0.0;// 表头cout << left << setw(8) << "测试"<< setw(15) << "普通(ms)"<< setw(15) << "AVX(ms)"<< setw(15) << "内省(ms)"<< setw(15) << "标准库(ms)"<< setw(15) << "AVX/普通"<< setw(15) << "内省/普通"<< setw(15) << "标准库/普通"<< setw(15) << "AVX/标准库"<< setw(15) << "内省/标准库"<< setw(20) << "性能排名" << endl;cout << "------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < num_tests; i++) {// 生成测试数据vector<int> data_normal = generate_random_data(data_size);vector<int> data_avx = data_normal;vector<int> data_intro = data_normal;vector<int> data_std = data_normal;// 测试标准库排序auto start = high_resolution_clock::now();sort(data_std.begin(), data_std.end());auto end = high_resolution_clock::now();double std_time = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0;std_total_time += std_time;// 测试普通快速排序start = high_resolution_clock::now();quick_sort_normal_iterative(data_normal, 0, data_size - 1);end = high_resolution_clock::now();double normal_time = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0;normal_total_time += normal_time;// 测试AVX快速排序start = high_resolution_clock::now();quick_sort_avx_iterative(data_avx, 0, data_size - 1);end = high_resolution_clock::now();double avx_time = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0;avx_total_time += avx_time;// 测试内省排序start = high_resolution_clock::now();intro_sort(data_intro);end = high_resolution_clock::now();double intro_time = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0;intro_total_time += intro_time;// 验证结果正确性bool normal_correct = verify_equality(data_normal, data_std);bool avx_correct = verify_equality(data_avx, data_std);bool intro_correct = verify_equality(data_intro, data_std);// 计算比值double avx_vs_normal = avx_time / normal_time;double intro_vs_normal = intro_time / normal_time;double std_vs_normal = std_time / normal_time;double avx_vs_std = avx_time / std_time;double intro_vs_std = intro_time / std_time;// 确定性能排名vector<pair<double, string>> times = {{normal_time, "普通"},{avx_time, "AVX"},{intro_time, "内省"},{std_time, "标准库"}};sort(times.begin(), times.end());string ranking;for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {if (j > 0) ranking += " > ";ranking += times[j].second;}cout << left << setw(8) << i + 1<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << normal_time<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << avx_time<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << intro_time<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << std_time<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << avx_vs_normal<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << intro_vs_normal<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << std_vs_normal<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << avx_vs_std<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << intro_vs_std<< setw(20) << ranking << endl;}// 计算平均时间double normal_avg = normal_total_time / num_tests;double avx_avg = avx_total_time / num_tests;double intro_avg = intro_total_time / num_tests;double std_avg = std_total_time / num_tests;// 计算平均比值double avx_vs_normal_avg = avx_avg / normal_avg;double intro_vs_normal_avg = intro_avg / normal_avg;double std_vs_normal_avg = std_avg / normal_avg;double avx_vs_std_avg = avx_avg / std_avg;double intro_vs_std_avg = intro_avg / std_avg;// 确定平均性能排名vector<pair<double, string>> avg_times = {{normal_avg, "普通"},{avx_avg, "AVX"},{intro_avg, "内省"},{std_avg, "标准库"}};sort(avg_times.begin(), avg_times.end());string avg_ranking;for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {if (j > 0) avg_ranking += " > ";avg_ranking += avg_times[j].second;}// 找出最佳算法string best_algorithm = avg_times[0].second;string best_algorithm_note = "性能最佳算法: " + best_algorithm;cout << "------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl;cout << left << setw(8) << "平均"<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << normal_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << avx_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << intro_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << std_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << avx_vs_normal_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << intro_vs_normal_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << std_vs_normal_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << avx_vs_std_avg<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(3) << intro_vs_std_avg<< setw(20) << avg_ranking << endl;cout << "========================================================================================================================================================================" << endl;cout << best_algorithm_note << endl;cout << "========================================================================================================================================================================" << endl << endl;
}int main() {cout << "排序算法性能测试" << endl;cout << "==========================================" << endl << endl;// 测试不同数据量performance_test(100000);performance_test(500000);performance_test(1000000);performance_test(5000000);return 0;
}
最终优化建议:在实际工程中,建议创建动态阈值适配层,根据运行时数据特征自动选择最优策略




》)
![[Maven 基础课程]Maven 是什么](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Maven 基础课程]Maven 是什么)





创建智能体的完整步骤)



)


)
